An Unsupervised Neural Attention Model for Aspect Extraction (2017)
Contents
-
Abstract
- Introduction
- Model Description
- Sentence Embedding with Attention
- Sentence Reconstruction with Aspect Embeddings
- Training Objective
- Regularization Term
0. Abstract
“Neural” approach for “Aspect Extraction (AE)”
- distribution of word co-occurences, via “embedding”
- “attention” to de-emphasize irrelevant words
1. Introduction
example)
- [ sentence ] “The beef was tender and melted in my mouth”
- [ aspect term ] “beef”
2 subtasks in AE
- 1) extract all aspect terms
- ex) “beef”
- 2) cluster aspect terms
- ex) “beef”, “chicken”, “hamburger” \(\rightarrow\) “food”
Previous works
-
1) rule-based
-
2) supervised
-
3) unsupervised
-
ex) LDA : models the ..
- corpus as “mixture of topics(aspects)”
- topics as “distribution over word types”
-
problems of LDA :
-
do not directly encode word co-occurrence statistics
-
only implicitly capture such patterns, by modeling word generation from ‘document level’
( assumption : word is generated “INDEPENDENTLY” )
-
BUT…..review documents tend to be short!
-
-
ABAE (Attention-based Aspect Extraction)
- tackle the problem of LDA
- Two key points
- 1) embedding ( co-occur \(\rightarrow\) close embedding space )
- 2) attention ( filter (un)important words )
2. Model Description
(1) goal : learn a set of “aspect embeddings”
(2) notation :
- feature vector \(\mathbf{e}_{w} \in \mathbb{R}^{d}\)
- word embedding matrix : \(\mathbf{E} \in \mathbb{R}^{V \times d}\)
- aspect embedding matrix : \(\mathbf{T} \in \mathbb{R}^{K \times d}\)
- size
- \(V\) : vocabulary size
- \(d\) : latent dimension
- \(K\) : number of aspects ( « \(V\) )
(3) input : list of indexes for words ( in a review sentence )
(4) Flow
- 1) dimension reduction
- 2) reconstruction
(5) Process ( in detail )
- step 1) filter away non-aspect words
- by “down weighting”, via “attention”
- step 2) construct sentence embedding \(\mathbf{z}_{s}\)
- from “weighted” word embeddings
- step 3) reconstruct sentence embedding \(\mathbf{r}_{s}\)
- linear combination of aspect embeddings ( from \(\mathbf{T}\) )
( Summary )
- transform sentence embeddings of filtered sentences \(\mathbf{z}_{s}\)
- into their reconstruction \(\mathbf{r}_{s}\)
- with the least possible amount of distortion
- preserve most of the info of aspect words in \(K\) embedded aspects
3.1 Sentence Embedding with Attention
Construct \(\mathbf{z}_{s}\) ( sentence embedding )
-
want to capture most relevent info w.r.t “ASPECT” of sentence
-
\(\mathbf{z}_{s}\) = weighted sum of word embeddings \(\mathbf{e}_{w_{i}}, i=1, \ldots, n\)
-
\(\mathbf{z}_{s}=\sum_{i=1}^{n} a_{i} \mathbf{e}_{w_{i}}\).
-
\(a_{i}\) : attention weight
( probability that \(w_i\) is the appropriate word to focus on (to capture main topic) )
- \(a_{i} =\frac{\exp \left(d_{i}\right)}{\sum_{j=1}^{n} \exp \left(d_{j}\right)}\).
- \(d_{i} =\mathbf{e}_{w_{i}}^{\top} \cdot \mathbf{M} \cdot \mathbf{y}_{s}\).
- \(\mathbf{M} \in \mathbb{R}^{d \times d}\) : mapping between “global context embedding \(\mathbf{y_s}\)” & “word embedding \(\mathbf{e}_{w}\)”
- \(\mathbf{y}_{s} =\frac{1}{n} \sum_{i=1}^{n} \mathbf{e}_{w_{i}}\). ( = average of word embeddings )
-
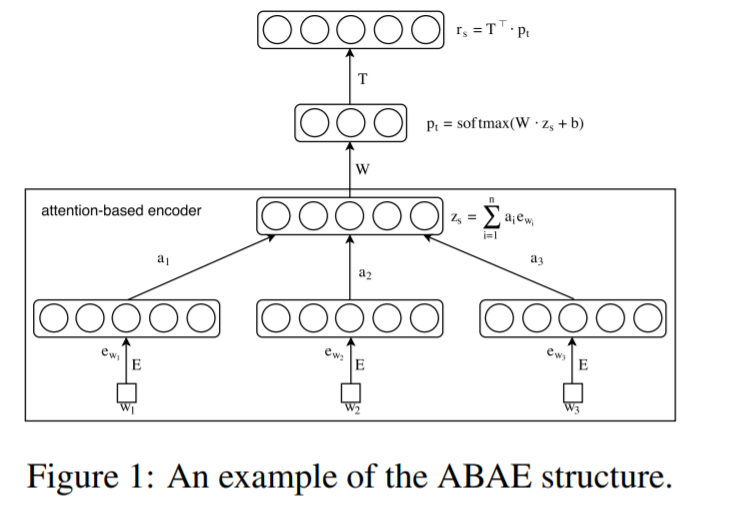
3-2. Sentence Reconstruction with Aspect Embedding
-
Similar to Autoencoder
-
Reconstruction = linear combination of aspect embeddings from \(\mathbf{T}\)
\(\mathbf{r}_{s}=\mathbf{T}^{\top} \cdot \mathbf{p}_{t}\).
- \(\mathbf{r}_{s}\) :
- reconstructed vector representation
- \(\mathbf{p}_{t}\) :
- weight vector over \(K\) aspect
- obtained by reducing \(\mathbf{z}_{s}\) from \(d\) to \(K\)
- \(\mathbf{p}_{t}=\operatorname{softmax}\left(\mathbf{W} \cdot \mathbf{z}_{s}+\mathbf{b}\right)\).
- \(\mathbf{T}\) :
- aspect embedding matrix
3-3. Training Objective
minimize “RECONSTRUCTION error”
- ( max-margin objective function )
Negative Sampling
- randomly sample \(M\) sentences
Goal : make the “reconstructed embedding \(\mathbf{r}_s\)”
-
similar to the “target sentence embedding \(\mathbf{z_s}\)“
-
different from “negative samples”
\(J(\theta)=\sum_{s \in D} \sum_{i=1}^{m} \max \left(0,1-\mathbf{r}_{s} \mathbf{z}_{s}+\mathbf{r}_{s} \mathbf{n}_{i}\right)\).
3-4. Regularization Term
Aspect embedding matrix \(\mathbf{T}\) :
- may suffer from “redundancy problem”
To ensure DIVERSITY, add regularization term
- \(U(\theta)=\left\|\mathbf{T}_{n} \cdot \mathbf{T}_{n}^{\top}-\mathbf{I}\right\|\).
Final Objective
- \(L(\theta)=J(\theta)+\lambda U(\theta)\).
