Representation Learning with Contrastive Predictive Coding
Contents
- Abstract
- Contrastive Predictive Coding
- Motivation & Intuition
- Contrastive Predictive Coding
- Info NCE & Mutual Information Estimation
0. Abstract
“Contrastive Predictive Coding (CPC)”
-
universal UNsupervised learning approach to extract useful representations from HIGH-dim data
-
details
- by predicting the future in the latent space with autoregressive models
- use a probabilistic contrastive loss
- tractable by using negative sampling
1. Contrastive Predictive Coding
(1) Motivation & Intuition
Main intution
-
encode the underlying SHARED information between different parts of HIGH-dim signal
( + discard LOW-level information & noise )
-
Slow features ( = shared info, global structure … )
- the further in the future, amount of shared info becomes lower
Challenges in predicting high-dim data
-
(1) unimodal losses ( ex. MSE, CE ) are not useful
-
(2) generative models : computationally intense
-
waste in capturing relationships in data \(x\), ( ignoring context \(c\) )
-
modling \(p(x \mid c)\) directly ?
\(\rightarrow\) may not be optimal for the purpose of extracting shared info between \(x\) & \(c\)
-
This paper :
-
encode the target \(x\) ( future ) & context \(c\) ( present) into compact distributed vector,
in a way that maximally preserves the MUTUAL information of \(x\) & \(c\)
-
\(I(x ; c)=\sum_{x, c} p(x, c) \log \frac{p(x \mid c)}{p(x)}\).
(2) Contrastive Predictive Coding
a) architecture
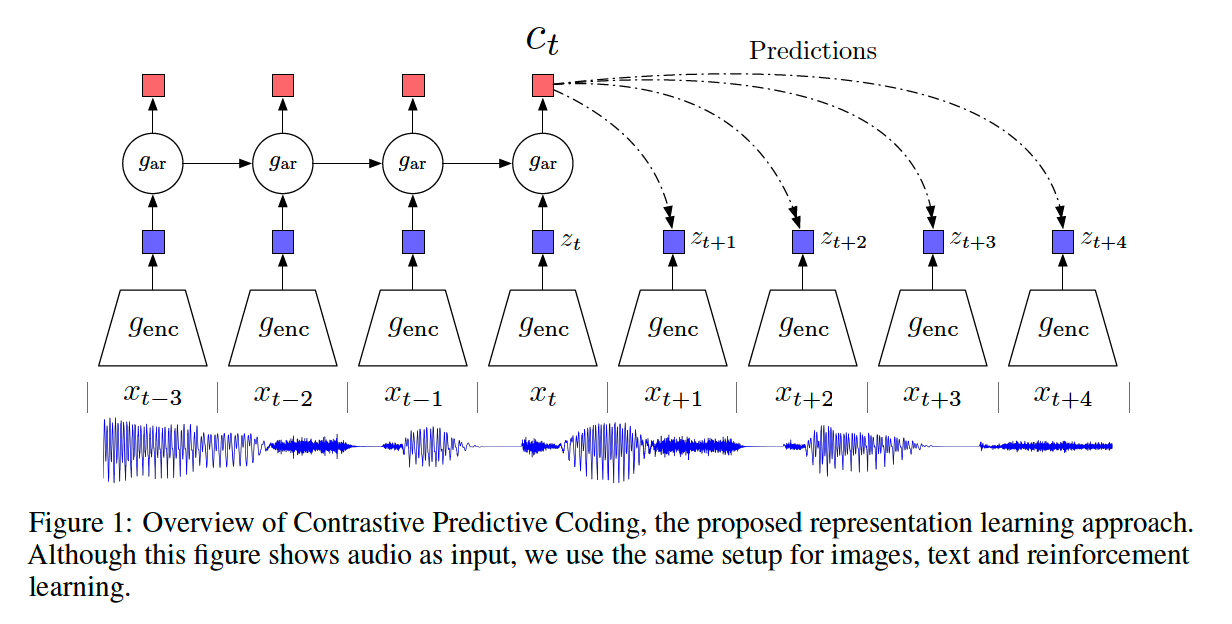
b) notation
Model :
- [encoder] \(g_{\text {enc }}\) ……… \(z_{t}=g_{\text {enc }}\left(x_{t}\right)\)
- [AR model] \(g_{\mathrm{ar}}\) ………. summarizes all \(z_{\leq t}\) in the latent space & produce context \(c_{t}=g_{\mathrm{ar}}\left(z_{\leq t}\right)\)
c) mutual information
do not predict \(x_{t+k}\) directly with generative model \(p_{k}\left(x_{t+k} \mid c_{t}\right)\)
\(\rightarrow\) instead, model a density ratio ( which preserves mutual information between \(x_{t+k}\) & \(c_t\) )
Density ratio
-
\(f_{k}\left(x_{t+k}, c_{t}\right) \propto \frac{p\left(x_{t+k} \mid c_{t}\right)}{p\left(x_{t+k}\right)}\).
( \(f\) can be unnroamlized )
-
use a log-bilinear model, \(f_{k}\left(x_{t+k}, c_{t}\right)=\exp \left(z_{t+k}^{T} W_{k} c_{t}\right)\)
- linear transformation \(W_{k}^{T} c_{t}\) is used for prediction, with different \(W_k\) for every step \(k\)
Working in LOW-dim
-
by using density ratio & inferring \(z_{t+k}\) with encoder,
\(\rightarrow\) relieve the model from modeling the high-dim \(x\)
(3) Info NCE & Mutual Information Estimation
Encoder & AR model : jointly optimized, based on NCE ( = InfoNCE )
Notation
- \(X=\left\{x_{1}, \ldots x_{N}\right\}\) of \(N\) random samples
- pos & neg
- 1 pos ~ \(p\left(x_{t+k} \mid c_{t}\right)\)
- (N-1) neg ~ \(p\left(x_{t+k}\right)\)
InfoNCE loss : \(\mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{N}}=-\underset{X}{\mathbb{E}}\left[\log \frac{f_{k}\left(x_{t+k}, c_{t}\right)}{\sum_{x_{j} \in X} f_{k}\left(x_{j}, c_{t}\right)}\right]\)
- optimizing InfoNCE = estimating density ratio
Optimal probability for this loss : \(p\left(d=i \mid X, c_{t}\right)\)
- meaning of \([d=i]\) : \(x_i\) is positive sample
- \(\begin{aligned}
p\left(d=i \mid X, c_{t}\right) &=\frac{p\left(x_{i} \mid c_{t}\right) \prod_{l \neq i} p\left(x_{l}\right)}{\sum_{j=1}^{N} p\left(x_{j} \mid c_{t}\right) \prod_{l \neq j} p\left(x_{l}\right)}=\frac{\frac{p\left(x_{i} \mid c_{t}\right)}{p\left(x_{i}\right)}}{\sum_{j=1}^{N} \frac{p\left(x_{j} \mid c_{t}\right)}{p\left(x_{j}\right)}}
\end{aligned}\).
- probability that \(x_i\) was drawn from \(p\left(x_{t+k} \mid c_{t}\right)\), rather than \(p\left(x_{t+k}\right)\)
minimizing InfoNCE loss (\(L_N\)) = maximize the lower bound of MI (Mutual Information)
\(I\left(x_{t+k}, c_{t}\right) \geq \log (N)-\mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{N}}\).
( proof )
\(\begin{aligned} \mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{N}}^{\mathrm{opt}} &=-\underset{X}{\mathbb{E}} \log \left[\frac{\frac{p\left(x_{t+k} \mid c_{t}\right)}{p\left(x_{t+k}\right)}}{\frac{p\left(x_{t+k} \mid c_{t}\right)}{p\left(x_{t+k}\right)}+\sum_{x_{j} \in X_{\text {neg }}} \frac{p\left(x_{j} \mid c_{t}\right)}{p\left(x_{j}\right)}}\right] \\ &=\underset{X}{\mathbb{E}} \log \left[1+\frac{p\left(x_{t+k}\right)}{p\left(x_{t+k} \mid c_{t}\right)} \sum_{x_{j} \in X_{\text {neg }}} \frac{p\left(x_{j} \mid c_{t}\right)}{p\left(x_{j}\right)}\right] \\ & \approx \underset{X}{\mathbb{E}} \log \left[1+\frac{p\left(x_{t+k}\right)}{p\left(x_{t+k} \mid c_{t}\right)}(N-1) \underset{x_{j}}{\mathbb{E}} \frac{p\left(x_{j} \mid c_{t}\right)}{p\left(x_{j}\right)}\right] \\ &=\underset{X}{\mathbb{E}} \log \left[1+\frac{p\left(x_{t+k}\right)}{p\left(x_{t+k} \mid c_{t}\right)}(N-1)\right] \\ & \geq \underset{X}{\mathbb{E}} \log \left[\frac{p\left(x_{t+k}\right)}{p\left(x_{t+k} \mid c_{t}\right)} N\right] \\ &=-I\left(x_{t+k}, c_{t}\right)+\log (N), \end{aligned}\).
