CRPS (Continuous Ranked Probability Score)
Contents
- Motivation
- CRPS (Continuous Ranked Probability Score)
- Intuition
1. Motivation
Metric for DISTRIBUTION
Bayseian ML’s prediction
- point-wise (X)
- distribution (O)
Prediction could be ..
-
(parametric) estimated parameters of a distribution
-
(nonparametric) samples from MCMC
So … how to evaluate??
\(\rightarrow\) Continuous Ranked Probability Score
2. CRPS (Continuous Ranked Probability Score)
Score function ( = metric ) that compares
- (1) single GT
- (2) predicted CDF
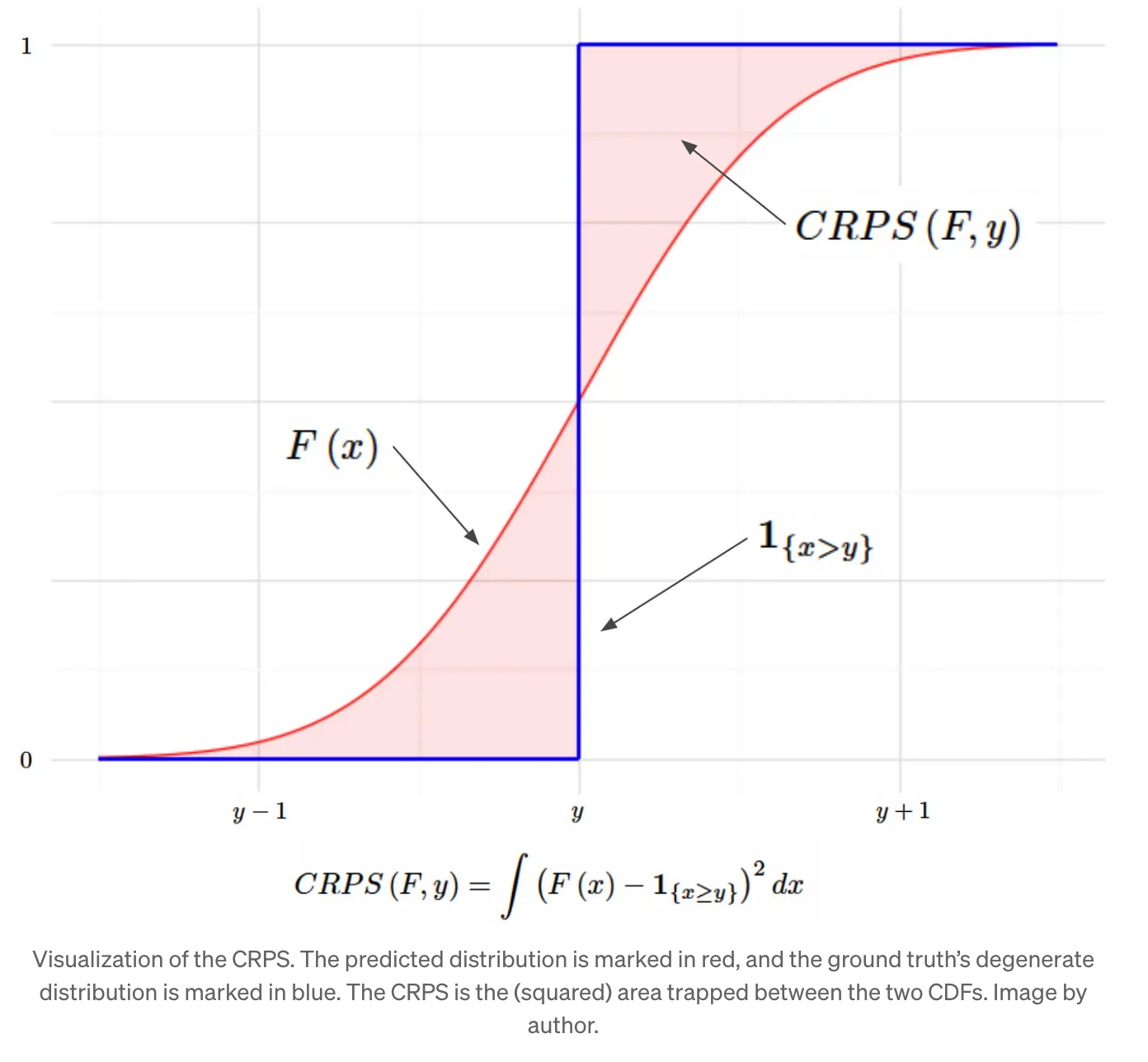
\(C R P S(F, y)=\int\left(F(x)-\mathbf{1}_{\{x \geq y\}}\right)^2 d x\).
- both applicable to …
- parametric : CRPS
- non-parametric : eCDF ( emprical CDF )
Compute CRPS for each observation ( in test data )
& Aggregate them using (weighted) average
\(\sum_i w_i \cdot \int\left(\hat{F}_i(x)-\mathbf{1}_{\left\{x \geq y_i\right\}}\right)^2 d x ; \quad \sum_i w_i=1\).
3. Intuition
point-wise vs distn \(\rightarrow\) distn vs distn
( feat degenerate distn )
Example) if GT point-wise value is 7 …
\(P(7 \leq y)=1_{\{y \geq 7\}}= \begin{cases}0 & \text { if } y<7 \\ 1 & \text { else }\end{cases}\).
( = valid CDF … since it satisfies all the requirements of CDF )
We want the predictied distn & point-wise\(\rightarrow\) degenerate distn to be close!
= the red area below to be SMALL
Reference
- https://towardsdatascience.com/crps-a-scoring-function-for-bayesian-machine-learning-models-dd55a7a337a8
