[code review] CGAN with pytorch
참조 : https://github.com/Lornatang/CGAN-PyTorch/tree/master/cgan_pytorch/models
 .
.
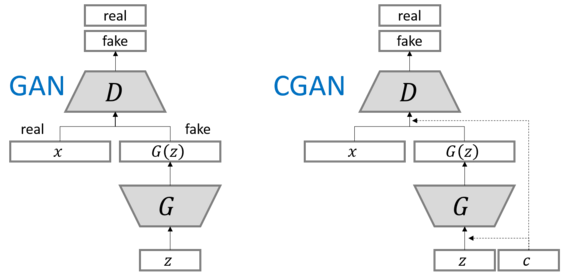
“CONDITION”에 대하여
-
여기서 말하는 “condition”은, MNIST 처럼 “숫자 3을 만들어줘”! 처럼 반드시 “특정 class 지정과 같이 명시적인 조건일 필요가 없다”
-
“conditon”을, 조금 더 broad한 개념으로 생각해보자면
CycleGAN에서 “얼룩무늬가 띈” 말을 만들어달라고 하는 것 또한,
일종의 condition을 부여한 CGAN의 확장판으로도 볼 수 있지 않을까?
Import Packages
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
(1) Discriminator
Input :
- 1) Generator가 만들어낸 Fake Image
- 2) 원하는 condition ( integer -> One-hot-encoding - > embedding 으로 들어가짐 )
Output:
-
sigmoid를 거쳐서 나온 0~1사이 값
( 0 for fake image, 1 for real image )
Structure
- 3-hidden layer NN
- activation function : Leaky Relu ( 0.2 )
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, image_size: int = 28, channels: int = 1, num_classes: int = 10):
super(DiscriminatorForMNIST, self).__init__()
self.label_embedding = nn.Embedding(num_classes, num_classes)
self.layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(channels * image_size * image_size + num_classes, 512),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Linear(512, 256),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Linear(256, 1),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, inputs: torch.Tensor, labels: list = None):
inputs = torch.flatten(inputs, 1)
conditional = self.label_embedding(labels)
final_input = torch.cat([inputs, conditional], dim=-1)
out = self.layers(final_input)
return out
(2) Generator
Input :
- 1) noise ( $z$ )
- 2) 원하는 condition ( integer -> One-hot-encoding - > embedding 으로 들어가짐 )
Output:
- fake image
Structure
- 5-hidden layer NN
- activation function : Leaky Relu ( 0.2 )
유의
- output의 shape : NxCxHxW
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, image_size: int = 28, channels: int = 1, num_classes: int = 10):
super(Generator, self).__init__()
self.image_size = image_size
self.channels = channels
self.label_embedding = nn.Embedding(num_classes, num_classes)
self.layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(100 + num_classes, 128),
nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Linear(128, 256),
nn.BatchNorm1d(256),
nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Linear(256, 512),
nn.BatchNorm1d(512),
nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Linear(512, 1024),
nn.BatchNorm1d(1024),
nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Linear(1024, channels * image_size * image_size),
nn.Tanh()
)
def forward(self, inputs: torch.Tensor, labels: list = None):
final_input = torch.cat([inputs, self.label_embedding(labels)], dim=-1)
fake_image = self.layers(final_input)
fake_image = fake_image.reshape(fake_image.size(0), self.channels,
self.image_size, self.image_size)
return fake_image
(3) Training 과정 (일부 발췌)
Process 간단 요약
- 1) dataloader에서 매 step마다 batch size만큼의 data를 불러와 ( + gpu / cpu 선택 )
- 3) label 붙이기
real_label: real image의 경우의 label인 1짜리 batch size크기의 벡터만들기fake_label: fake image의 경우의 label인 0짜리 batch size크기의 벡터만들기
- 4) noise & condition 랜덤 샘플
- 5) 학습 시작 (아래의 [1]과 [2]가 iteratively하게 진행)
- [1] Discriminator 업데이트하기
- (loss 1-1) real을 1에 가깝게 해야하는 loss 부분
- (loss 1-2) fake을 0에 가깝게 해야하는 loss 부분
- [2] Generator 업데이트하기
- (loss 2) 만들어낸 fake를 1에 가깝게 해야하는 loss 부분
- [1] Discriminator 업데이트하기
for i, (inputs, target) in enumerate(dataloader):
# Move data to special device.
if args.gpu is not None:
inputs = inputs.cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
target = target.cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
batch_size = inputs.size(0)
# The real sample label is 1, and the generated sample label is 0.
real_label = torch.full((batch_size, 1), 1, dtype=inputs.dtype).cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
fake_label = torch.full((batch_size, 1), 0, dtype=inputs.dtype).cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
noise = torch.randn([batch_size, 100])
conditional = torch.randint(6, 7, (batch_size,))
# Move data to special device.
if args.gpu is not None:
noise = noise.cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
conditional = conditional.cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
##############################################
# (1) Update D network: max E(x)[log(D(x))] + E(z)[log(1- D(z))]
##############################################
# Set discriminator gradients to zero.
discriminator.zero_grad()
# Train with real. (loss 1-1)
real_output = discriminator(inputs, target)
d_loss_real = adversarial_criterion(real_output, real_label)
d_loss_real.backward()
d_x = real_output.mean()
# Train with fake.(loss 1-2)
fake = generator(noise, conditional)
fake_output = discriminator(fake.detach(), conditional)
d_loss_fake = adversarial_criterion(fake_output, fake_label)
d_loss_fake.backward()
d_g_z1 = fake_output.mean()
# Count all discriminator losses.
d_loss = d_loss_real + d_loss_fake
discriminator_optimizer.step()
##############################################
# (2) Update G network: min E(z)[log(1- D(z))]
##############################################
# Set generator gradients to zero.
generator.zero_grad()
# (loss 2)
fake_output = discriminator(fake, conditional)
g_loss = adversarial_criterion(fake_output, real_label)
g_loss.backward()
d_g_z2 = fake_output.mean()
generator_optimizer.step()
