( 참고 : Fastcampus 강의 )
[ 14. Monte Carlo Control 실습 ]
1. 환경 설정하기
1-1. Import Packages
import sys; sys.path.append('..')
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from src.part2.monte_carlo import ExactMCAgent, MCAgent
from src.common.gridworld import GridworldEnv
from src.common.grid_visualization import visualize_value_function, visualize_policy
np.random.seed(0)
1-2. Make Environment
nx, ny = 4, 4
env = GridworldEnv([ny, nx])
1-3. Environment 소개
print(env.nS) ## 16
print(env.nA) ## 4
print(env.P_tensor.shape) # 4x16x16
print(env.R_tensor.shape) # 16x4
2. Agent 초기화
mc_agent = MCAgent(gamma=1.0,
lr=1e-3,
num_states=nx * ny,
num_actions=4,
epsilon=1.0) # 모든 행동을 같은 확률로!
Agent의 input
gamma: 감가율num_states: 상태공간의 크기 (4x4)num_actions: 행동공간의 크기 (4)epsilon: \(\epsilon\)-greedy policy의 parameter
3. Update 함수
- \(V\)와 \(Q\) 함수를 update한다.
- 계산 : 효율성을 위해 역순으로!
def update(self, episode):
states, actions, rewards = episode
states = reversed(states)
actions = reversed(actions)
rewards = reversed(rewards)
iter = zip(states, actions, rewards)
cumulative_R = 0
for s, a, r in iter:
cumulative_R *= self.gamma
cumulative_R += r
self.v[s] += self.lr * (cumulative_R - self.v[s])
self.q[s, a] += self.lr * (cumulative_R - self.q[s, a])
4-1. Policy Evaluation
한 번의 epsiode를 run하는 함수
timeout : Agent의 잘못된 정책 학습으로 인해 epsiode가 끝나지 않고 계속 반복되는 것을 방지하기 위해, 강제로 종료하게 만드는 장치 ( time )
def run_episode(env, agent, timeout=1000):
env.reset()
states = []
actions = []
rewards = []
i = 0
timeouted = False
while True:
state = env.s
action = agent.get_action(state)
next_state, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
states.append(state)
actions.append(action)
rewards.append(reward)
if done:
break
else:
i += 1
if i >= timeout:
timeouted = True
break
if not timeouted:
episode = (states, actions, rewards)
agent.update(episode)
get_action 함수 들여다보기
-
default값으로 \(\epsilon\)을 1로 설정했기 때문에, 항상 랜덤한 행동을 한다
(
action = np.random.choice(range(self.num_actions)))
def get_action(self, state):
prob = np.random.uniform(0.0, 1.0, 1)
if prob <= self.epsilon: # (1) random 행동
action = np.random.choice(range(self.num_actions))
else: # (2) greedy 행동
action = self._policy_q[state, :].argmax()
return action
5,000번의 epsiode를 run하기
for _ in range(5000):
run_episode(env, mc_agent)
4-2. Policy Improvement
소스코드를 들여다보면, MCAgent class는 ExactMCAgent class를 상속받는다.
이 강의에서는, policy evaluation 과 policy improvement 과정을 분리하여 명시적으로 표현한다.
-
1) policy evaluation :
run_episode(env, mc_agent)으로 수행 -
2) policy improvement :
mc_agent.improve_policy()으로 수행def improve_policy(self): self._policy_q = self.q.copy() self.reset_values() self.reset_statistics()
4-3. Visualization
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,2, figsize=(12,6))
visualize_value_function(ax[0], mc_agent.v, nx, ny)
_ = ax[0].set_title("Value pi")
visualize_policy(ax[1], mc_agent.q, nx, ny)
_ = ax[1].set_title("Greedy policy")
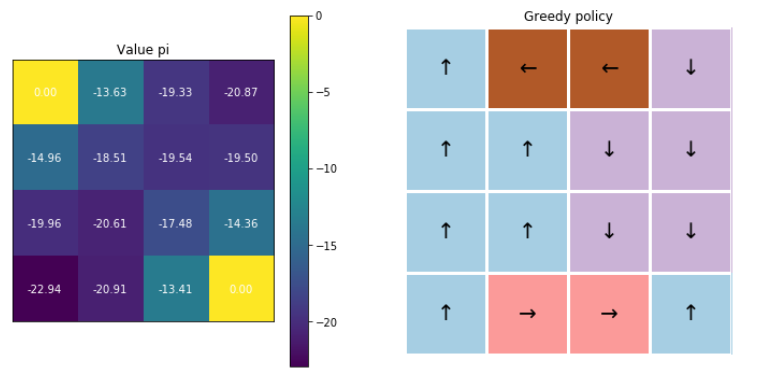
5. \(\epsilon\)-greedy 정책
( 앞서서는 \(\epsilon=1\) …. 늘 random한 행동을 했었다 )
이번엔, \(\epsilon\)을 점차 줄여갈 것! ( decay )
def decaying_epsilon(self, factor):
self.epsilon *= factor
def decaying_epsilon_and_run(agent, env,
decaying_factor:float,
n_runs:int = 5000):
# (1) Weight Decay
agent.decaying_epsilon(decaying_factor)
# (2) 초기화
agent.reset_statistics()
# (3) 5000 epsiode 돌기
for _ in range(n_runs):
run_episode(env, agent)
# (4) Policy Improvement
agent.improve_policy()
Run \(\epsilon\)-greedy!
- 1~5000번의 iteration : decay rate=0.9
- 5001~10000번의 iteration : decay rate=0.9
- 10001~15000번의 iteration : decay rate=0.1
- 15001~20000번의 iteration : decay rate=0.1
- 20001~25000번의 iteration : decay rate=0.1
- 25001~30000번의 iteration : decay rate=0.1
decaying_epsilon_and_run(mc_agent, env, 0.9)
decaying_epsilon_and_run(mc_agent, env, 0.9)
decaying_epsilon_and_run(mc_agent, env, 0.1)
decaying_epsilon_and_run(mc_agent, env, 0.1)
decaying_epsilon_and_run(mc_agent, env, 0.1)
decaying_epsilon_and_run(mc_agent, env, 0.0)
최종 결과 :
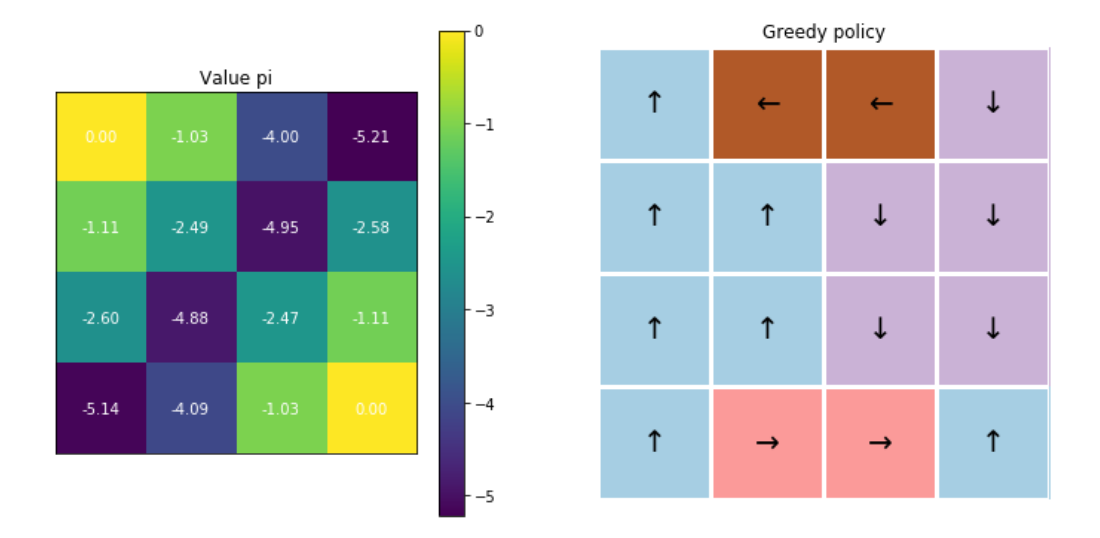
6. 성급한 decay 시
mc_agent = MCAgent(gamma=1.0,lr=1e-3,
num_states=nx * ny,
num_actions=4,
epsilon=1.0)
decay rate으로 “0”을 줄 경우! 최적의 정책을 잘 찾지 못하는 것을 알 수 있다.
decaying_epsilon_and_run(greedy_mc_agent, env, 0.0, 5000)
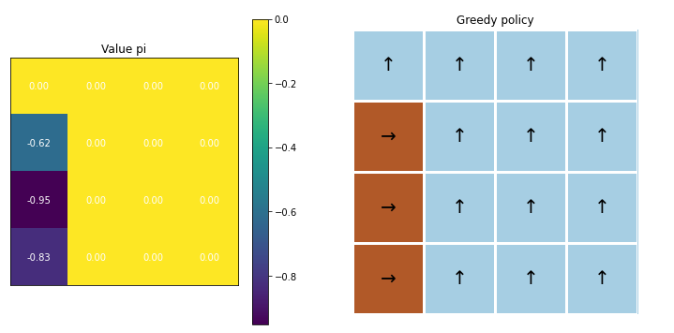
결론 : 섬세한 hyperparameter tuning is needed!
