( 출처 : 연세대학교 데이터베이스 시스템 수업 (CSI6541) 강의자료 )
Indexing & Hashing
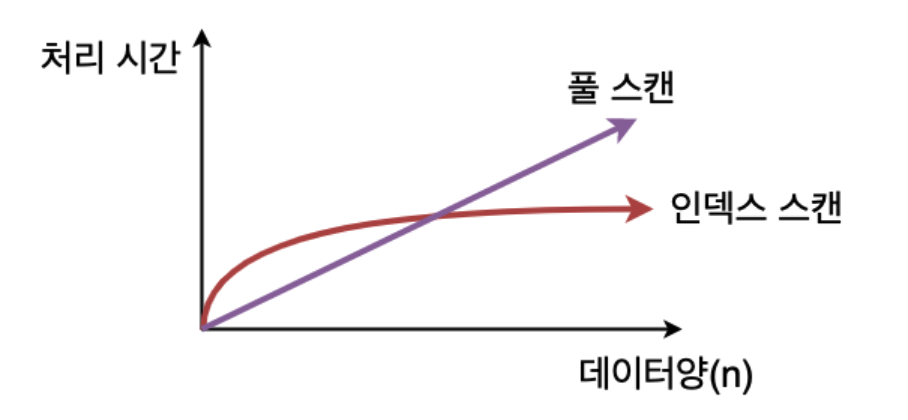
DB에서 데이터 가져오는 방법
- (1) full scan : 전체 데이터 조사
- 데이터 파일의 record를 순차적으로 확인 -> 매우 느림
- (2) indexed access : 인덱스 파일
- not only 데이터 파일, but also 인덱스 파일
- 인덱스 파일에 접근해서, 특정 record의 위치를 찾음
- 2가지 종류
- a) ordered indices : search key가 정렬된 형태
- b) hash indices : hash function을 사용해서, search key를 균등하가 bucket에 분포
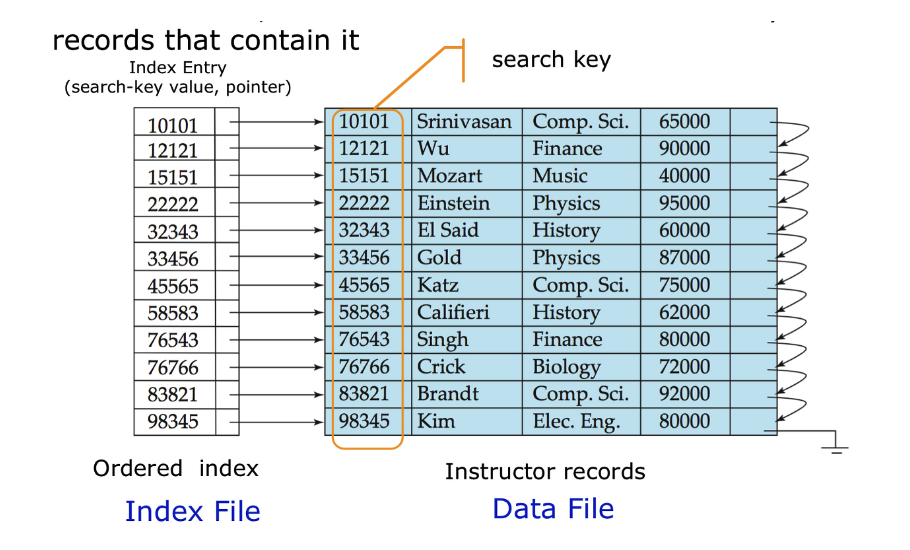
ordered index
- search key가 정렬된 형태
- index file을 순차적으로 내려가면서 찾음
- (vs Full Scan)
- Data file의 크기 » Index file의 크기
- Data file에서 순차적으로 찾을 경우…
- 매우 많은 block들이 buffer를 거침
- Index file에서 순차적으로 찾을 경우…
- 훨씬 적은 block들이 buffer를 거침
- ex) id = 83821인 record 찾을 때..
- case 1) ordered index 사용 시 : 1개의 블록만을 거치면됨
- case 2) full scan 시 : 6개의 블록을 거쳐야됨
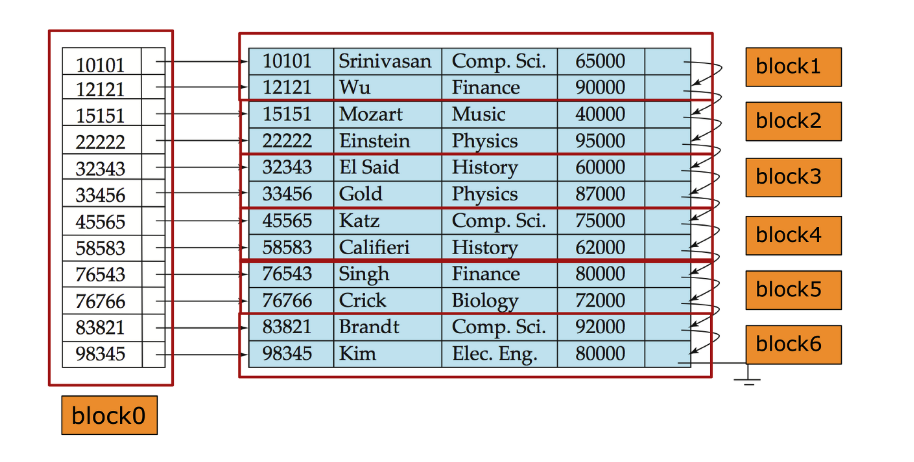
Index access의 단점 = “UPDATE”
- data file 변경 시, index file도 변경해줘야! ( = maintenance 비용 )
Primary Index ( = Clustering index )
- primary key를 search key로 한 index
- 1개만 존재 ( DBMS가 자동으로 생성 )
- index file의 순서 = data file의 순서
Secondary Index ( = Non-clustering index )
- index file의 순서 != data file의 순서
- 여러 개 존재 OK ( 사용자가 직접 생성 )
Hashing : for “file organization”
-
hash function을 사용하여 bucket에 데이터를 분배
( 하나의 block이 하나의 bucket 역할 )
-
bucket overflow (공간 부족) 시, 새로운 block을 사용 ( = overflow chaining )
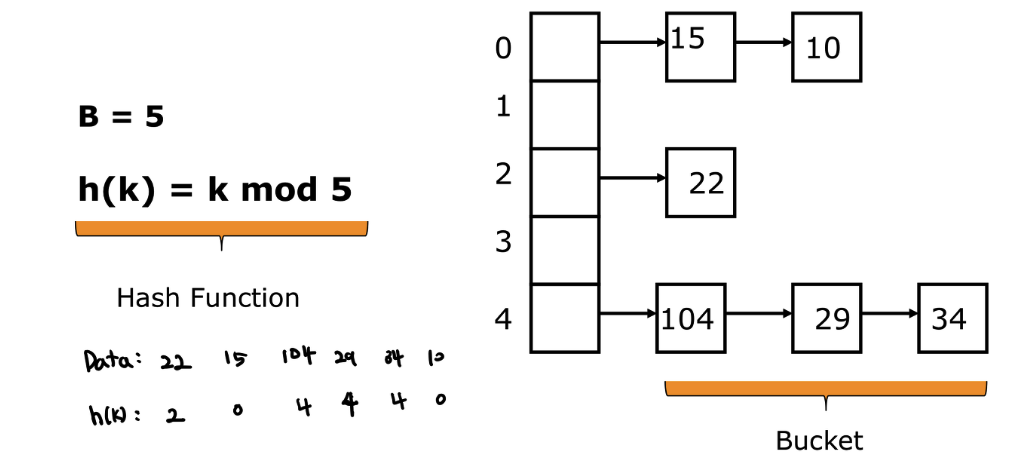
Hashing example 1)
- B ( 버킷 개수 ) = 5
- h(k) = k % 5
Hashing example 2)
- physics 레코드를 찾을 경우 ….
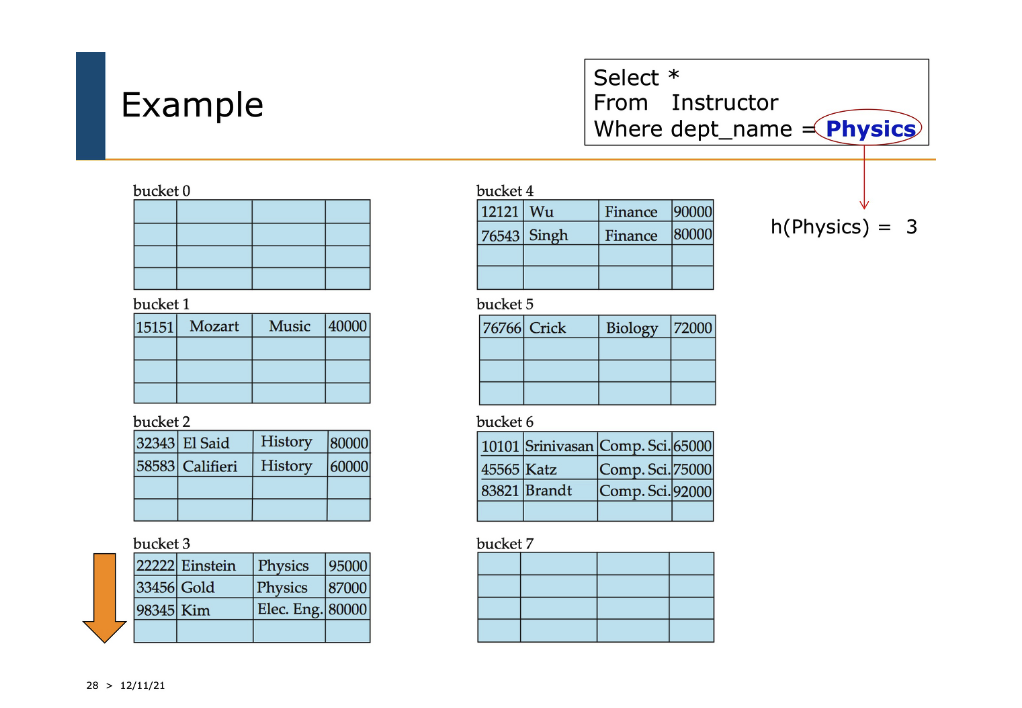
Hash Index : for “index-structure”
- 성능은 fast, but only EQUAL 연산 시에만 가능
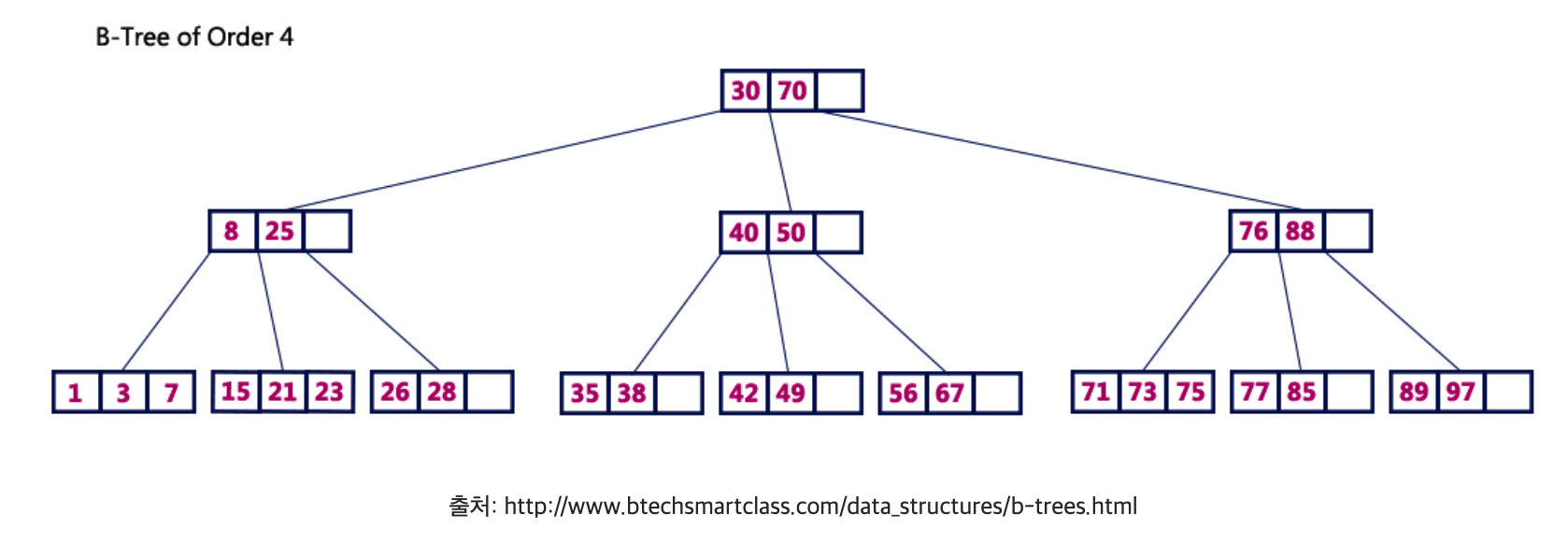
B-tree
- tree 구조 : “탐색” 시, fast
- B-tree의 핵심 : 데이터가 “정렬된 상태” 로 유지
- 용어) root / branch / leaf node
- ex) B-tree of order 4
B-tree vs Binary search tree
- (B-tree) node 1개당 “2개 이상”의 node
- (Binary search tree) node 1개당 “2개”의 node
B-Tree of Order m has the following properties…
- Property #1 - All leaf nodes must be at same level.
- Property #2 - All nodes except root must have …
- at least [m/2]-1 keys (nodes) and maximum of m-1 (nodes)
- Property #3 - All non leaf nodes except root (i.e. all internal nodes) …
- at least [m/2] children (주소 공간) and maximum of m children (주소 공간)
- Property #4 - If the root node is a non leaf node, then it must have atleast 2 children.
- Property #5 - A non leaf node with n-1 keys must have n number of children.
- Property #6 - All the key values in a node must be in Ascending Order.
B-tree가 빠른 이유?
-
장점) 균일성 = 어떠한 값에 대해도, “같은 시간에 결과를 얻을 수 있음” ( \(O(\log N)\) )
-
균형 트리
-
root ~ leaf 까지의 “거리가 일정”
-
성능이 안정화
( but INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE 등으로 균형이 깨지고, 성능 악화 )
-
어느 정도 균형 회복 기능 O
( but 너무 잦은 갱신 시, index 재구성하기! )
-
-
데이터 양에 비례해서 효과 상승
B+tree
-
B-tree의 확장 개념
-
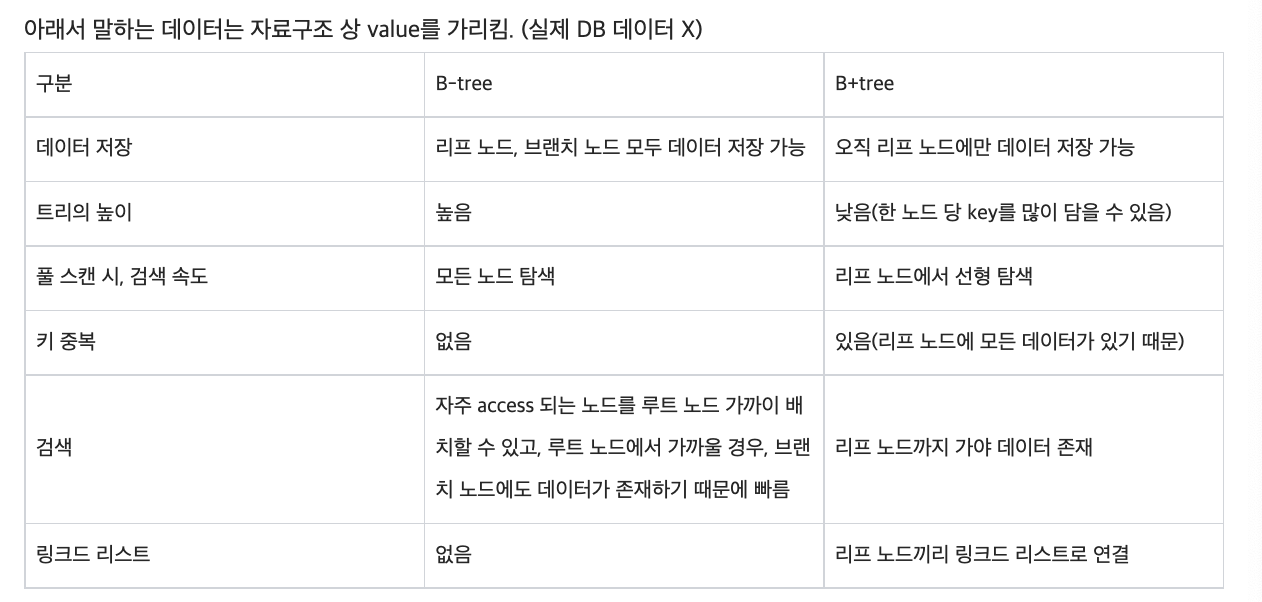
B-tree vs B+tree
-
( B-tree )
- internal / branch / leaf 노드 : key & data
-
( B+tree )
-
internal / branch 노드 : key
-
leaf 노드 : key & data
( leaf 노드들 끼리 linked list로 연결되어 있음 )
-
-
-
장점 )
-
(1) leaf 노드 제외 데이터가 없기 때문에, 더 많은 memory 확보 가능
-
하나의 node에 더 많은 key 수용 가능
\(\rightarrow\) 더 낮은 tree의 높이 ( cache hit를 높일 수 있음 )
-
-
(2) full-scan시, leaf 노드에 전부 데이터가 있으므로 “1번의 선형 탐색”만 해도!
( \(\leftrightarrow\) B-tree : 모든 node 확인해야! )
-
B-tree vs B+tree 비교
Reference
- https://ahn3330.tistory.com/163
- https://zorba91.tistory.com/293
- http://www.btechsmartclass.com/data_structures/b-trees.html
