Demystifying the Fourier Transform: The Intuition
참고 : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XQ45IgG6rJ4&list=PL-wATfeyAMNqIee7cH3q1bh4QJFAaeNv0&index=1
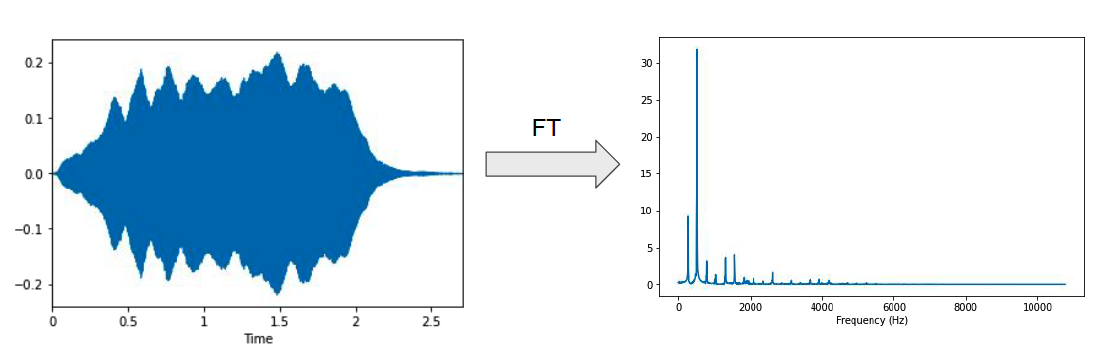
1. Intuition FT
Decompose sound into multiple frequency components
( frome TIME domain to FREQUENCY domain )
Summary
Compare signal with sinusoids of various freuqencies
- for each frequency, opbtain (1) magnitude & (2) phase
- high magnitude = high similarity btw signal & sinusoid
Sine wave
\(\sin (2 \pi \cdot(f t-\varphi))\).
- \(f\) : frequency
- \(\varphi\) : phase
2. Procedure of FT
Step 1) Choose a frequency
Step 2) Optimize phase \(\varphi\)
- that maximizes the similarity with the signal
Step 3) Calculate magnitude
- magnitude = similarity btw signal & sinusoid of chosen frequency
\(\rightarrow\) REPEAT 1~3 for all possible frequencies ( inifinte..? )
Optimizing a phase
\(\varphi_f=\operatorname{argmax}_{\varphi \in[0,1)}\left(\int s(t) \cdot \sin (2 \pi \cdot(f t-\varphi)) \cdot d t\right)\).
-
\(s(t) \cdot \sin (2 \pi \cdot(f t-\varphi))\) : multiplying signal & sinusoid
-
\(\operatorname{argmax}_{\varphi \in[0,1)}\) : selecting the phase that maximizes the area
Calculate the (largest possible) area
( with the chosen best \(\varphi\) )
\(d_f=\max _{\varphi \in[0,1)}\left(\int s(t) \cdot \sin (2 \pi \cdot(f t-\varphi)) \cdot d t\right)\).
BUT …. infinite range!
- \(t \in R\).
- \(f \in R\).
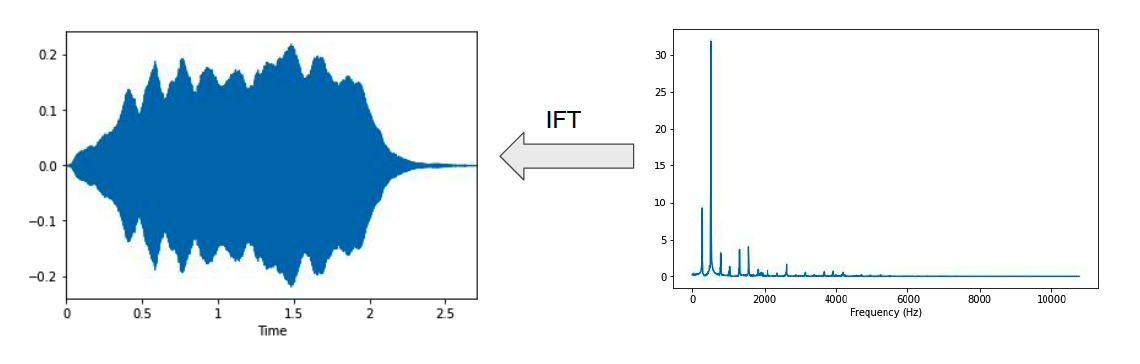
3. Inverse Fourier Transform
Reconstructing the original signal