Multi-scale temporal feature extraction based GCN with Attention for MTS Prediction (2022)
Contents
-
Abstract
-
Introduction
- EMD
- GCN
-
Related Works
-
Preliminaries
- EMD
- TCN
-
Proposed Approach
- Feature Extraction of TS by EMD
- Graph Generation
- Node Feature updating
-
Establishment of Temporal relationships
- Loss Function
0. Abstract
Overview
-
propose a novel GNN, based on MULTI_scale temporal feature extraction
-
use attention mechanism
3 key points
(1) Empirical Modal Decomposition (EMD)
- to extract time-domain features
(2) GCN
- to generate node embeddings that contain spatial relationships
(3) TCN
- to capture temporal relationships for the node embedding
1. Introduction
(1) EMD ( Empirical Mode Decomposition )
- signal processing tehcnique
- to deal with unstable & non-linear sequences
- used to “extract TEMPORAL FEATURES at DIFFERENT TIME SCALES”
(2) GCN
- used for node feature updating
- and generating node embeddings
2. Related Works
( check GConvLSTM & GConvGRU )
appropriate temporal feature extraction methods are crucial!!
3. Preliminaries
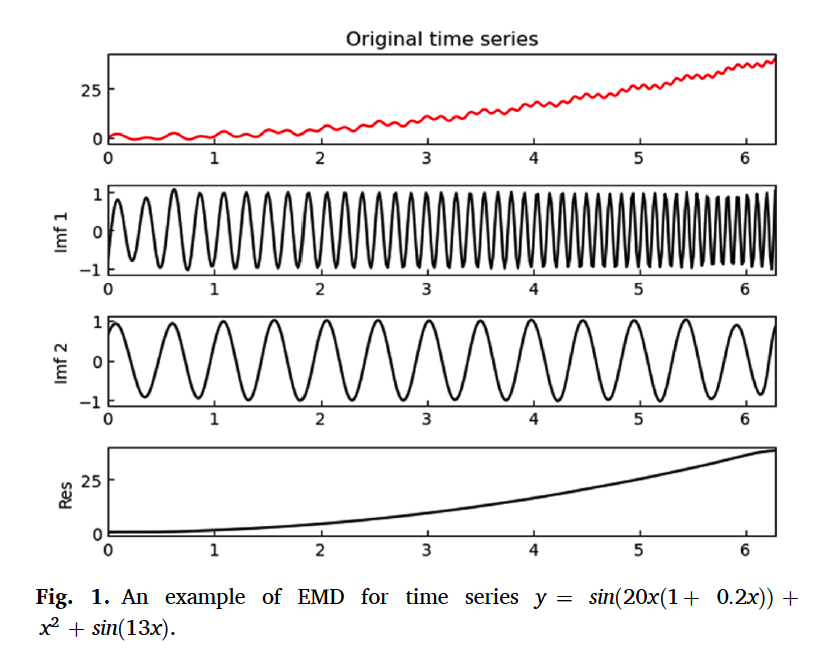
(1) EMD ( Empirical Mode Decomposition )
Decompose TS into several different intrinsic mode functions (IMFs) & residuals
\(\boldsymbol{x}=\sum_{i=1}^{N} \boldsymbol{i m} \boldsymbol{f}_{i}+\boldsymbol{r}_{N}4\).
- \(\boldsymbol{i m f}_{i}\) : the \(i\) th IMF
- \(N\) : number of IMFs.
(2) TCN
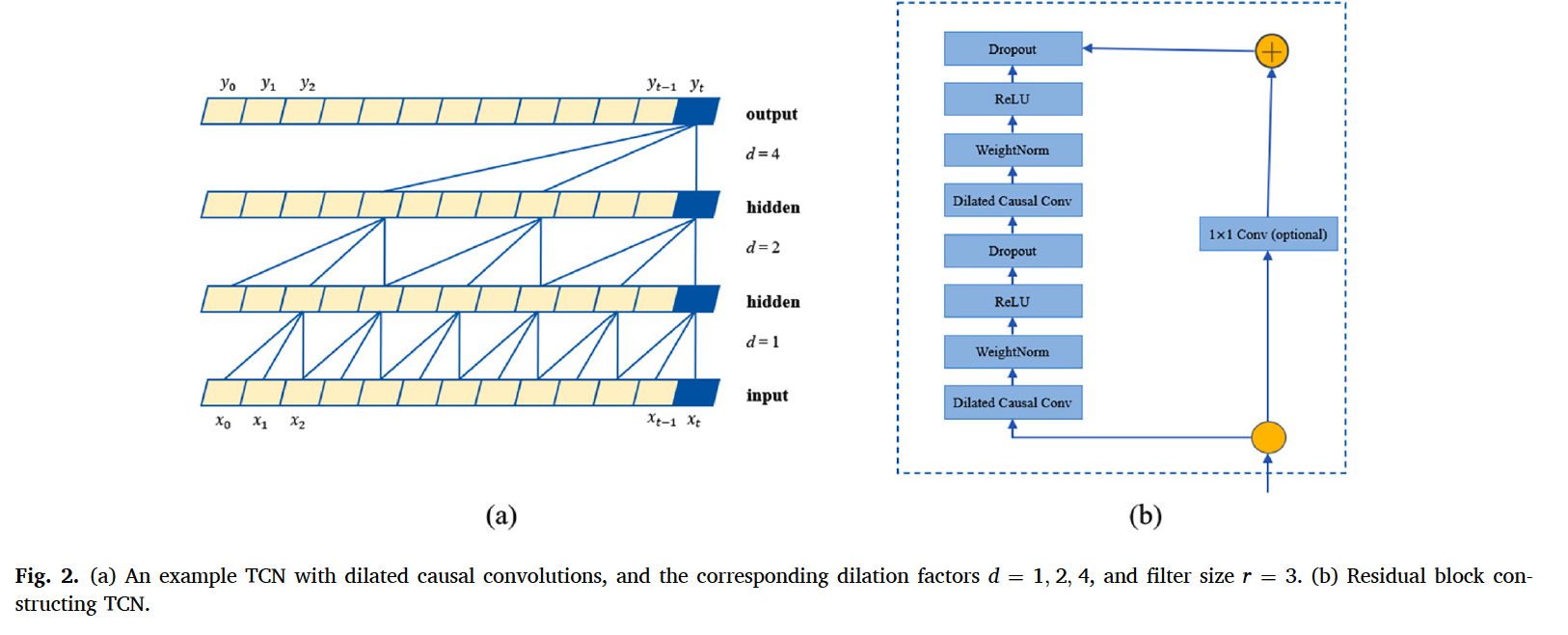
- able to capture long-term dependencies
- use residual blocks
4. Proposed Approach
consists of 4 parts
- Feature Extraction
- Graph Generation
- Node Feature Updating
- Establishment of Temporal Relationship
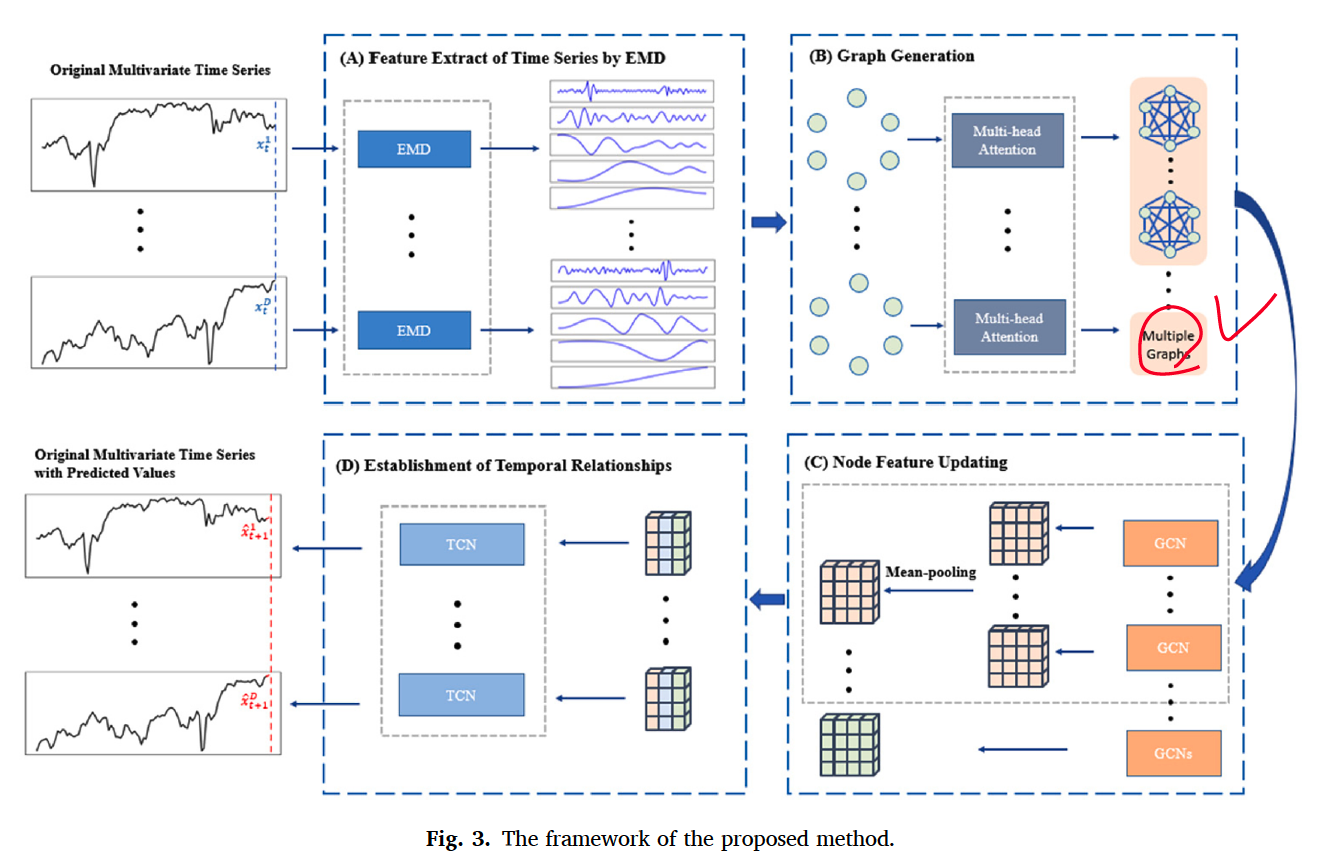
(1) Feature Extraction of TS by EMD
Original TS : noisy & outliers
use EMD to decompose original TS
- meaning of each component : different time scale features
- can mitigate effect of noise
MTS : \(\boldsymbol{X}=\left\{\boldsymbol{x}_{1}, \boldsymbol{x}_{2}, \ldots, \boldsymbol{x}_{T}\right\}\).
- where \(\boldsymbol{x}_{t} \in \mathbb{R}^{D}\)
- \(j^{th}\) dimensional TS : \(\boldsymbol{X}^{j}=\{\left.x_{1}^{j}, x_{2}^{j}, \ldots, x_{T}^{j}\right\}\)
Decomposition of \(\boldsymbol{X}^{j}\)
- \(\boldsymbol{X}^{j}=\sum_{i=1}^{N} \boldsymbol{i m f}_{i}^{j}+\boldsymbol{r}_{N}^{j}\).
Matrix Notation
\(\boldsymbol{M}^{j}=\left[\begin{array}{cccc} i m f_{1}^{j}(1) & i m f_{1}^{j}(2) & \cdots & i m f_{1}^{j}(T) \\ i m f_{2}^{j}(1) & i m f_{2}^{j}(2) & \cdots & i m f_{2}^{j}(T) \\ \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\ i m f_{N}^{j}(1) & \operatorname{imf}_{N}^{j}(2) & \cdots & i m f_{N}^{j}(T) \\ r_{N}^{j}(1) & r_{N}^{j}(2) & \cdots & r_{N}^{j}(T) \end{array}\right]\).
- each subsequence obtained by EMD : used as node features
(2) Graph Generation
each subsequence obtained by EMD
= different time scale features of original TS
\(\rightarrow\) used to characterize nodes
Sliding window ( size \(k\) )
- divide each dimensional feature matrix
- obtain \(\boldsymbol{M}^{1}[T-k+1: T]\) ….\(\boldsymbol{M}^{D}[T-k+1: T]\)
Concatenate “IMFs” & “residuals”
\(\boldsymbol{V}_{t}=\left[\boldsymbol{v}_{t}^{1}, \boldsymbol{v}_{t}^{2}, \ldots, \boldsymbol{v}_{t}^{D}\right]^{T}=\left[\begin{array}{ccccc} \operatorname{imf}_{1}^{1}(T-t+1) & \operatorname{imf}_{2}^{1}(T-t+1) & \cdots & \operatorname{imf}_{N}^{1}(T-t+1) & r_{N}^{1}(T-t+1) \\ \operatorname{imf}_{1}^{2}(T-t+1) & \operatorname{imf}_{2}^{2}(T-t+1) & \cdots & \operatorname{imf}_{N}^{2}(T-t+1) & r_{N}^{2}(T-t+1) \\ \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots & \vdots \\ \operatorname{imf}_{1}^{D}(T-t+1) & \operatorname{imf}_{2}^{D}(T-t+1) & \cdots & \operatorname{imf}_{N}^{D}(T-t+1) & r_{N}^{D}(T-t+1) \end{array}\right]\).
- \(V_{t} \in \mathbb{R}^{D \times(N+1)}\) : initial node feature matrix at \(t\) moment
- \(v_{t}^{j} \in \mathbb{R}^{N+1}\) : initial feature vector of the \(j\) th node of the graph at \(t\) moment.
Multi-head attention
\(\tilde{\boldsymbol{A}}^{i}=\operatorname{softmax}\left(\frac{\boldsymbol{Q} \boldsymbol{W}_{i}^{Q} \times\left(\boldsymbol{K} \boldsymbol{W}_{i}^{K}\right)^{T}}{\sqrt{N+1}}\right)\).
-
\(\boldsymbol{Q} \in \mathbb{R}^{D \times(N+1)}\) & \(\boldsymbol{K} \in \mathbb{R}^{D \times(N+1)}\) : node feature matrix
- \(N+1\) : dimension of node features
-
\(\tilde{\boldsymbol{A}}^{i}\) : \(i\)th adjacency matrix
-
\(i \in\{1, 2, \ldots, \alpha\}\). ( number of heads )
-
When the prior knowledge of MTS ….
\(\widetilde{\boldsymbol{A}}^{i}=\operatorname{softmax}\left(\frac{\boldsymbol{Q} \boldsymbol{W}_{i}^{Q} \times\left(\boldsymbol{K} \boldsymbol{W}_{i}^{K}\right)^{T}}{\sqrt{N+1}}\right) \boldsymbol{A}\).
-
Learnt adjacency matrix
-
varies with input!
-
multiple matrices, with multi-head attention
( \(\alpha\) FC graphs for all \(k\) moments )
(3) Node feature updating
-
use GCN to generate embeddings of nodes
-
for \(i^{th}\) graph at a given moment..
- \(\boldsymbol{H}_{i}^{l+1}=\rho\left(\widetilde{\boldsymbol{A}}^{i} \boldsymbol{H}_{i}^{l} \boldsymbol{W}_{i}^{l+1}+\boldsymbol{b}_{i}^{l+1}\right)\).
- \(\boldsymbol{H}_{i}^{l} \in \mathbb{R}^{D \times h_{\text {din }}}, l=\{1,2, \ldots, J\}\) : hidden matrix
- \(\boldsymbol{H}_{i}^{0}\) : initial node feature matrix
- \(\boldsymbol{H}_{i}^{l+1}=\rho\left(\widetilde{\boldsymbol{A}}^{i} \boldsymbol{H}_{i}^{l} \boldsymbol{W}_{i}^{l+1}+\boldsymbol{b}_{i}^{l+1}\right)\).
Embedding for the \(t\) moment :
- \(\boldsymbol{E}_{t}=\) MeanPooling \(\left(\boldsymbol{H}_{i}^{J}, \alpha\right)\)
- \(\boldsymbol{E}_{t}=\left[\boldsymbol{e}_{t}^{1}, \boldsymbol{e}_{t}^{2}, \ldots, \boldsymbol{e}_{t}^{D}\right]^{T}, t=\{1,2, \ldots, k\}\),
- \(\boldsymbol{e}_{t}^{j} \in \mathbb{R}^{h_{\text {ouput }}}\) : \(j\) th node embedding at the \(t\) moment
(4) Establishment of temporal relationships
Input : \(\boldsymbol{E}^{j}=\left[\boldsymbol{e}_{1}^{j}, \boldsymbol{e}_{2}^{j}, \ldots, \boldsymbol{e}_{k}^{j}\right]\)
use TCN
(5) Loss Function
\(\operatorname{loss}=\frac{1}{D(T-1)} \sum_{j=1}^{D} \sum_{t=1}^{T}\left(x_{t}^{j}-\widehat{x}_{t}^{j}\right)^{2}\).
- GCN & TCN are jointly learned
