Continual Learning with Deep Generative Replay
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Related Works
- Comparable Methods
- Deep Generative Models
- Generative Replay
- Proposed Method
0. Abstract
Catastrophic Forgetting 해결 위해, replay all previous data?
\(\rightarrow\) 효과는 있겠지만… LARGE memory 필요
이 논문은 인간의 뇌 부분인 hippocampus에 영감을 받아, Deep Generative Replay를 제안함
DGR의 두 main model
- 1) generator ( = deep generative model )
- 2) solver ( = task solving model )
1. Introduction
Catastrophic forgetting = training new objective causes forgetting of former knowledge!
이를 해결하기 위한 시도로, 제안되었던 “memory-based approach”
- 과거의 data를 저장하는 episodic memory system에 의존
- 한계점 ) require large memory!
이에 대한 대안으로, Deep Generative Replay를 제안
-
과거 데이터를 저장하지 않는 DNN 알고리즘!
-
그렇다면 과거 데이터를 어떻게 활용?
\(\rightarrow\) concurrent replay of generated pseudo-data
-
past data를 mimic하기 위해, GAN framework 사용
2. Related Works
2-1. Comparable Methods
(1) Optimization
- regularization
- ex) dropout, L2, EWC
(2) Sequentially train
-
( multiple task를 수행할 수 있는 ) sequentially train DNN
-
ex) augment networks with task-specific parameters
( input 부근의 parameter는 common param, output 부근은 task-specific )
-
lower learning rates on some parameter 또한 forgetting 방지하는 것으로 알려짐
2-2. Deep Generative Models
GAN framework 사용
- \(\min _{G} \max _{D} V(D, G)=\mathbb{E}_{\boldsymbol{x} \sim p_{\text {data }}(\boldsymbol{x})}[\log D(\boldsymbol{x})]+\mathbb{E}_{\boldsymbol{z} \sim p_{z}(\boldsymbol{z})}[\log (1-D(G(\boldsymbol{z})))]\).
3. Generative Replay
Notation :
-
task sequence : \(\mathbf{T}=\left(T_{1}, T_{2}, \cdots, T_{N}\right)\).
-
task의 data : \(D_{i}\)….. \(\left(\boldsymbol{x}_{i}, \boldsymbol{y}_{i}\right)\) sample을 뽑음
-
scholar : \(H=\langle G, S\rangle\)
-
여기서 \(G\) (generator)는, GAN의 generator & discriminator를 모두 포함한 개념
-
\(S\) (solver) : classifier
\(\rightarrow\) solver는 \(\mathbf{T}\)의 모든 task에 대해서 수행한다 ( loss function = \(\mathbb{E}_{(\boldsymbol{x}, \boldsymbol{y}) \sim D}[L(S(\boldsymbol{x} ; \theta), \boldsymbol{y})]\) )
-
3-1. Proposed Method
Sequential Training ( task들이 순차적으로 유입됨 )
과거의 DB를 사용하는 것이 아니라, 과거의 DB를 생성해낼 법한 generator를 학습시킴
- generator는 cumulative하게 모든 task들의 data를 잘 생성해내는 방향으로 학습됨
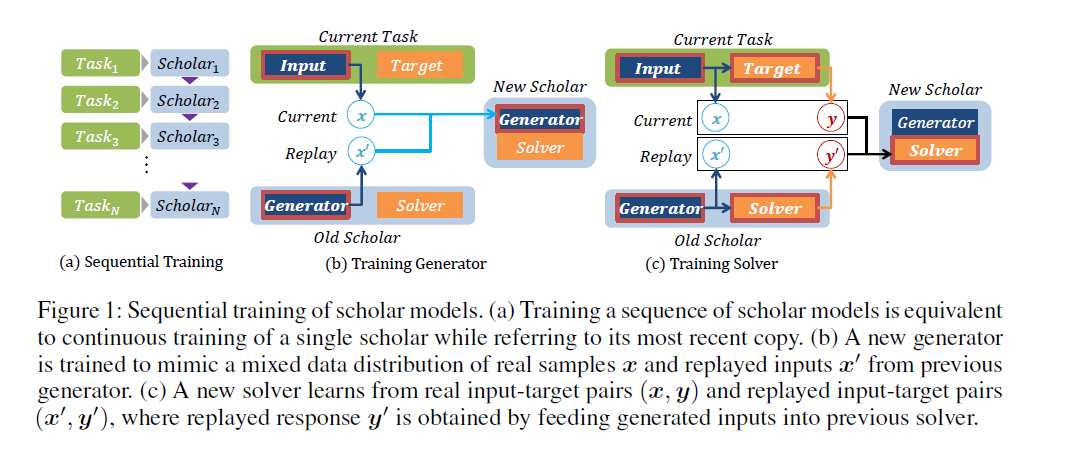
-
Step 1) [Generator] \(x\)를 사용하여, replayed input \(x^{'}\)를 생성하는 모델 학습
-
Step 2) [Solver] 아래의 두 종류의 데이터를 사용하여 모델 학습
-
데이터 1) real input : \((x,y)\)
-
데이터 2) generated inputs : \((x^{'},y^{'})\)
( 여기서 \(y^{'}\)는 previous solver에 input을 넣었을때 나오는 output값이다 )
-
