Exploring Simple Siamese Representation Learning
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Method
- Pseudocode
0. Abstract
Siamese Networks
- common structure in unsupervised visual representation learning
- Maximizes the similarity between 2 augmentations of one image
Propose a simple Siamese networks , using none of…
- (1) negative sample pairs
- (2) large batches
- (3) momentum encoders
stop-gradient operation plays an essential role in preventing collapsing
1. Introduction
Collapsing problem of Siamese networks… Solutions?
(1) SimCLR ( contrastive learning )
- repulses negative pairs
- attracts positive pairs
(2) SwAV
- use online clustering
(3) BYOL
- relies only on positive pairs,
- but does not collapse in case a momentum encoder is used
(4) SimSiam ( Proposed )
- none of the above strategies!
2. Method
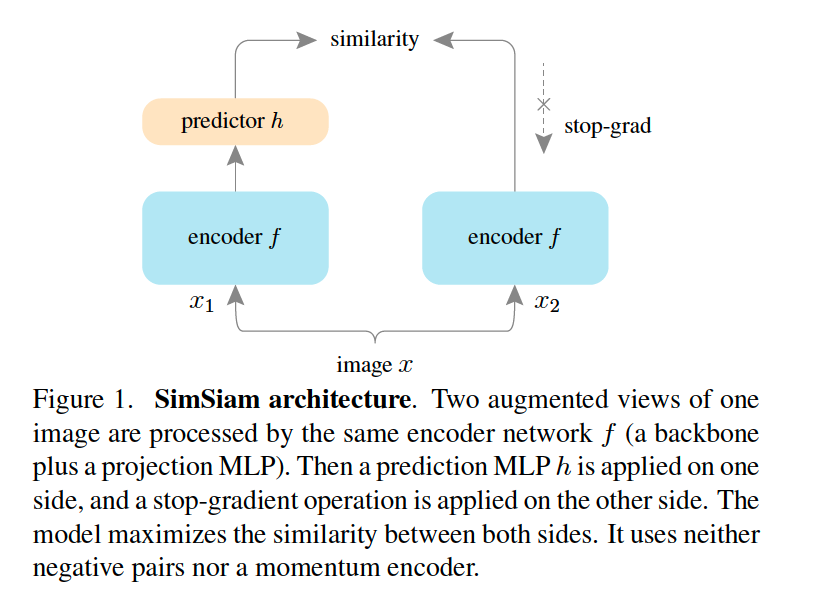
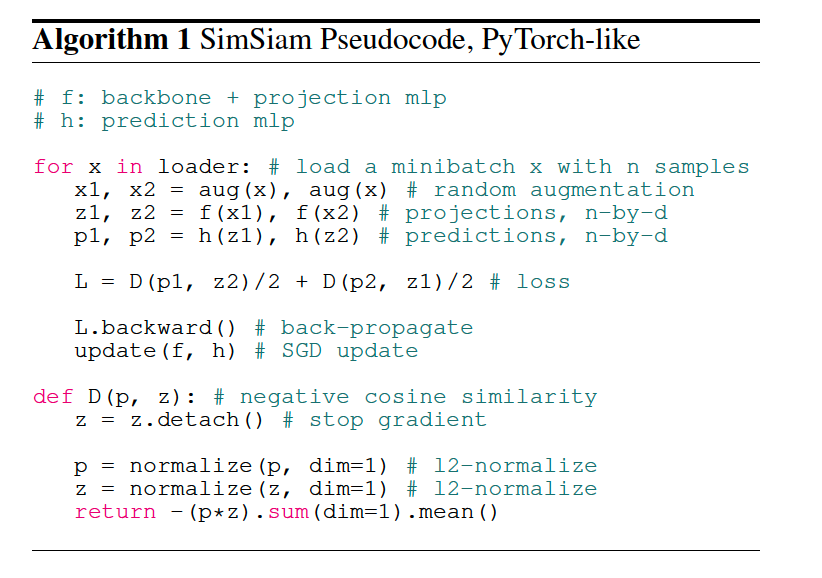
Input : 2 randomly augmented views ( = \(x_1\) & \(x_2\) )
Model
- (1) encoder network \(f\)
- (1-1) backbone ( = ResNet )
- (1-2) projection MLP
- (2) prediction MLP head \(h\)
- transforms the output of one view & matches it to other view
Notation
- 2 output vectors :
- \(p_{1} \triangleq h\left(f\left(x_{1}\right)\right)\).
- \(z_{2} \triangleq f\left(x_{2}\right)\).
Loss Function
- minimize negative cosine similarity :
- \(\mathcal{D}\left(p_{1}, z_{2}\right)=-\frac{p_{1}}{ \mid \mid p_{1} \mid \mid _{2}} \cdot \frac{z_{2}}{ \mid \mid z_{2} \mid \mid _{2}}\).
-
Symmetric loss
-
\(\mathcal{L}=\frac{1}{2} \mathcal{D}\left(p_{1}, z_{2}\right)+\frac{1}{2} \mathcal{D}\left(p_{2}, z_{1}\right)\).
-
defined for each image
-
minimimum : -1
-
Stop-gradient
- ( gradient O )
- \(\mathcal{D}\left(p_{1}, z_{2}\right)\) .
- \(\mathcal{L}=\frac{1}{2} \mathcal{D}\left(p_{1}, z_{2}\right)+\frac{1}{2} \mathcal{D}\left(p_{2}, z_{1}\right)\).
- ( gradient X )
- \(\mathcal{D}\left(p_{1}, \text { stopgrad }\left(z_{2}\right)\right)\).
- \(\mathcal{L}=\frac{1}{2} \mathcal{D}\left(p_{1}, \text { stopgrad }\left(z_{2}\right)\right)+\frac{1}{2} \mathcal{D}\left(p_{2}, \text { stopgrad }\left(z_{1}\right)\right)\).
3. Pseudocode