Unsupervised Extractive Summarization by Pre-training Hierarchical Transformers (2020)
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Model
- Document Modeling
- Pre-training
- Unsupervised summarization
0. Abstract
Unsupervised Extractive Document summarization
-
중요 sentence 고르기, without labeled summaries
-
최근에 주로 사용되는 방법들은 대부분 GRAPH-based
- node : 문장
- edge (weight) : 문장 유사도
Step 1) pre-train hierarchical transformer with UN-labeled documents
Step 2) RANK sentences
- sentence-level self-attention를 사용해서!
1. Introduction
Document summarization의 두 종류
- 1) extractive
- 2) abstractive
\(\rightarrow\) 대부분의 summarization model들은 labeled data를 요구한다.
( 하지만 TOO EXPENSIVE )
따라서, 이 paper는 UNSUPERVISED summarization에 focus한다!
Extractive
- 즉, identify salient sentence!
- 그런 뒤 sentence들 ranking하기
- ex) graph ranking method
Abstractive
-
최근들어 increasing interest!
( 특히 Unsupervised abstractive summarization )
-
주로 seq2seq based, sequential denoising AutoEncoder
-
하지만, 문법적으로 좋다는 & 의미적으로 맞다는 guarantee X
HIBERT for document modeling
- Zhang et al (2019)
- supervised extractive summarization
\(\rightarrow\) 이 논문은, 위의 HIBERT의 self-attention score가 유의미할거라 생각함!
Proposal
-
[ 한 줄 요약 ]
(sentence-level) transformer attention (in hierarchical transformer) can be used to rank sentences for unsupervised extractive summarization
-
(1) Hierarchical Transformer를 위한 2개의 pre-training task를 소개함
( = extended HIBERT )
-
(2) 그런 뒤, sentence를 ranking하는 method를 소개함
2. Model
Unsupervised Summarization Model인 STAS 를 소개한다
( = Sentence-level Transformer based Attentive Summarization )
[ 소개 순서 ]
- 2-1) Document Modeling
- document encoding이 어떻게 이루어지는지
- 2-2) Pre-training
- document encoder를 pre-train 하는 방법
- 3) Unsupervised summarization
- pre-trained encoder로 Unsupervised summarization 수행
2-1) Document Modeling
Notation
- document : \(\mathcal{D}=\left(S_{1}, S_{2}, \ldots, S_{ \mid \mathcal{D} \mid }\right)\)
- sentence in \(\mathcal{D}\) : \(S_{i}=\left(w_{0}^{i}, w_{1}^{i}, w_{2}^{i}, \ldots, w_{ \mid S_{i} \mid }^{i}\right)\)
- 2개의 special token : \(w_{0}^{i}=\langle\mathrm{s}\rangle\) and \(w_{ \mid S_{i} \mid }^{i}=\langle/ \mathrm{s}\rangle\)
- Hierarchical Transformer encoder의 구성
- 1) token-level transformer : \(\text{Trans}^T\)
- 2) sentence-level transformer : \(\text{Trans}^S\)
Trans \(^{T}\) 는 \(\mathcal{D}\) 를 flat sequence로 본다
- \[D=\left(S_{1}\left\ \mid S_{2}\right\ \mid \ldots \ \mid S_{ \mid \mathcal{D} \mid }\right)\]
\(\mathcal{D}\)를 Trans \(^{T}\) 에 통과시킨 뒤, contextual representation을 얻는다.
- \(\left(\mathrm{v}_{0}^{1}, \mathrm{v}_{1}^{1}, \ldots, \mathrm{v}_{ \mid S_{1} \mid }^{1}, \ldots, \mathrm{v}_{j}^{i}, \ldots, \mathrm{v}_{0}^{ \mid \mathcal{D} \mid }, \ldots, \mathrm{v}_{ \mid S_{ \mid \mathcal{D} \mid } \mid }^{ \mid \mathcal{D} \mid }\right)\).
- 1개의 document - 여러 개의 문장 - 여러 여러개의 단어
맨 앞 token ( = <s> token )을 문장 전체를 represent하는 것으로 봄!
- \(\mathcal{D}\) 내의 모든 문장들에 대한 각각의 representation : \(\mathbf{V}=\left(\mathbf{v}_{0}^{1}, \mathbf{v}_{0}^{2}, \ldots, \mathbf{v}_{0}^{ \mid \mathcal{D} \mid }\right) .\)
이 \(\mathbf{V}\)를 Trans \(^{S}\) 에 통과시켜서, (1) & (2)를 얻어낸다.
\(\mathrm{H}, \mathrm{A}=\text { Trans }^{S}(\mathrm{~V})\).
- (1) \(\mathrm{H}\) : final representation of \(S_i\)
- (2) \(\mathrm{A}\) : (self-)Attention matrix
- \(\mathrm{A}\)를 얻기 위해, average the attention score across different heads & across different layers
2-2) Pre-training
- Hierarchical document encoder를 pre-train한다
- pre-train을 하기 위한 2개의 task 소개
[Task 1] MSP ( Masked Sentence Prediction )
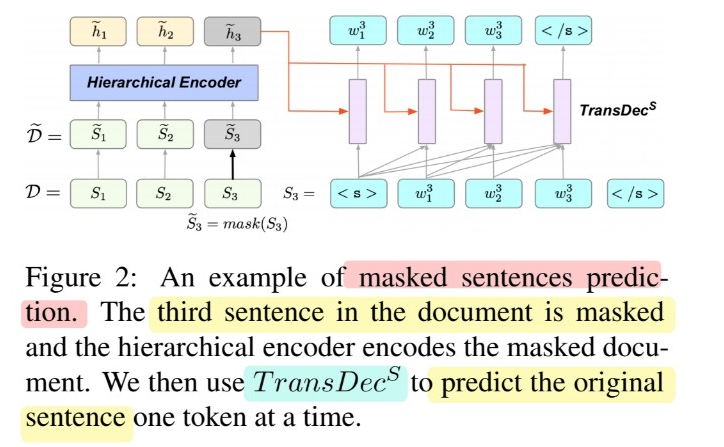
( HIBERT를 소개한 Zhang et al (2019) 참고 )
- Masking (X) : 85%
- Masking (O) : 15%
- [MASK] 토큰 : 80%
- random sentence : 10%
- 그대로 냅두기 : 10%
- 구체적인 수식은 논문 참조!
[Task 2] Sentence Shuffling
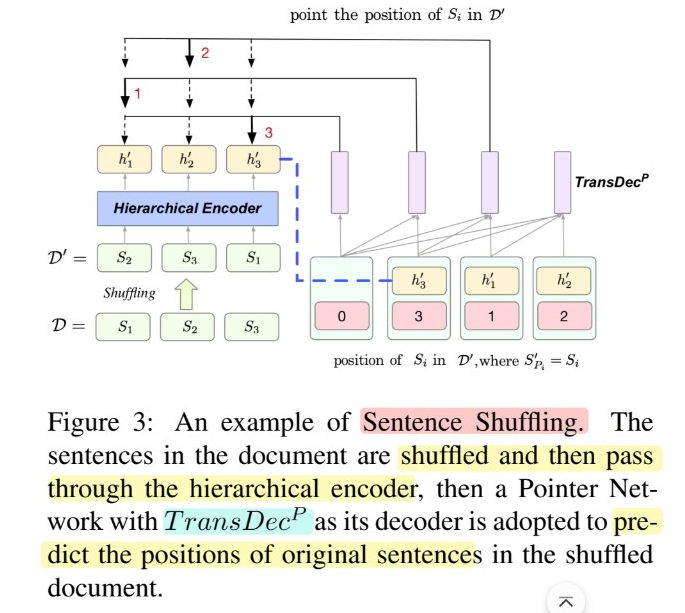
- (shuffle 이전) \(\mathcal{D}=\left(S_{1}, S_{2}, \ldots, S_{ \mid \mathcal{D} \mid }\right)\)
- (shuffle 이후) \(\mathcal{D}^{\prime}=\left(S_{1}^{\prime}, S_{2}^{\prime}, \ldots, S_{ \mid \mathcal{D} \mid }^{\prime}\right)\)
- position \(\mathcal{P}=\left(P_{1}, P_{2}, \ldots, P_{ \mid \mathcal{D} \mid }\right)\)를 예측하기, by using Pointer Network
- 구체적인 수식은 논문 참조!
2-3) Unsupervised summarization
기존에 많이 쓰이던 supervised 방식이 아닌, UNSUPERVISED 방식의 summarization을 제안한다.
앞선 단계에서 “hierarchical encoder를 pre-train 완료”한 이후, 이제 “ranking”을 할 차례!
( additional fine-tuning 필요 X )
Ranking Criteria #1
probability : \(p(\mathcal{D})=\prod_{i=1}^{ \mid \mathcal{D} \mid } p\left(S_{i} \mid S_{1: i-1}\right) \approx \prod_{i=1}^{ \mid \mathcal{D} \mid } p\left(S_{i} \mid \mathcal{D}_{\neg S_{i}}\right)\)
- document : \(\mathcal{D}=\left(S_{1}, S_{2}, \ldots, S_{ \mid \mathcal{D} \mid }\right)\)
- 의미 : probabilities of a sentences in a document
- \(p\left(S_{i} \mid S_{1: i-1}\right)\)를 directly estimate하기 어려워서, MSP에서 사용한 \(p\left(S_{i} \mid \mathcal{D}_{\neg S_{i}}\right)\)로 대체하여 근사!
\(i\) 번째 문장에 대한 score
-
(normalize 이전) \(\hat{r}_{i}=\frac{1}{ \mid S_{i} \mid } \sum_{j=1}^{ \mid S_{i} \mid } p\left(w_{j}^{i} \mid w_{0: j-1}^{i}, \mathcal{D}_{\neg S_{i}}\right)\).
-
(normalize 이후) \(\widetilde{r}_{i}=\frac{\hat{r}_{i}}{\sum_{j=1}^{ \mid \mathcal{D} \mid } \hat{r}_{j}}\).
Ranking Criteria #2
Contributions of other sentences to current sentences
-
document \(\mathcal{D}\)를 일종의 directed graph로 본다
( node는 sentence들 )
-
\(\mathbf{A}_{j, i}\) : attention score from \(S_j\) to \(S_i\)
\(i\) 번째 문장에 대한 score
- \(r_{i}^{\prime}=\sum_{j=1, j \neq i}^{ \mid \mathcal{D} \mid } \mathbf{A}_{j, i} \times \widetilde{r}_{j}\).
위의 두 score를 아래와 같이 최종적으로 종합한다!.
Final ranking score of \(S_i\) : \(r_{i}=\gamma_{1} \widetilde{r}_{i}+\gamma_{2} r_{i}^{\prime}\)
