STFT with Python
참고 : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fMqL5vckiU0&list=PL-wATfeyAMNrtbkCNsLcpoAyBBRJZVlnf
1. Import Packages
import os
import librosa
import librosa.display
import IPython.display as ipd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2. Import Dataset
scale_file = "audio/scale.wav"
debussy_file = "audio/debussy.wav"
redhot_file = "audio/redhot.wav"
duke_file = "audio/duke.wav"
listen to music!
ipd.Audio(redhot_file)
scale, sr = librosa.load(scale_file)
debussy, _ = librosa.load(debussy_file)
redhot, _ = librosa.load(redhot_file)
duke, _ = librosa.load(duke_file)
3. Extract STFT
- Frame size : size of the window
- Hop size : size of the window stride
FRAME_SIZE = 2048
HOP_SIZE = 512
librosa.stft
S_scale = librosa.stft(scale, n_fft=FRAME_SIZE, hop_length=HOP_SIZE)
print(S_scale.shape)
print(type(S_scale[0][0]))
(1025, 342)
numpy.complex64
- 1025 : number of frequency bins
- 1025 = (2048/2 + 1)
- 342 : number of frames
4. Calculate Spectogram
Scale : \(\mid S \mid^2\)
Y_scale = np.abs(S_scale) ** 2
print(Y_scale.shape)
print(type(Y_scale[0][0]))
(1025, 342)
numpy.float32
- taking magnitude => getting real number!
5. Visualization
def plot_spectrogram(Y, sr, hop_length, y_axis="linear"):
plt.figure(figsize=(25, 10))
librosa.display.specshow(Y,
sr=sr,
hop_length=hop_length,
x_axis="time",
y_axis=y_axis)
plt.colorbar(format="%+2.f")
<br.
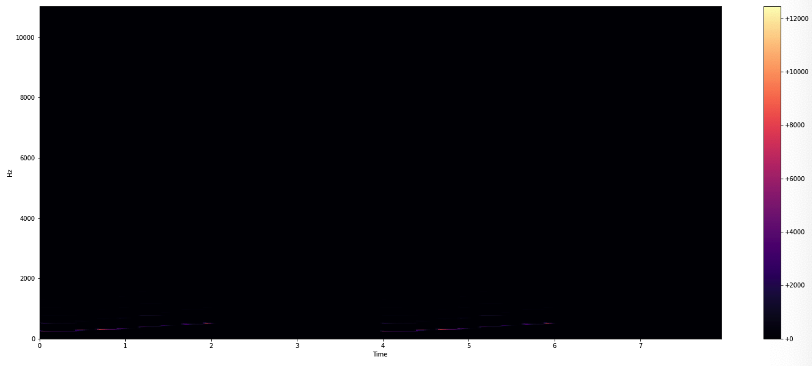
(1) Raw-scale
plot_spectrogram(Y_scale, sr, HOP_SIZE)
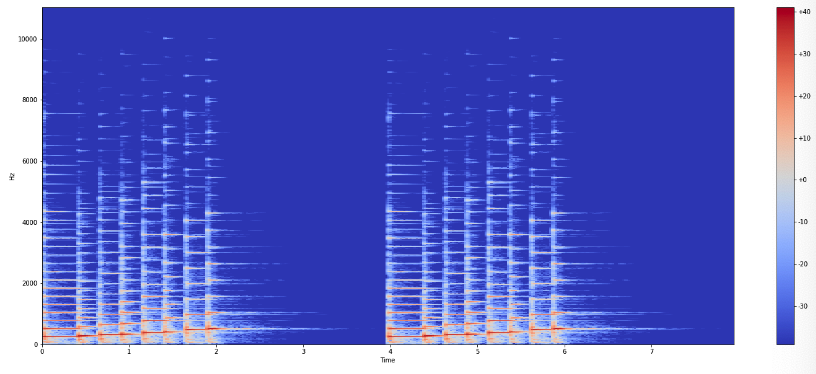
(2) Log-amplitude
Y_log_scale = librosa.power_to_db(Y_scale)
plot_spectrogram(Y_log_scale, sr, HOP_SIZE)
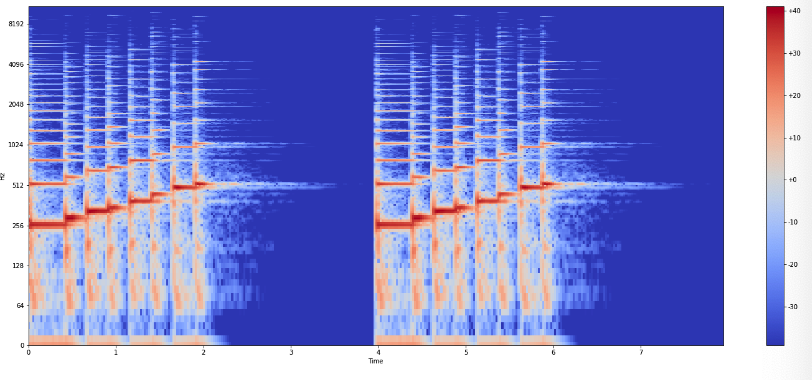
(3) Log-frequency
plot_spectrogram(Y_log_scale, sr, HOP_SIZE, y_axis="log")