( 출처 : 연세대학교 데이터베이스 시스템 수업 (CSI6541) 강의자료 )
Chapter 11. Introduction to Redis
Contents
- Remind
- NoSQL
- In-memorry Key-Value Storage
- Redis Data Types
- Hash-Structure
- RDB & AOF
- Redis Cluster
(1) Remind
Big data = 3V
- (1) Volume, (2) Variety, (3) Velocit
Requirements of Big data
-
a) require very high scalability
\(\rightarrow\) Distributed File Systems (Hadoop)
-
b) need to support non-relation data
\(\rightarrow\) NoSQL (Redis, RocksDB)
(2) NoSQL ( = Not Only SQL )
next generation DBMS addresses…
- (1) being non-relational
- (2) distributed
- (3) open-source
- (4) horizontally scalable
Characteristics of NoSQL
- (1) flexible to accommodate
- (2) better scalability
- (3) complex-free working
- (4) independent of schema
NoSQL Types
- Key-Value DB
- data storage for storing, retrieving, managing associative arrays
- ex) Redis, RocksDB
- Document DB
- Documents encapsulate & encode data in some standard formats (e.g. xml, json)
- Column Family DB
- DB object that contains colummns of related data
- Graph DB
- DB that uses graph structures for semantic queries with nodes/edges and properties to represent & store data
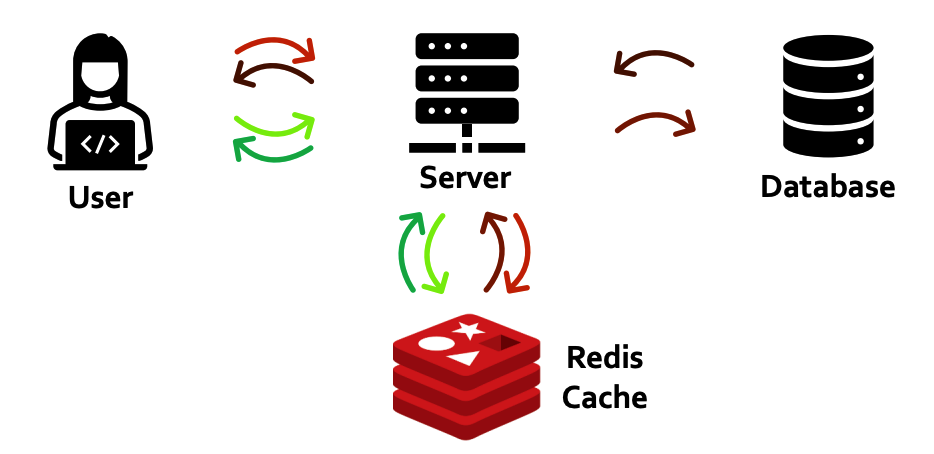
(3) In-memory Key-Value Storage
- 데이터를 key-value 형태로 메모리(DRAM)에 저장
- 고속 처리 가 요구되는 시스템에 적합한 DB
- 다른 DB와 연계하여, 중간 계층에서의 cache 저장 용도로 활용 가능
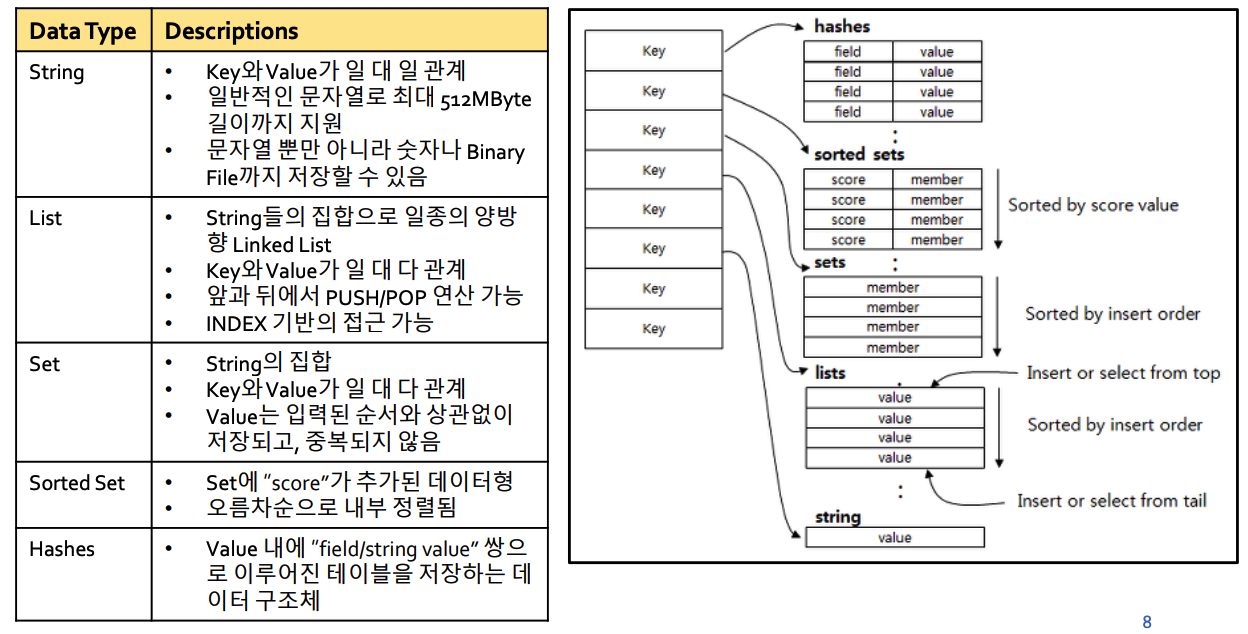
(4) Redis Data Types
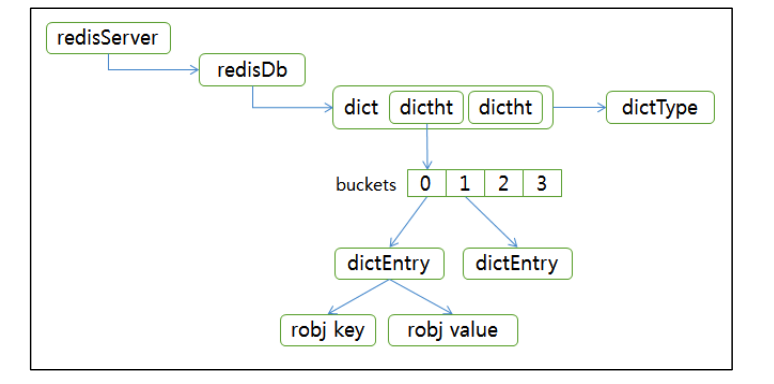
(5) Hash-Structure
-
Redis DB의 내부는 hash 구조 로 이루어짐
-
Hash Function ( = Key )에 해당하는 Hash table의 index에 Key-Value pair ( = Entry )를 저장함
-
Incremental rehashing
- hash table의 크기 변경 시, 요청 처리 속도에 지장 없도록 점진적으로 rehashing 작업을 수행
(6) RDB & AOF
Persistence (지속성)
Redis는 in-memory DBMS
\(\rightarrow\) 서버가 비정상적으로 종료되면 “데이터 유실 위험”이 있음
\(\rightarrow\) 유실 문제 완화 위해, 데이터 복원 위한 2종류의 절차
-
(1) RDB ( Snapshotting )
- Redis에 저장된 데이터들을 Binary dump 형식 log로 저장
- 일정 간격으로, 전체 데이터셋에 대한 snap shot 저장
- 장 & 단
- 장) snapshot loading 작업으로 빠르게 데이터 복구
- 단) snapshot 생성 기간이 길고, 생성 이후에 추가된 데이터는 유실
-
(2) AOF ( Append-Only File )
-
Memory state를 변경시키는 명령어를 log로 저장
-
장 & 단
-
장) RDB에 비해 데이터 유실이 적음
-
단)
-
log 기록을 위한 disk I/O가 빈번하여 Redis 성능 저하
-
기록된 명령어들의 재실행을 통해 데이터를 복구
\(\rightarrow\) 복구 시간이 오래 걸림
-
-
-
(7) Redis Cluster
Redis는 분산 시스템 구성을 위한 Cluster 기능 제공
-
한 곳의 node 자원만이 아니라, 여러 node 자원을 통합
\(\rightarrow\) 저장 공간을 증대!
특징
- (1) horizontally scalable ( = scale out )
- (2) Auto data sharding
- (3) Fault tolerant
- (4) Decentralized cluster management ( = gossip )
## b) Auto Data Sharding Load Balancing (Data Sharding) - 빅데이터 $$\rightarrow$$ 여러 node에 data를 분산하여 저장 - DBMS 밖에서 데이터를 나누는 방식이기 때문에, **Shard 수에 따라 여러 대의 DBMS 설치가 필요** 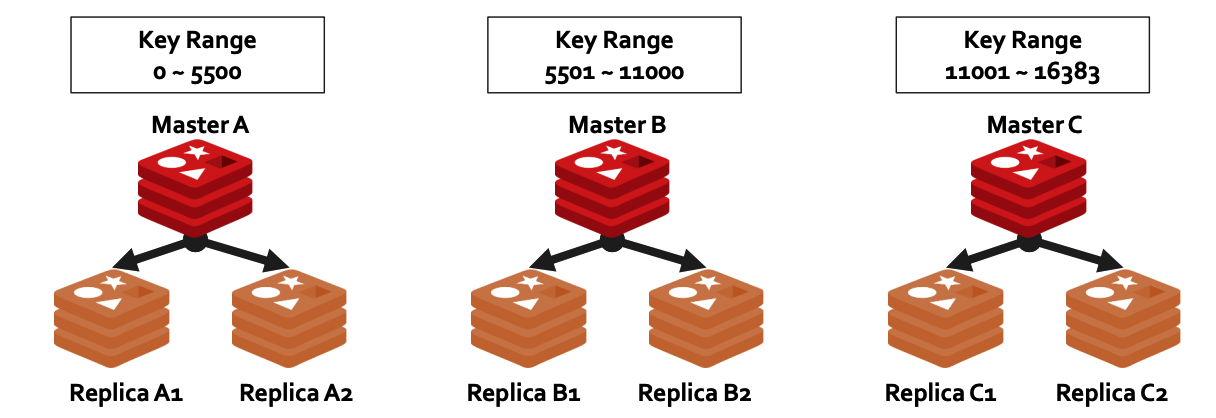
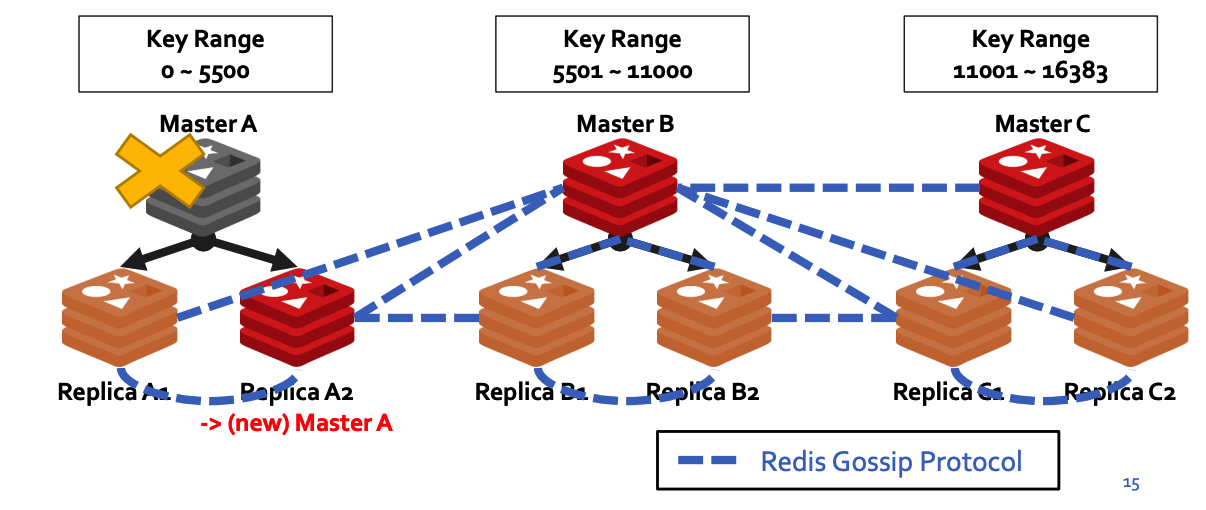
## c) Fault Tolerance Master-Slave Replication - Master node는 실시간으로 **자신의 데이터를 Slave node로 복제**함 - ***Failover*** : Slave node를 **master로 승급시키는 명령** - Master 노드가 다운되면, slave 노드를 master로 승격하여 cluster 정상 운영 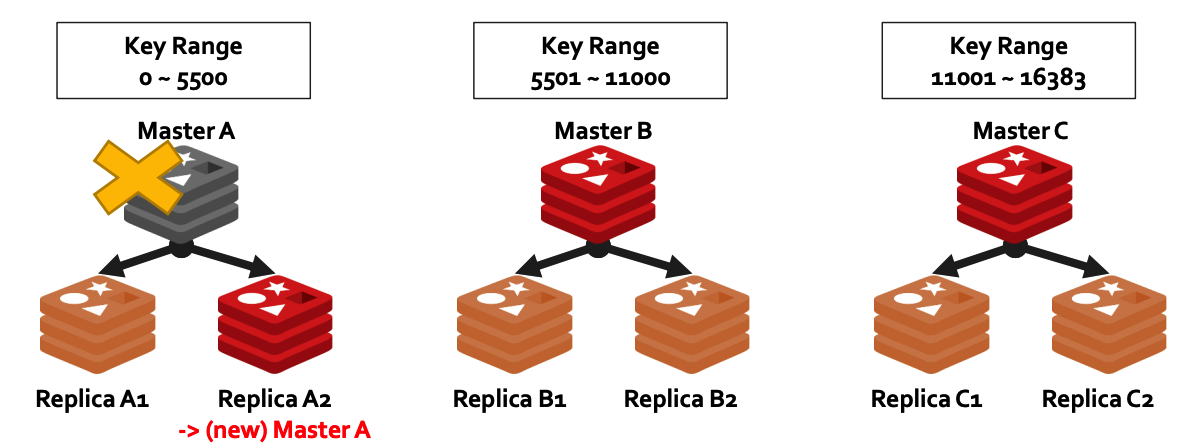
## d) Decentralized cluster management Gossip protocol - To discover new nodes - To **send ping packets** to make sure **all the other nodes are working** properly - To send **cluster messages** needed to signal specific conditions.