STCGAT : Spatial-temporal Causal Networks for complex urban road traffic flow prediction (2022)
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Methods
- Problem Formulation
- Model Architecture
- Spatial Dependence Modeling
- Temporal Dependence Modeling
- Traffic Flow Forecasting Layer
0. Abstract
Traffic Data
- nonlinear & complex spatial correlations
- have Spatial-temporal relationships
Existing methods
- usually use FIXED traffic road network topology map
- usually use INDEPENDENT TS modules
to capture “Spatial-temporal relationships”
Modules
- GAT ( Graph Attention Networks )
- dynamically captures the spatial dependence of the traffic network
- CTCN ( Causal Temporal Convolutional Network )
- analyze the causal relationship of the traffic data
- obtain the overall temporal dependence
1. Introduction
Basic models
- CNN : spatial dependence ( + Euclidean data)
- RNN : temporal dependence
- GCN : spatial dependence ( + non-Euclidean data)
Hybrid models
-
GCN + RNN : have still drawbacks…
-
(1) since GCN uses Laplacian feature matrix of graph
to compute/update feature info of all nodes
\(\rightarrow\) poor flexible & scalable
-
(2) chain sructure design of RNNs
\(\rightarrow\) strictly follow the chronological development
\(\rightarrow\) unable to predict the future & can’t capture the potential causal relationships
-
STCGAT ( Spaital-Temporal Causal Graph Attention Network )
-
STCGAT = (1) GAT + (2) CTCN
-
Adaptively models the traffic road network spatially
& dynamically captures the spatial dependencies
Contribution
- propose a new spatial-temporal network for modeling spatial-temporal data
- use GAT to model spatial information
- use CTCN for modeling TS data
- captures the overall temporal dependence
- uncover potential causal associations
2. Methods
(1) Problem Formulation
Traffic Information
- traffic flow
- traffic density
- traffic speed
Notation
- Graph : \(G=(V, E, L)\)
- node : \(V=\left\{v_{1}, v_{2}, \cdots, v_{N}\right\}, \mathrm{N}\)
- edge : \(E\)
- Relationship with neighboring nodes :
- \(v_{i, j}= \begin{cases}\frac{1}{d_{i, j}}, & \text { if } v_{i} \text { and } v_{j} \text { are connected } \\ 0, & \text { otherwise. }\end{cases}\),
- Distance between \(v_i\) & \(v_j\) : \(d_{i,j}\)
- Connectivity matrix : \(L\)
- \(L = D^{-\frac{1}{2}}AD^{-\frac{1}{2}}\).
- \(D\) : degree matrix of adjacency matrix \(A\)
- \(L = D^{-\frac{1}{2}}AD^{-\frac{1}{2}}\).
- Feature Matrix : \(M=\left\{X_{t-n}, X_{t-(n-1)}, \cdots, X_{t}\right\}\)
- Model :
- \(\left[X_{t+1}, \cdots, X_{t+T}\right]=f\left(G ;\left(X_{t-n}, X_{t-(n-1)}, \cdots, X_{t}\right)\right)\).
- Dimension :
- \(M \in R^{N \times n}\),
- \(X_{i} \in R^{N \times 1}\).
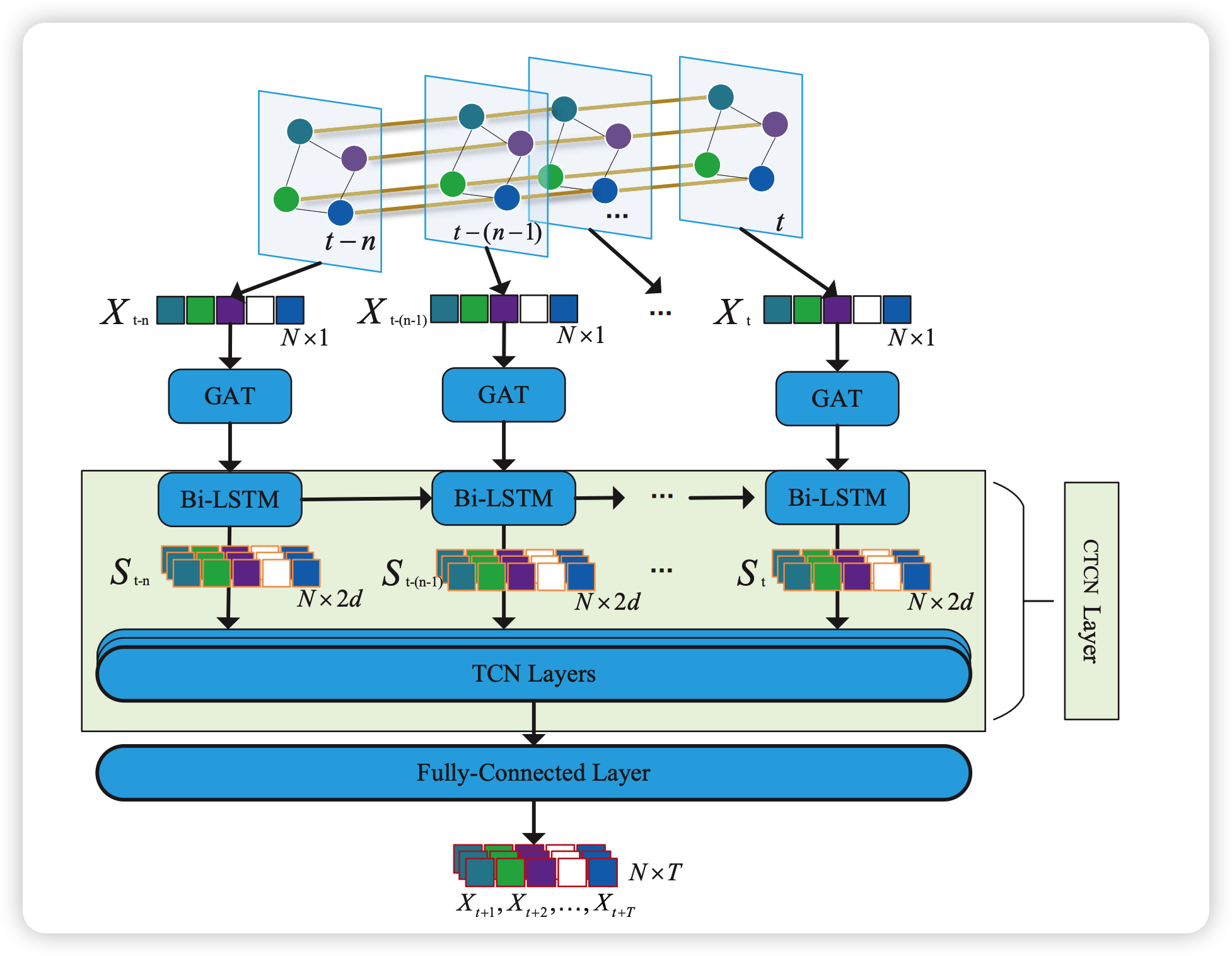
(2) Model Architecture
STCGAT consists of 3 components
- (1) GAT layer : spatial correlation between road nodes
- (2) CTCN layer : causal temporal CNN
- mainly composed of combination of BiLSTM & TCN
- (3) Prediction layer : FC network
(3) Spatial Dependence Modeling (GAT)
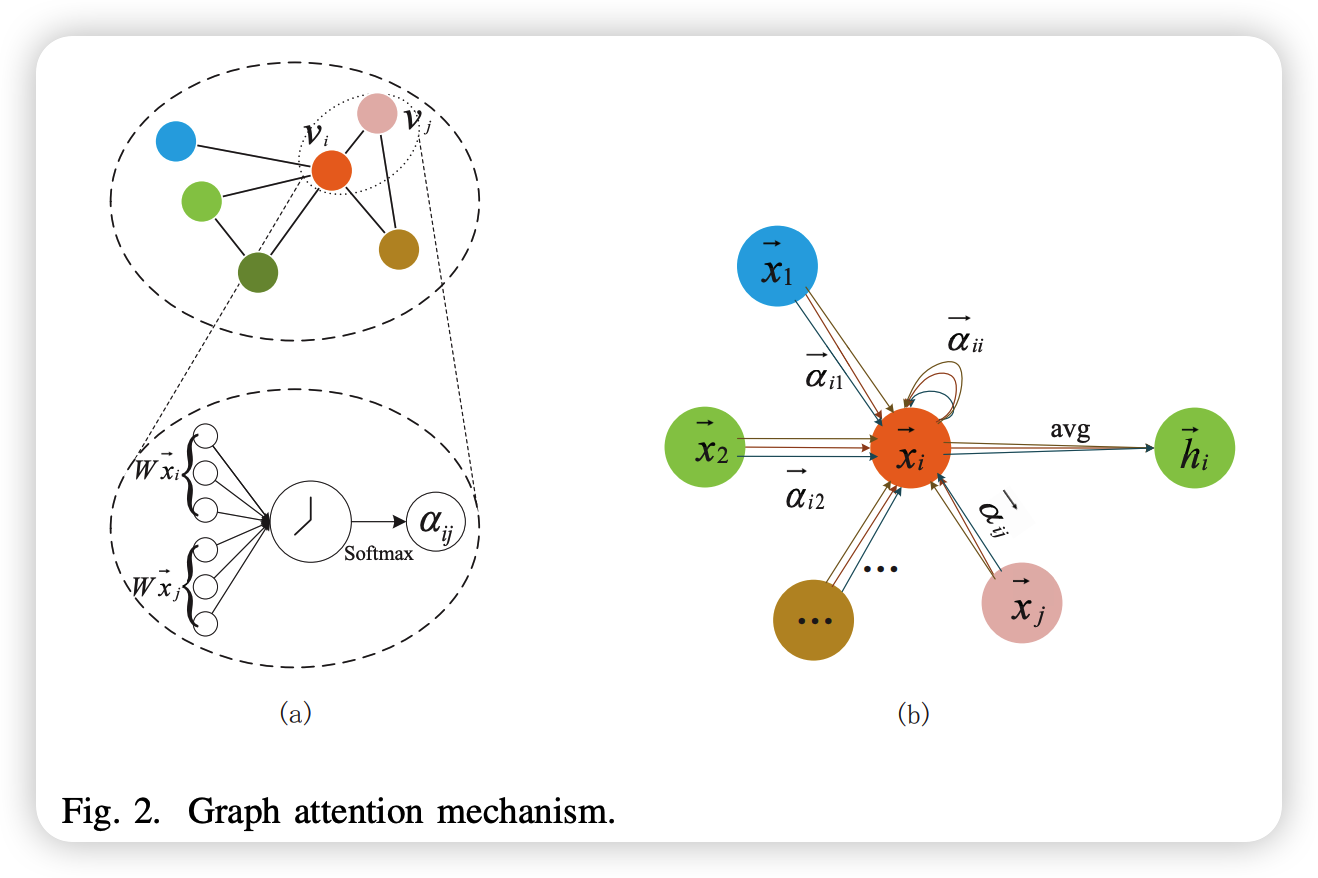
Use attention of GAT to calculate the attention chef between road nodes
Notation ( of 2 inputs to GAT )
- set of feature vector : \(X=\left\{\overrightarrow{x_{1}}, \overrightarrow{x_{2}}, \cdots, \overrightarrow{x_{N}}\right\}\left(\overrightarrow{x_{i}} \in R^{N \times F}\right)\)
- \(F\) : numer of node features
- topology graph : \(G\)
using GAT, get new set of node feature vectors
- \(H=\left\{\overrightarrow{h_{1}}, \overrightarrow{h_{2}}, \cdots, \overrightarrow{h_{N}}\right\}, \overrightarrow{x_{i}} \in \mathbb{R}^{F^{\prime}}\), where
- \(\overrightarrow{h_{i}}=\sigma\left(\frac{1}{P} \sum_{p=1}^{P} \sum_{j \in N_{i}} \alpha_{i j}^{p} W^{p} \vec{x}_{j}\right)\)…. \(\overrightarrow{x_{i}} \in \mathbb{R}^{F^{\prime}}\)
(4) Temporal Dependence Modeling (CTCN)
Capture time-dependent information from complex traffic data
[RNN]
- RNN can not capture hidden causal relationship well
- ex) sudden traffic accident on current road may affect adjacent road afterward
- traffic data are not always sequentiall correlated
- Ex) unscheduled traffic road maintenance
\(\rightarrow\) Propose CTCN
CTCN
- [purpose] capture the TS’s potential causality & temporal dependence
- consists of 2 parts
- (1) BiLSTM
- to analyze the contextual information of timing data
- to fuse the Spatial temporal relationships, use the node space feature set output from GAT as the input of BiLSTM
- (2) TCN
- to paralleize the temporal data output from BiLSTM,
- to obtain global temporal correlation & long term dependence
- use Causal Convolution & Dilated Convolution
- (1) BiLSTM
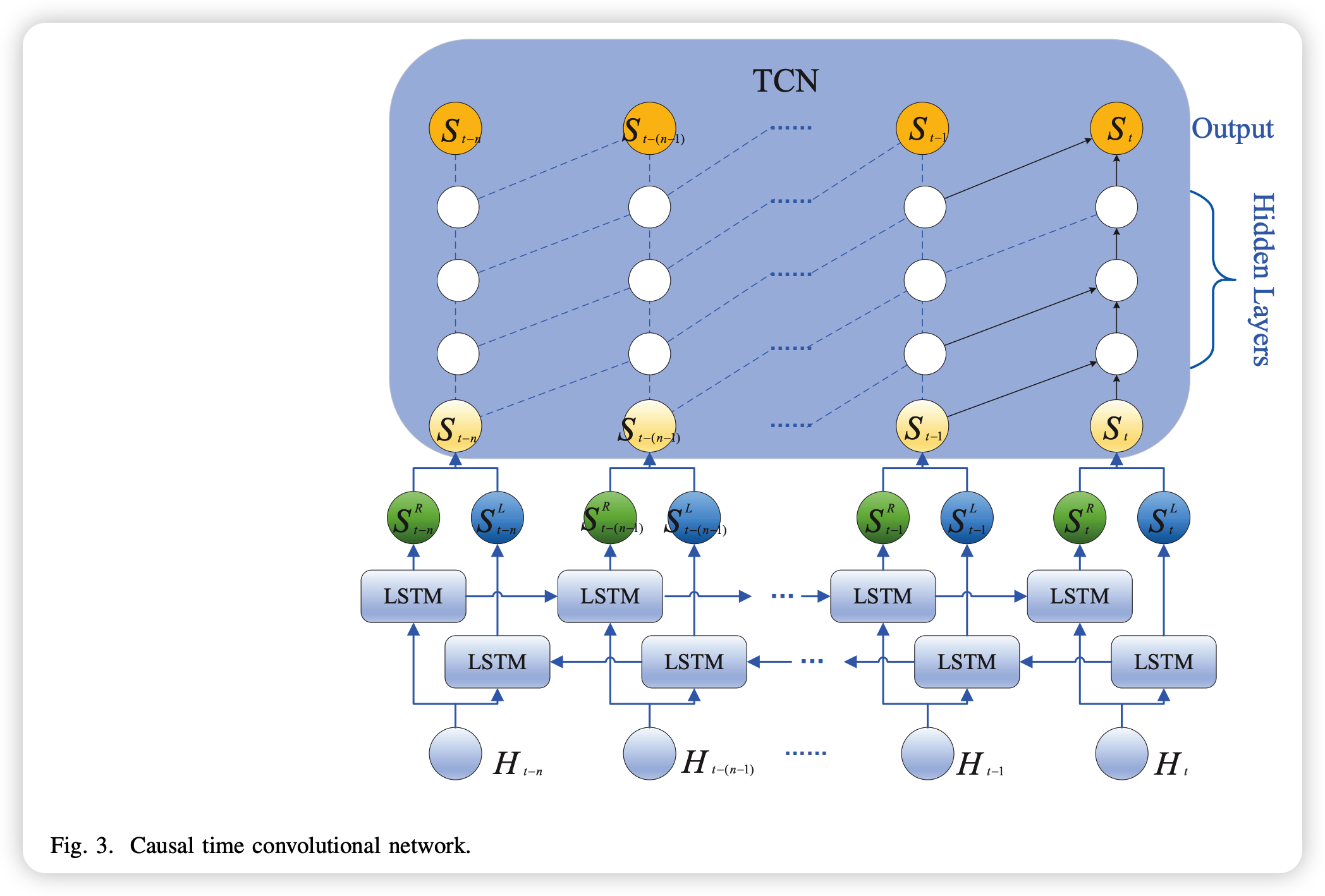
- combine (1) BiLSTM + (2) TCN
- input the sequence of BiLSTM output into TCN at one time
- output of BiLSTM \(S \in R^{N \times 2 d} \text { with feature vector } s^{i} \in \mathbb{R}^{2 d}\)
- use the parallism of TCN & prediction mechanism to obtain global time dependence & capture longer time correlation
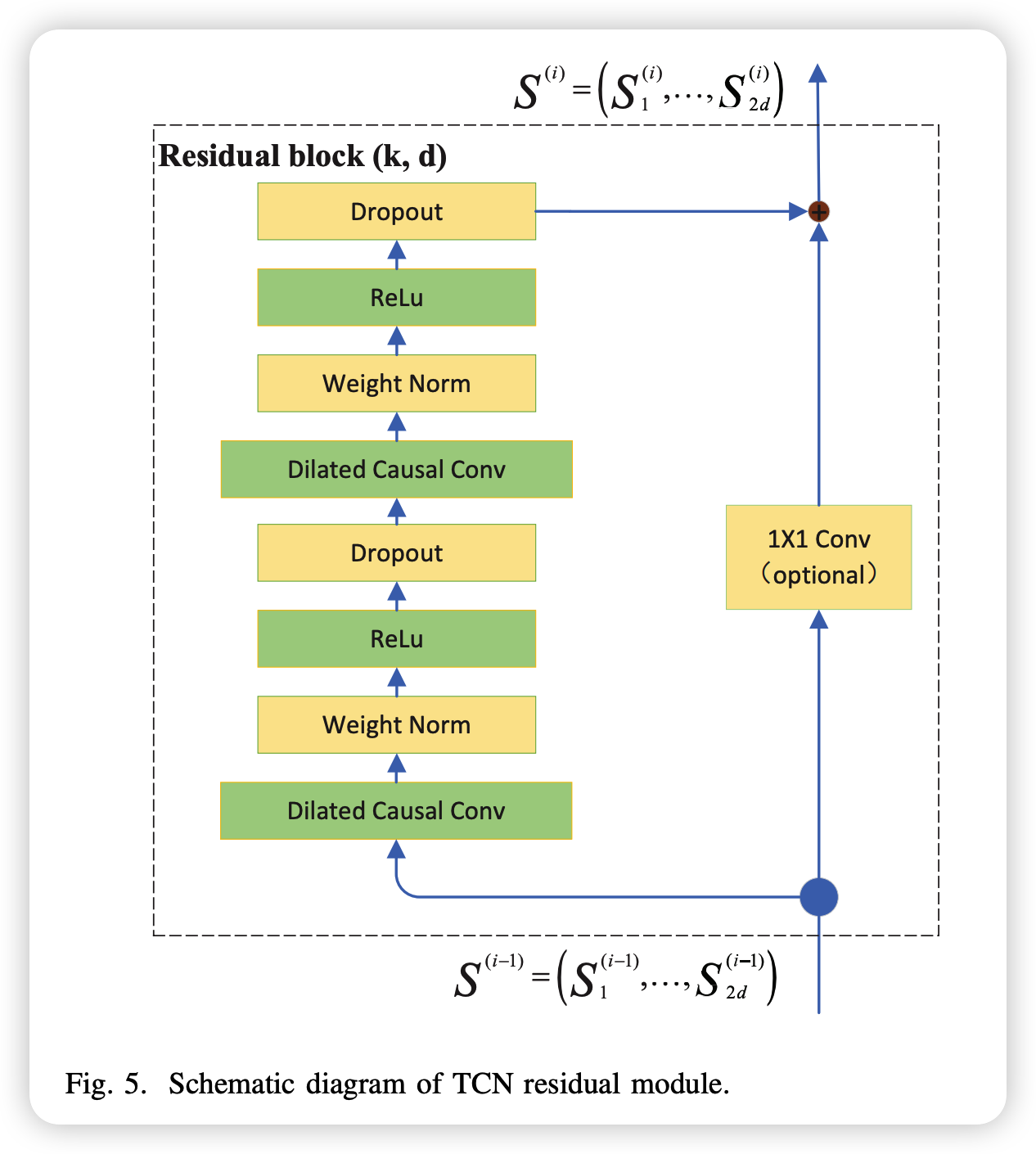
TCN uses residual connectivity
-
\(S^{i}=S^{i-1}+\phi\left(S^{i-1}\right)\),
-
\(S^{i} \in R^{N \times 2 d}\) is the output result of the i-th residual module
-
\(S^{i-1} \in R^{N \times 2 d}\) is the output result of the previous residual
-
-
final output result: \(\widetilde{S} \in R^{N \times 2 d}\).
(5) Traffic Flow Forecasting Layer
use FC network to process the CTCN output \(\widetilde{S} \in R^{N \times 2d}\)
\[Y^{\prime}=\left[X_{t+1}, X_{t+2}, \cdots, X_{t+T}\right]=\delta\left(W_{f} \cdot \widetilde{S}+b_{f}\right)\]- where \(Y^{\prime} \in R^{N \times T}\)
- where \(W_{f} \in R^{2 d \times T}\) is the weight matrix