Transfer Learning with Deep Tabular Models (ICLR 2023)
https://openreview.net/pdf?id=b0RuGUYo8pA
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- TL setup in Tabular Domain
- MetaMIMIC for TL
- Tabular models
- TL setups and baselines
- Results for TL
- SSL pretraining
- MLM
- CL
- Sup vs. Self-Sup pretraining
- Pseudo features
Abstract
Major advantage of NN :
- easily fine-tuned in NEW domains & learn REUSABLE features
Propose Transfer Learning (TL) with Tabular DL
1. Introduction
Design a benchmark TL task using MetaMIMIC repository
-
Compare GBDT methods vs. DL methods
-
Compare Supervised pre0training vs. Self-supervised pre-training
Propose pseudo-feature method
- for case when UPstream data features \(\)\neq\(\) DOWNstream data features
- ex) \(\)x_i\(\) is only in DOWNsteam data
- Details
- Step 1) pretrain with UPSTREAM (w/o \(\)x_i\(\))
- Step 2) finetune with DOWNSTREAM
- task: predicting \(\)x_i\(\)
- Step 3) assign pseudo-values \(\)\hat{x_i}\(\) to UPSTREAM
- Step 4) pretrain with UPSTREAM (with \(\)\hat{x_i}\(\))
- Step 5) finetune with DOWNSTREAM
Contributions
- Deep Tabular models + TL
- Compare two pre-training settings
- (1) SUPERVISED pre-training
- (2) SELF-SUPERVISED pre-training
- Pseudo-feature method
- to algin UPstream & DOWNstream features
2. TL setup in Tabular Domain
(1) MetaMIMIC for TL
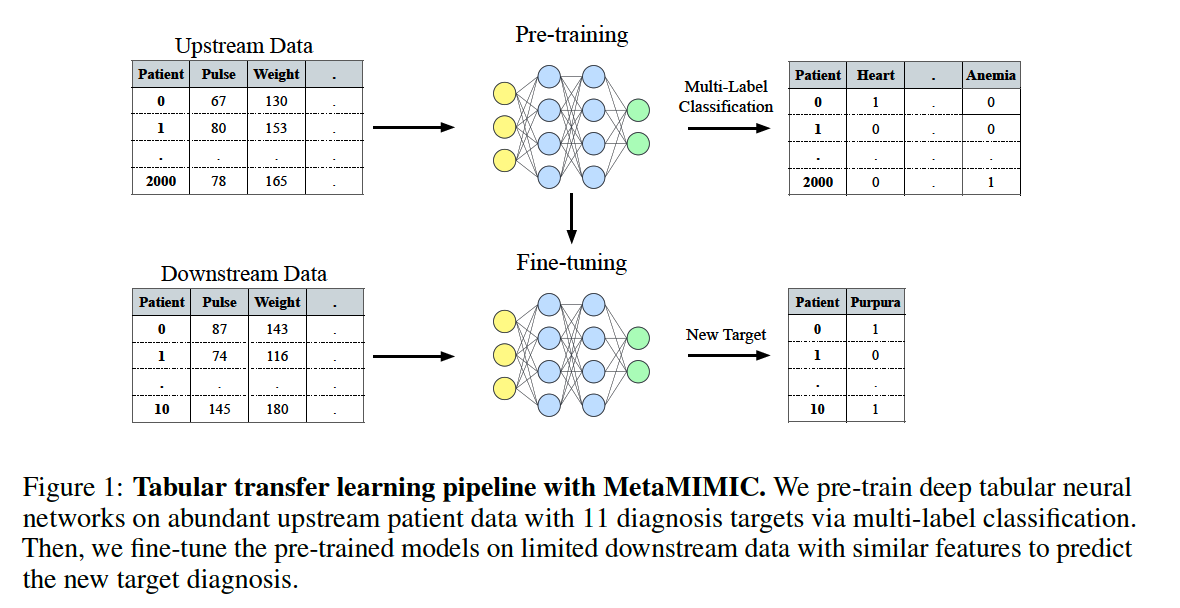
a) MetaMIMIC
- medical diagnosis data
- contains similar test results (features) across patients
- 12 binary prediction tasks
- related tasks of varied similarity \(\)\rightarrow\(\) suitable for TL
- 34925 patients
- 172 features ( 1 categorical … gender )
b) UPstream & DOWNstream tasks
By splitting MetaMIMIC data (12)
= (11) upstream + (1) downstream
- # of data in downstream: 4/10/20/100/200 ( 5 scenarios )
\(\)\rightarrow\(\) total of 60 combinations
(2) Tabular models
6 models = 4 DL + 2 GBDT
- 4 DL = FT-Transformer + TabTransformer + MLP + ResNet
- 2 GBDT = Catboost + XGBoost
(3) TL setups and baselines
For downstream classification head.. 4 options
- (1) classification head: Linear vs MLP
- (2) fine-tune vs freeze
Baselines
-
NN from scratch ( on downstream data )
-
Catboost & XG boost
- with stacking
- without stacking
( stacking = 11 upstream targets as input features of downstream task )
3. Results for TL
Compare DL methods vs GBDT methods
- Metric : rank aggregation metric
- rank = take into account statistical significance of performance differences
- Result : DL > GBDT at all data levels…especially in LOW data regime ( 4~20 downstream samples )
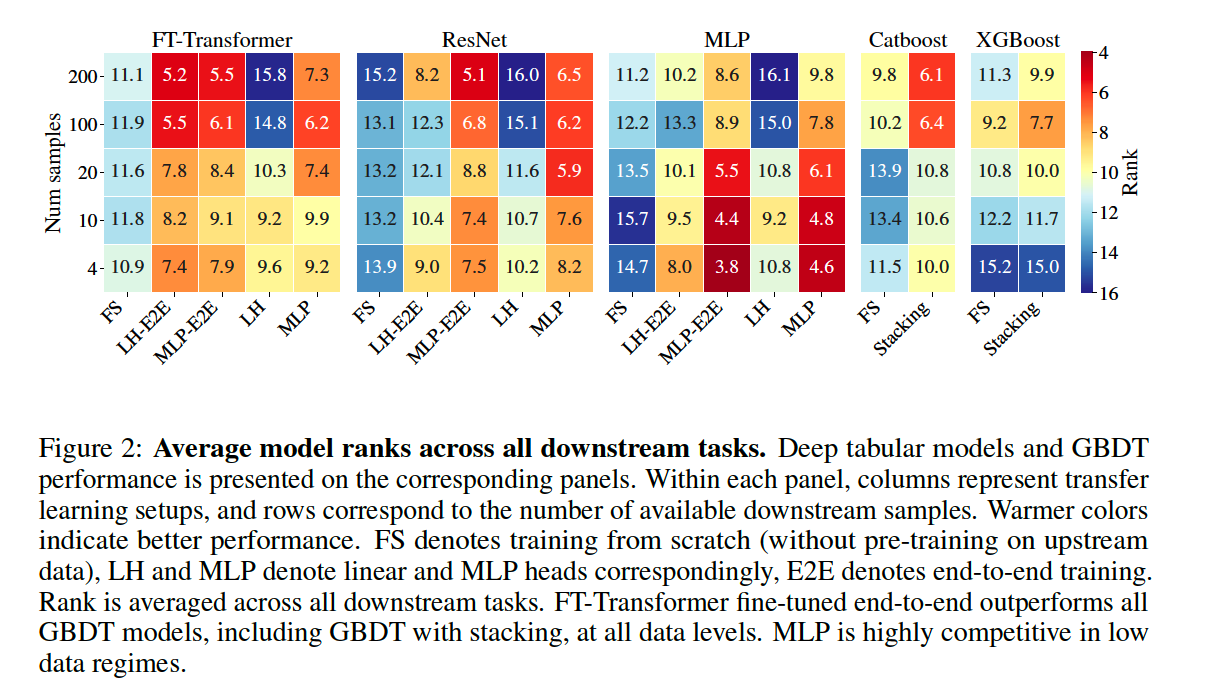
Summary
- MLP is competitive, especially in LOW data regime
- FT-Transformer offer consistent performance gains over GBDT on ALL data levels
- Representation learning with DL brings significant gain
- (most cases) MLP head > Linear head
4. SSL pretraining
(1) MLM
Randomly mask one feature & predict using other \(\)n-1\(\) features
(2) CL
( follow SAINT )
- Cutmix in the input sapce
- Mixup in the embedding space
(3) Sup vs. Self-Sup pretraining

- CL > FS(From Scratch)
- MLM < Supervised
5. Pseudo features
mentioned above
