A benchmark study on time series clustering (2020)
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Benchmark methods
- Clustering methods
- Evaluation methods
0. Abstract
8 popular clustering methods ( of 3 categories )
- 1) partitional
- 2) hierarchical
- 3) density-based
3 types of distance measures
- 1) Euclidean
- 2) DTW (Dynamic Time Warping)
- 3) shape-based
1. Introduction
data : UCR(University of California) time series
- 128 datasets
- split into train/test
- accompanied by 3 baseline straw man classification accuracy scores
2. Benchmark methods
(1) Clustering methods
2 major design criteria in clustering methods
- 1) clustering algorithm
- 2) distance measure
a) clustering algorithm
- [1] partitional
- ex) K-means, K-medoids, Fuzzy C-means
- [2] density-based
- ex) Density Peaks (2019)
- recent popularity, particularly for TS clustering
- not sensitive to density parameter
- needs the number of cluster \(k\) in advance
- 2 phases
- step 1) find centroids ( =density peaks )
- step 2) assign data points to closes centroid
- 2 input params :
- number of clusters (\(k\))
- local neighborhood distance (\(d\))
- ex) Density Peaks (2019)
- [3] hierarchical
- agglomerative (bottom-up) / divisive (top-down)
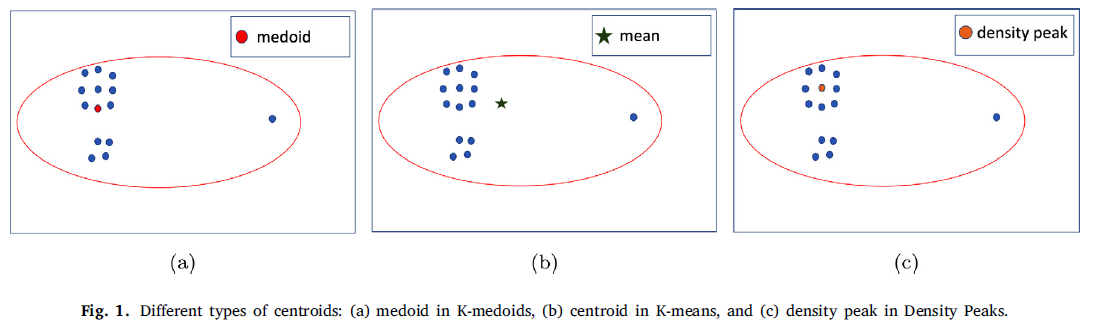
b) distance measure
- [1] Euclidean
- two time series \(T 1=\left(T 1_{1}, T 1_{2}, \ldots, T 1_{n}\right)\) and \(T 2=\left(T 2_{1}, T 2_{2}, \ldots, T 2_{n}\right)\)
- \(d(T 1, T 2)=\sqrt{\sum_{i}^{n}\left(T 1_{i}-T 2_{i}\right)^{2}}\).
- [2] Dynamic time warping
- mapping of points between a pair of time series, \(T_1\) & \(T_2\)
- designed to minimize pairwise Euclidean distance
- one of most accurate SIMILARITY measures for ts data
- [3] Shape-based distance
- shift-invariant & scale-invariant
- calculates cross-correlation between 2 t.s data
- value between 0.0~2.0
- 0.0 : identical
- 2.0 : maximally different shape
- to ensure scale-invariance…
- normalize! \(T^{\prime}=\frac{T-\mu}{\sigma}\).
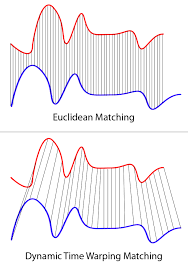
(2) Evaluation methods
metrics for assessing clustering : (1) external & (2) internal
- [1] external : with class labels
- ex) RI, ARI, AMI, FMS…
- [2] internal : without class labels
- ex) Silhouette score, Davies-Bouldin index, Calinski-Harabasz index…
