Semi-supervised Learning with Deep Generative Models (2014)
Contents
- Abstract
- DGM for Semi-supervised Learning
- Latent-feature discriminative model (M1)
- Generative semi-supervised model (M2)
- Stacked Generative Semi-supervised Model (M1+M2)
0. Abstract
Semi-supervised learning with generative models
- develop new models that allow for effective generalisation from small labelled data to large unlabelled data
Previous works
-
generative approaches : either inflexible, inefficient or non-scalable
-
proposed : DGM + approximate Bayesian Inference
\(\rightarrow\) make significant improvements
1. DGM for Semi-supervised Learning
Notation
- data : \((\mathbf{X}, \mathbf{Y})=\left\{\left(\mathbf{x}_1, y_1\right), \ldots,\left(\mathbf{x}_N, y_N\right)\right\}\)
- \(\mathbf{x}_i \in \mathbb{R}^D\) & \(y_i \in\{1, \ldots, L\}\)
- latent variable \(\mathbf{z}_i\) : indicate the observationess
- Labeled & Unlabeled
- Labeled subsets : \(\widetilde{p}_l(\mathbf{x}, y)\)
- Unlabeled subsets : \(\widetilde{p}_u(\mathbf{x})\)
(1) Latent-feature discriminative model (M1)
2-step process ( pre-trained & fine tuning )
-
step 1) with labeled, unlabeled data, pre-train VAE
-
step 2) use classifier/regressor at the end of VAE
& fine tuning ( = labeled task with labeled data )
VAE notation
- \(p(\mathbf{z})=\mathcal{N}(\mathbf{z} \mid \mathbf{0}, \mathbf{I})\)…….. prior
- \(p_\theta(\mathbf{x} \mid \mathbf{z})=f(\mathbf{x} ; \mathbf{z}, \boldsymbol{\theta})\)……. model
- \(f(\mathbf{x} ; \mathbf{z}, \boldsymbol{\theta})\) : likelihood function (e.g., a Gaussian or Bernoulli)
- \(p(\mathbf{z} \mid \mathbf{x})\) …….. posterior
- Samples from \(p(\mathbf{z} \mid \mathbf{x})\) are used as features to train classifier
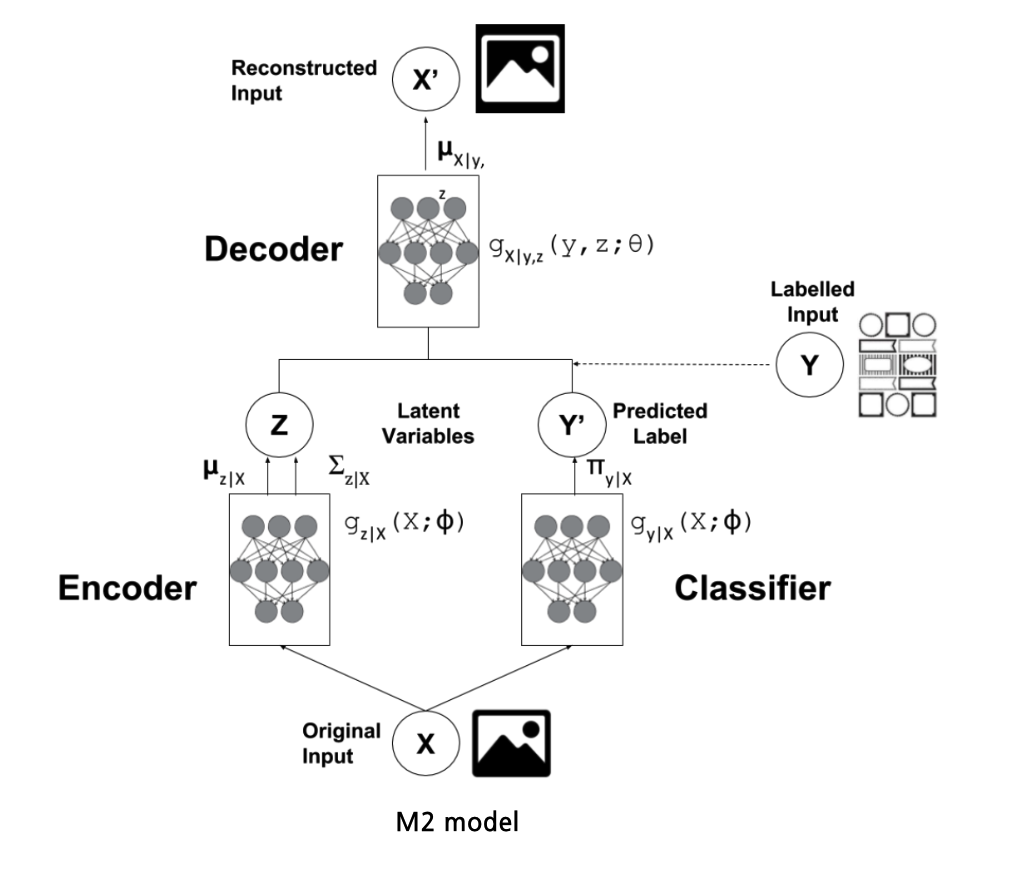
(2) Generative semi-supervised model (M2)
1-step process ( pre-trained & fine tuning )
- concatenate embedding \(\mathbf{z}\) with predicted label \(\mathbf{y}\)
Generative Process :
- \(p(y)=\operatorname{Cat}(y \mid \boldsymbol{\pi})\) : multinomial distn
- class labels \(y\) are treated as latent variables
-
\[p(\mathbf{z})=\mathcal{N}(\mathbf{z} \mid \mathbf{0}, \mathbf{I})\]
- \(\mathbf{z}\) : additional latent variable
\(\rightarrow\) \(p_\theta(\mathbf{x} \mid y, \mathbf{z})=f(\mathbf{x} ; y, \mathbf{z}, \boldsymbol{\theta})\)$$
(3) Stacked Generative Semi-supervised Model (M1+M2)
step 1) learn \(\mathbf{z_1}\) using generative model of M1
step 2) learn a generative semi-supervised model M2,
- with \(\mathbf{z_1}\) from step 1) ( instead of raw input \(\mathbf{x}\) )
