Duality
Contents
- Introduction
- LP에서의 Duality
- Lagrangian
- Lagrangian function
- Lagrangian Dual function
- Lagrangian Dual function의 2가지 특징
- Dual Problem
- 요약
- Strong duality
- Strong duality 예시
- Economic Interpretation
1. Introduction
Primal & Dual
- Primal : 원 문제
- Dual : 쌍대 문제
Dual Problem의 특징
- (1) concave function
- (2) Primal problem의 objective function의 lower bound
- 만약, Dual problem의 최대값 = Primal problem의 최소값 \(\rightarrow\) STRONG duality
KKT condition
- 최적화를 푸는 가장 일반적인 방법
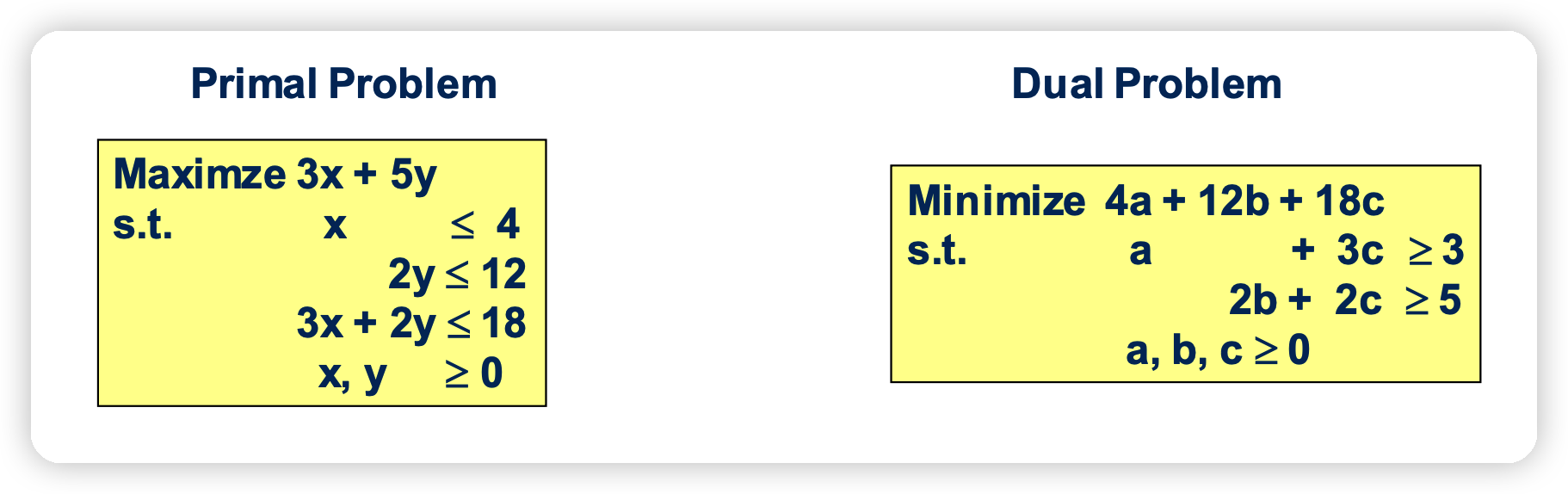
2. LP에서의 Duality
3. Lagrangian
minimize \(\quad f_{0}(x)\) subject to
- \[f_{i}(x) \leq 0, \quad i=1, \ldots, m\]
- \(h_{i}(x)=0, \quad i=1, \ldots, p\).
variable \(x \in \mathbf{R}^{n}\), domain \(\mathcal{D}\), optimal value \(p^{\star}\)
(1) Lagrangian function
- 목적 함수 & 제약식의 weighted sum 형태
- \(L(x, \lambda, \nu)=f_{0}(x)+\sum_{i=1}^{m} \lambda_{i} f_{i}(x)+\sum_{i=1}^{p} \nu_{i} h_{i}(x)\).
- \(\lambda_{i}\) is Lagrange Multiplier associated with \(\mathrm{f}_{i}(\mathrm{x}) \leq 0\)
- \(v_{i}\) is Lagrange Multiplier associated with \(\mathrm{h}_{i}(\mathrm{x})=0\)
example)
(1) Primal problem
- minimize \(f(x)=x_{1}^{2}+x_{2}^{2}\)
- subject to \(x_{1}+2 x_{2} \geq 2\)
(2) Standard form ( 제약식 : g(x) \(\leq\) k 꼴로 만들기! )
- minimize \(f(x)=x_{1}^{2}+x_{2}^{2}\)
- subject to \(-x_{1}-2 x_{2} \leq-2\)
(3) Lagrangian
- \(L(x, v)=x_{1}^{2}+x_{2}^{2}-v_{1}\left(x_{1}+2 x_{2}-2\right)\).
(2) Lagrangian Dual Function
\(g: \mathbf{R}^{m} \times \mathbf{R}^{p} \rightarrow \mathbf{R}\).
\(\begin{aligned} g(\lambda, \nu) &=\inf _{x \in \mathcal{D}} L(x, \lambda, \nu) \\ &=\inf _{x \in \mathcal{D}}\left(f_{0}(x)+\sum_{i=1}^{m} \lambda_{i} f_{i}(x)+\sum_{i=1}^{p} \nu_{i} h_{i}(x)\right) \end{aligned}\).
- 위 식에서 \(L\)은 Lagrangian function이다.
example)
(1) Lagrangian
- \(L(x, v)=x_{1}^{2}+x_{2}^{2}-v_{1}\left(x_{1}+2 x_{2}-2\right)\).
(2) Lagrangian Dual Function
- \(\begin{aligned}
g(v)=\inf _{x} L(x, v) &=\inf _{\mathrm{x}}\left[x_{1}^{2}+x_{2}^{2}-v_{1}\left(x_{1}+2 x_{2}-2\right)\right] \\
&=\inf _{x}\left[\left(x_{1}^{2}-v_{1} x_{1}\right)+\left(x_{2}^{2}-2 v_{1} x_{2}\right)+2 v_{1}\right]
\end{aligned}\).
- 이를 infimum을 달성하는 \(x_1\) 와 \(x_2\)를 ( v에 관한 식으로 ) 정리해서 대입하면…
- \(g(v) = -\frac{5}{4}v_1^2 + 2v_1\).
(3) Lagrangian Dual Function의 2가지 특징
1) concave function
\(g(\lambda, \nu) =\inf _{x \in \mathcal{D}}\left(f_{0}(x)+\sum_{i=1}^{m} \lambda_{i} f_{i}(x)+\sum_{i=1}^{p} \nu_{i} h_{i}(x)\right)\).
- (1) Lagrangian은 \(x\)에 관한 AFFINE function 이다
- (2) AFFINE function은 concave하다
- (3) 2개의 concave 함수의 minimum 또한 concave하다
\(\rightarrow\) \(\therefore\) \(g(\lambda, \nu)\)는 concave function이다.
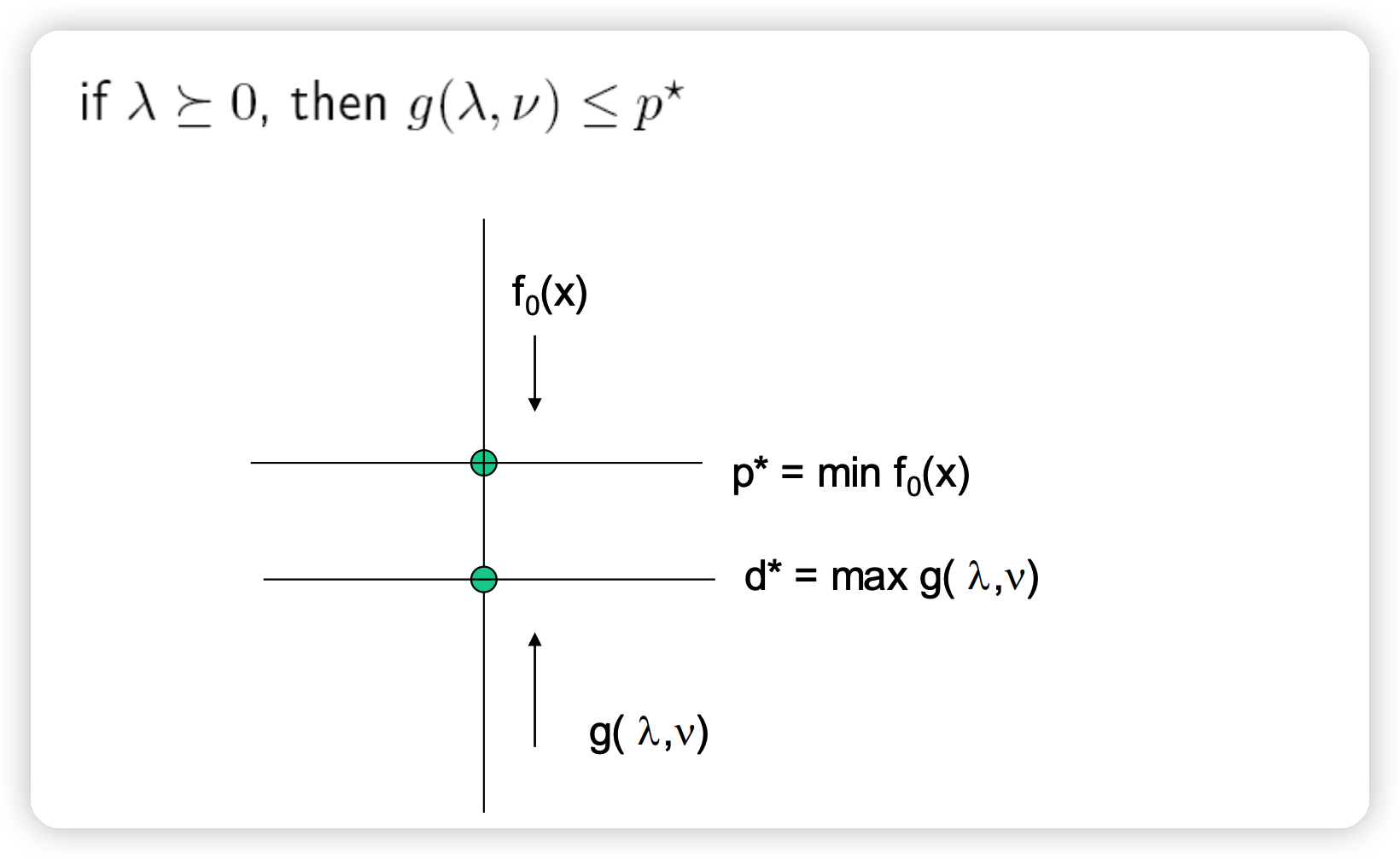
2) lower bound to original problem
4. Dual Problem
(1) 요약
Dual Problem : 항상 convex problem이다
- Primal Problem의 convex 여부와 무관
Weak duality ( \(p^{*} \geq d^{*}\) ) 는 항상 충족된다
Dual Problem을 품으로써, Primal Problem에 대한 좋은 lower bound를 얻을 수 있다.
(2) Strong duality : \(p^{*} = d^{*}\)
( 일반적으로, 잘 성립하지 않는다. Convex problem의 경우에 주로 성립한다 )
(1) Convexity
(2) Constraint Qualification
\(\rightarrow\) (1) & (2) implies STRONG duality
Slater’s Constraint Qualification
- there exists strictly feasible primal variables \(f_i(x)<0\).
(3) Strong duality 예시
아래의 문제가 Strong duality를 충족하는지 확인해보자.
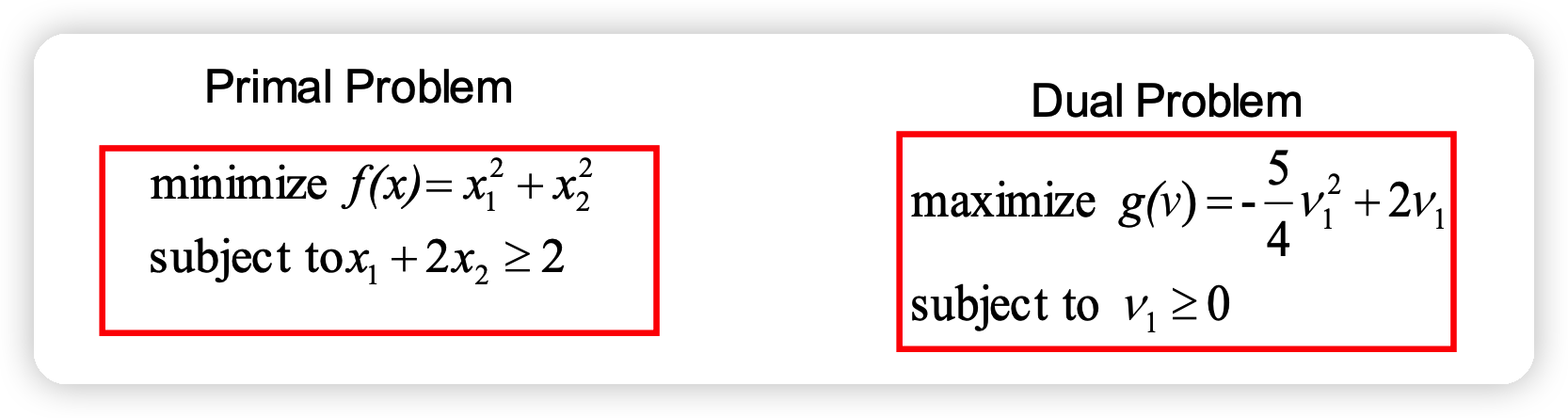
Dual Problem
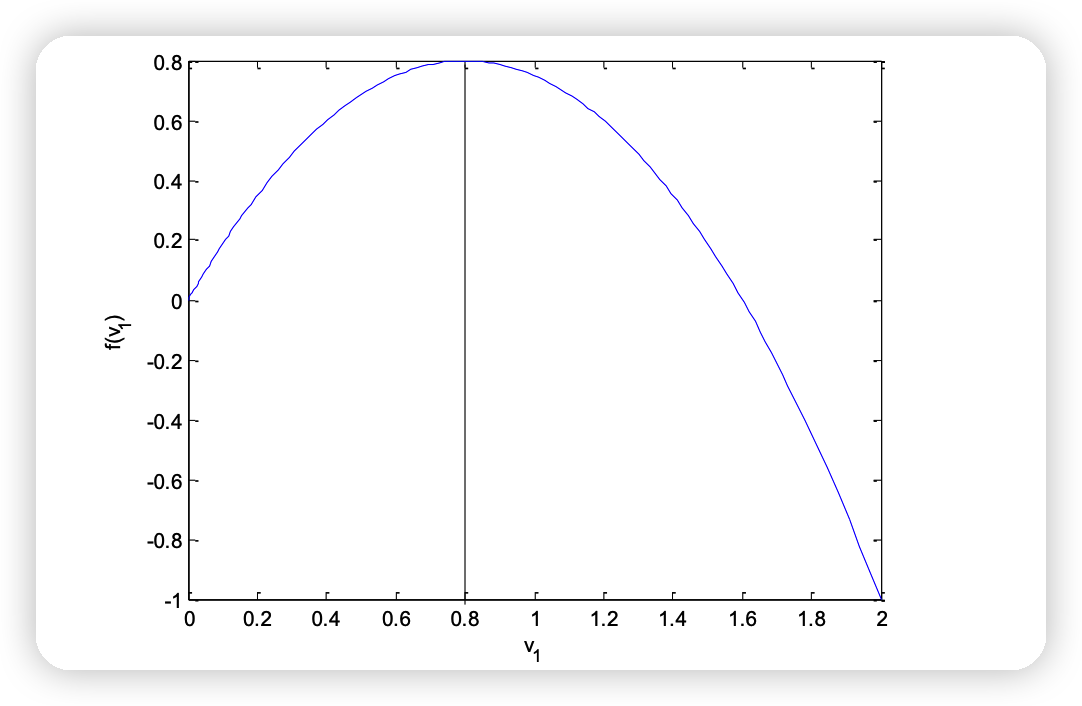
\(v_1\) 이 0.8일때, 최대값을 달성한다
( \(g(v^{*}) = g(0.8) = 0.8\) )
Primal Problem
\(x\)가 (0.4, 0.8)일때, 최소값을 달성한다
( \(f(x^{*}) = f(0.4 ,0.8) = 0.8\) )
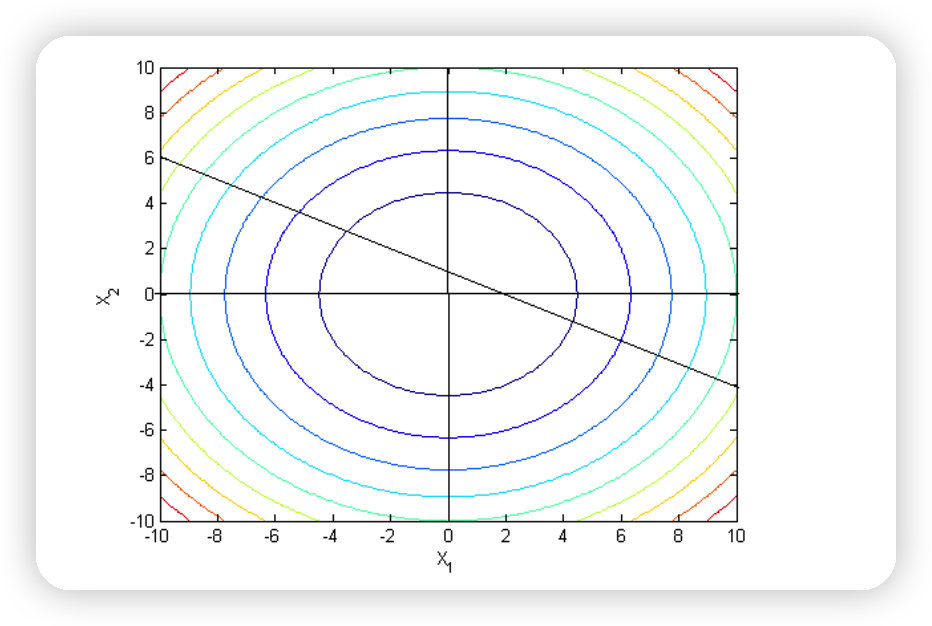
Strong duality를 충족함을 보였다!
5. Economic Interpretation
회사 XYZ가 운영비용을 최소화 하고자 한다.
Notation
-
\(x\) : 회사 운영 방식
-
\(f_0(x)\) : \(x\)와 같이 운영 시의 운영 비용
( \(-f_0(x)\) : 이익)
Goal : minimize \(f_0(x)\)
-
constraint : \(f_i(x) \leq 0\)
( ex. labor, warehouse, environmental … )
Lagrangian
- \(L(x, \lambda)=f_{0}(x)+\sum_{i=1}^{m} \lambda_{i} f_{i}(x)\).
Dual function
- \(g(\lambda)=\min L(x, \lambda)\).
