Probabilistic Forecasting of Sensory Data with Generative Adversarial Networks - ForGAN (2019)
Contents
- Abstract
- Methodology
- GAN
- CGAN
- Probabilistic Forecasting with CGAN
0. Abstract
ForGAN
- one step ahead probabilistic forecasting, with GAN
- utilizes the power of
- conditional GAN to learn data generating distn
- and compute probabilistic forecasts from it
1. Methodology
(1) GAN
\(\begin{aligned} \min _{G} \max _{D} V(D, G)=& \mathbb{E}_{x \sim \rho_{\text {data }}(x)}[\log D(x)]+ \mathbb{E}_{z \sim \rho_{\text {noise }}(z)}[\log (1-D(G(z)))] \end{aligned}\).
(2) CGAN
\(\begin{aligned} \min _{G} \max _{D} V(D, G)=& \mathbb{E}_{x \sim \rho_{\text {data }}(x)}[\log D(x \mid y)]+ \mathbb{E}_{z \sim \rho_{z}(z)}[\log (1-D(G(z \mid y)))] \end{aligned}\).
(3) Probabilistic Forecasting with CGAN
aim to model the probability distn of one step ahead value \(x_{t+1}\) ,given the historical data \(c=\left\{x_{0}, . ., x_{t}\right\}\)
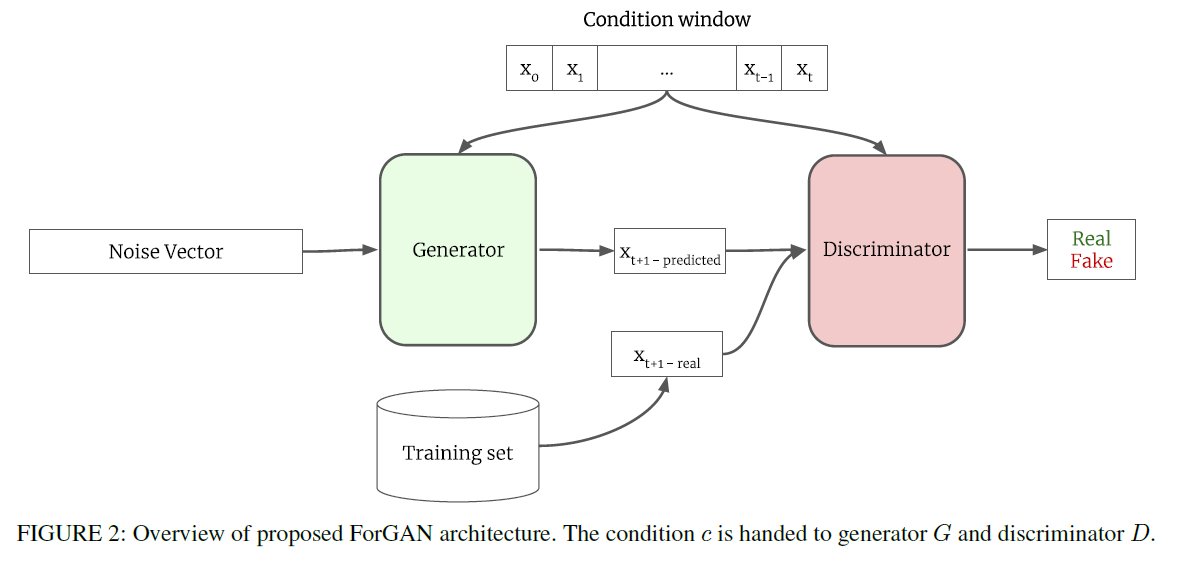
- historical data is provided to both G & D
- \(G\) : takes noise vector \(\sim N(0,1)\) & forecasts with regard to context window \(c\)
- \(D\) : takes \(x_{t+1}\) and inspects whether it is valid value to follow \(c\) or not
