( 참고 : 패스트 캠퍼스 , 한번에 끝내는 컴퓨터비전 초격차 패키지 )
02.Semantic Segmentation
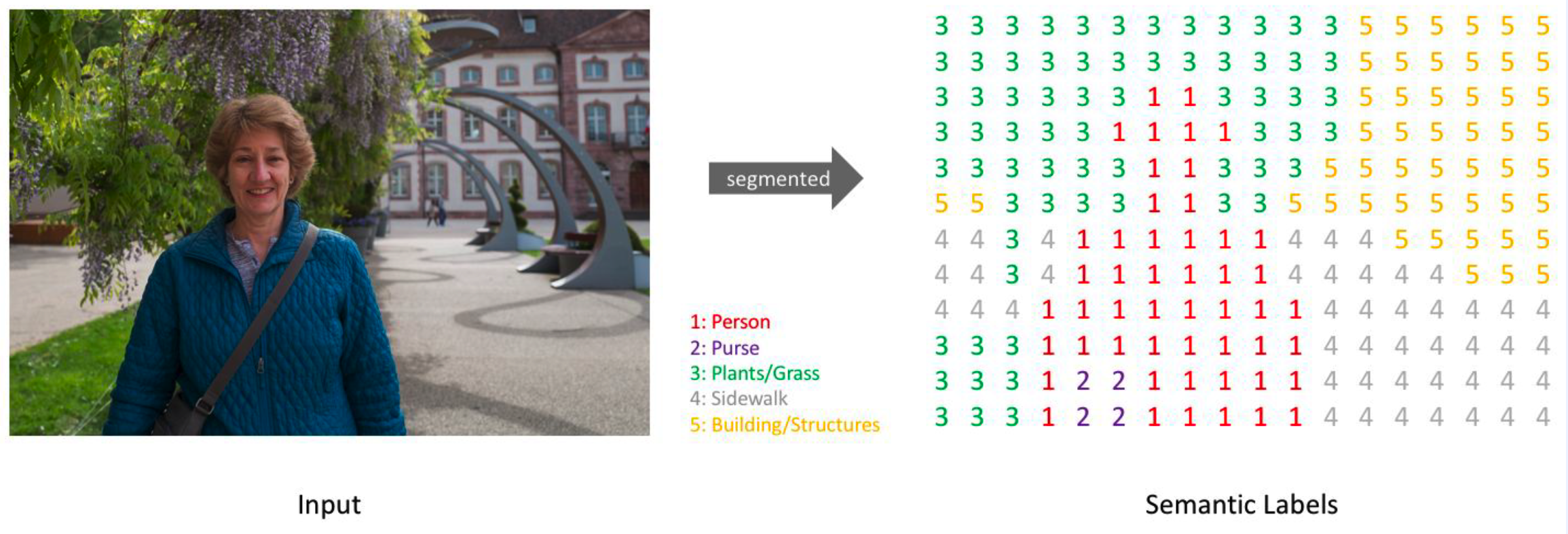
0. What is Semantic segmentation?
(1) PIXEL-level classification
( including background )
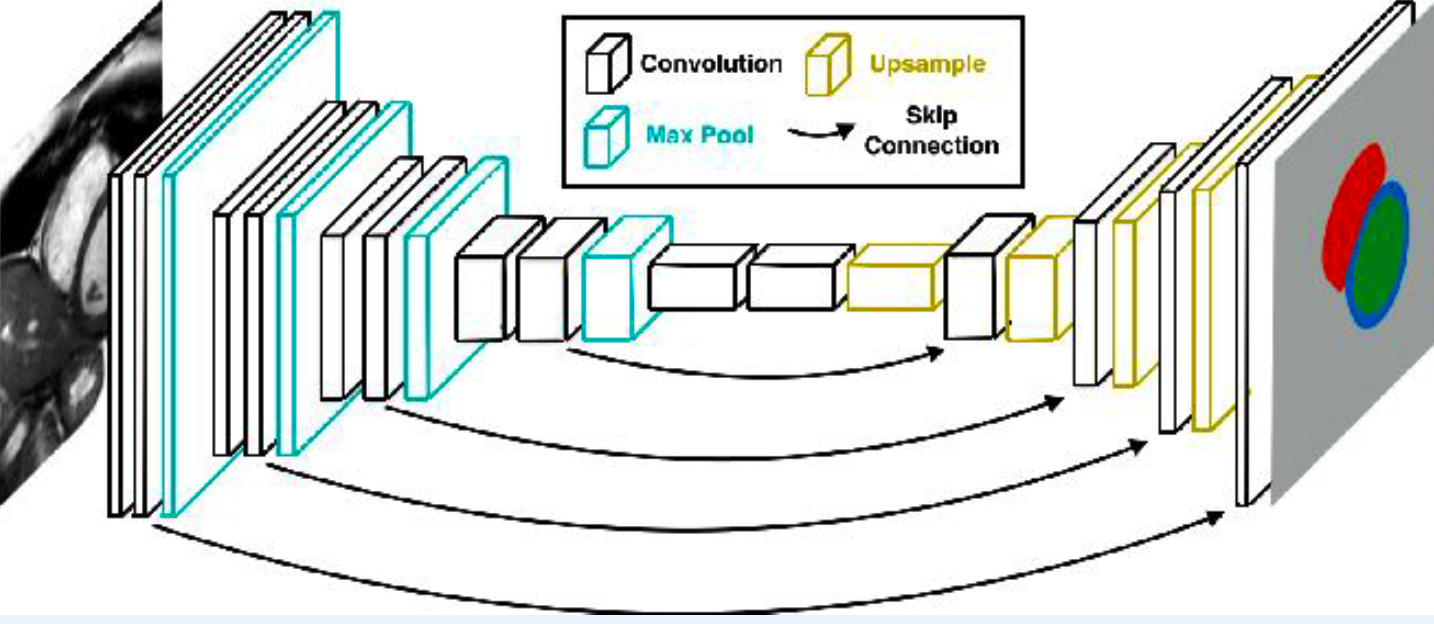
(3) FCN (Fully Convoluitonal Network)
-
no FC layer! only CNN layer!
-
retains spatial information
- Encoder CNN & Decoder CNN
- encoder : high-level feature extraction
- decoder : high resolution restoration
- (+ skip connection)
- for low-level feature interpolation
1. Import Packages & Datasets
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
Dataset :
- (1) Image (
.jpg) - (2) Mask (
.jpg)
data_dir = "../DATASET/Segmentation/"
data_df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(data_dir, "train.csv"))
data_df.head()
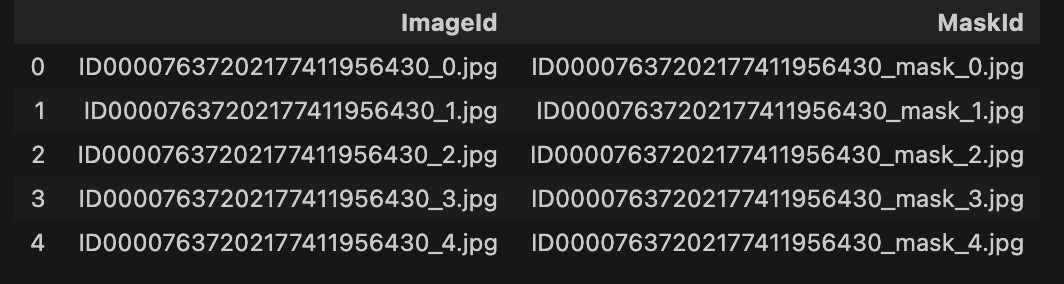
Add ID of image/mask ( data_df["Id"] )
- ex)
ID00007637202177411956430
\(\rightarrow\) split with _
def get_id(x):
return x.split("_")[0]
data_df["Id"] = data_df.ImageId.apply(lambda x : get_id(x))
112 unique IDs
data_df["Id"].nunique()
112
Get data of certain ID
def get_client_data(data_df, index):
client_ids = data_df["Id"].unique()
client_id = client_ids[index]
client_data = data_df[data_df["Id"] == client_id]
image_files = list(client_data["ImageId"])
mask_files = list(client_data["MaskId"])
return client_id, image_files, mask_files
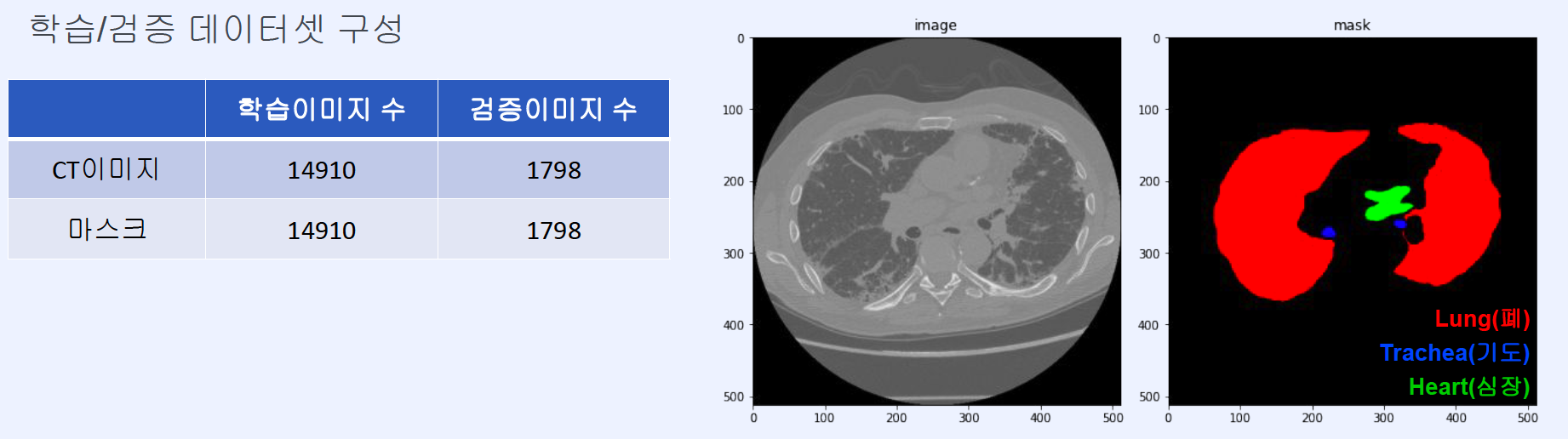
Regions : 3 + 1 (background)
- (1) background
- (2) trachea
- (3) heart
- (4) lung
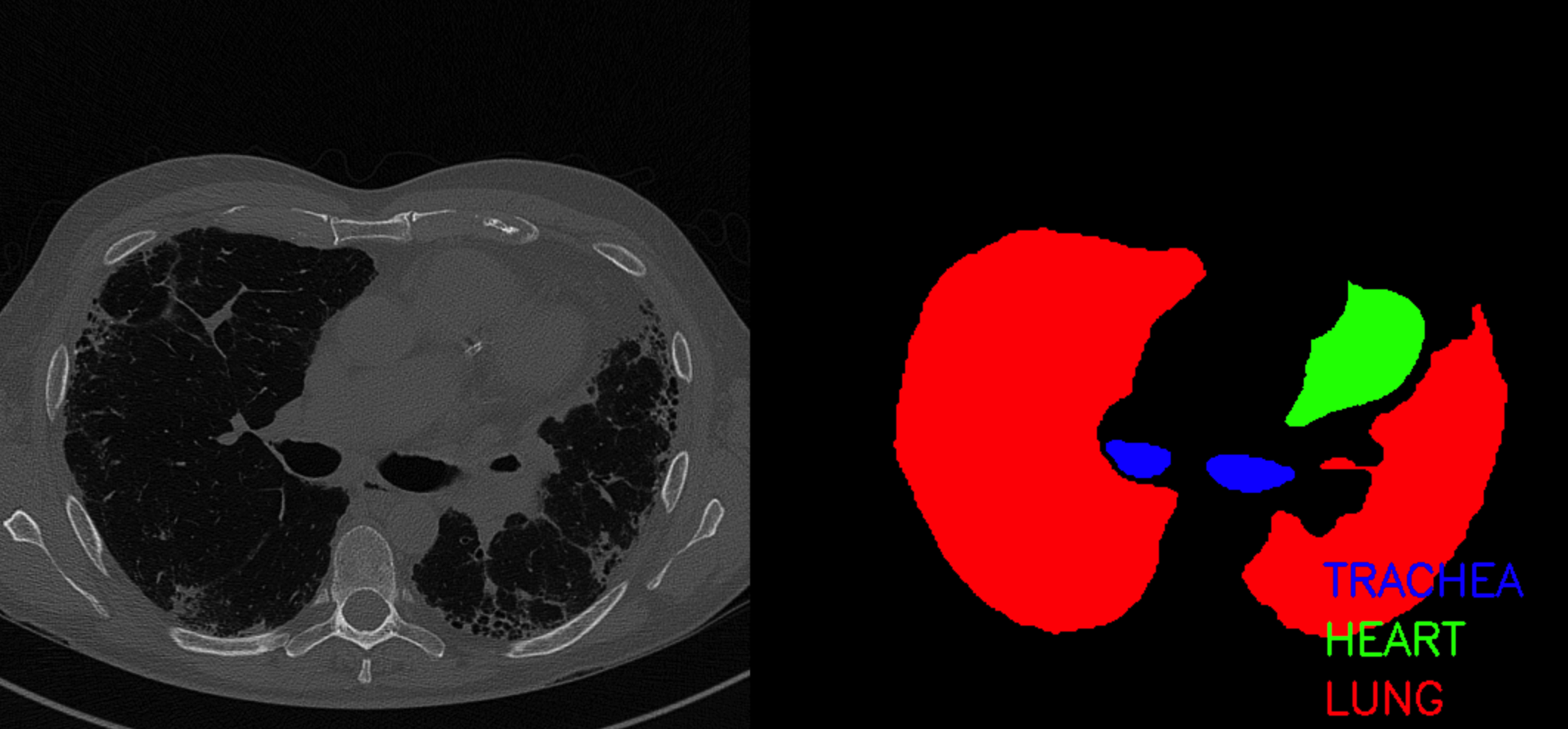
2. Visualize
Each region corresponds to colors below
regions = ["background", "trachea", "heart", "lung"]
colors = ((0,0,0), (255, 0, 0), (0, 255, 0), (0, 0, 255))
Get certain ID ( index = 50 )
index = 50
client_id, image_files, mask_files = get_client_data(data_df, index)
Image Size : (512,512,3)
\(\rightarrow\) visualize 2 images ( original image + mask )
canvas = np.zeros(shape=(512, 2*512+50, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
Read files & draw on canvas
for i in range(len(image_files)):
#============================================================#
# (1) read image & mask
image = cv2.imread(os.path.join(data_dir, "images", image_files[i]))
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
mask = cv2.imread(os.path.join(data_dir, "masks", mask_files[i]))
mask = cv2.cvtColor(mask, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
thres = 240
mask[mask < thres] = 0
mask[mask >= thres] = 255
#============================================================#
# (2) draw on canvas
## -- (L) image
## -- (R) mask
canvas[:, :512, :] = image
canvas[:, 512+50:2*512+50, :] = mask
#============================================================#
# (3) write text on canvas
text_buff = 410
for j in range(1, len(regions)):
cv2.putText(canvas, f'{regions[j].upper()}', (900, text_buff),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, colors[j], 2)
text_buff += 40
cv2.imshow('image', canvas)
key = cv2.waitKey(60)
if key == 27:
break
if key == ord('s'):
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
3. Build Dataset
IMAGE_SIZE = 224
class CT_dataset():
def __init__(self, data_dir, phase, transformer=None):
self.phase = phase # train / val
self.images_dir = os.path.join(data_dir, phase, "images")
self.masks_dir = os.path.join(data_dir, phase, "masks")
self.image_files = [filename for filename in os.listdir(self.images_dir) if filename.endswith("jpg")]
self.mask_files = [filename for filename in os.listdir(self.masks_dir) if filename.endswith("jpg")]
assert len(self.image_files) == len(self.mask_files)
self.transformer = transformer
def __len__(self):
return len(self.image_files)
def __getitem__(self, index):
#=============================================#
# (1) load image & mask
image = cv2.imread(os.path.join(self.images_dir, self.image_files[index]))
image = cv2.resize(image, dsize=(IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
mask = cv2.imread(os.path.join(self.masks_dir, self.mask_files[index]))
mask = cv2.resize(mask, dsize=(IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
mask[mask < 240] = 0
mask[mask >= 240] = 255
mask = mask / 255.
#=============================================#
# (2) shape of image/mask : (H,W,C=3)
mask_H, mask_W, _ = mask.shape
#=============================================#
# (3) definition of background:
## NO "trachea"
## NO "heart"
## NO "lung"
background = np.ones(shape=(mask_H, mask_W))
background[mask[..., 0] != 0] = 0
background[mask[..., 1] != 0] = 0
background[mask[..., 2] != 0] = 0
#=============================================#
# (4) expand mask
## before : (H,W,3)
## after : (H,W,4) ( = background + 3 )
mask = np.concatenate([np.expand_dims(background, axis=-1), mask], axis=-1)
# (H,W,4) -> (H,W) ( get the largest over 4 )
mask = np.argmax(mask, axis=-1)
if self.transformer:
image = self.transformer(image)
target = torch.from_numpy(mask).long()
return image, target
Transformation of images
- (1) convert to Tensor
- (2) Normalize
( Resizing is already done in above! no need to resize! )
from torchvision import transforms
def build_transformer():
transformer = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485,0.456,0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
return transformer
Build dataset
data_dir = "../DATASET/Segmentation/"
transformer = build_transformer()
train_dset = CT_dataset(data_dir = data_dir, phase = "train", transformer = transformer)
Check the shape of images
image_ex, target_ex = train_dset[0]
print(f"image shape: {image_ex.shape}")
print(f"target shape: {target_ex.shape}")
image shape: torch.Size([3, 224, 224])
target shape: torch.Size([224, 224])
4. Build Dataloader
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
Collate funcion
- how to output batch!
def collate_fn(batch):
images = []
targets = []
for img, tgt in batch:
images.append(img)
targets.append(tgt)
images = torch.stack(images, dim=0)
targets = torch.stack(targets, dim=0)
return images, targets
Build Dataloader
- use the collate function build above!
train_dloader = DataLoader(train_dset, batch_size=4, shuffle=True,
collate_fn=collate_fn)
Check the (batch size) of images/targets
for idx, batch in enumerate(train_dloader):
images = batch[0]
targets = batch[1]
print(f"images shape: {images.shape}")
print(f"targets shape: {targets.shape}")
break
images shape: torch.Size([4, 3, 224, 224])
targets shape: torch.Size([4, 224, 224])
Build dictionary of dataloaders ( train & val )
def build_dataloader(data_dir, batch_size=4):
transformer = build_transformer()
dataloaders = {}
train_dataset = CT_dataset(data_dir=data_dir, phase="train", transformer=transformer)
val_dataset = CT_dataset(data_dir=data_dir, phase="val", transformer=transformer)
dataloaders["train"] = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, collate_fn=collate_fn)
dataloaders["val"] = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, collate_fn=collate_fn)
return dataloaders
5. Implementation of U-Net
Goal : Implement U-Net with Pytorch
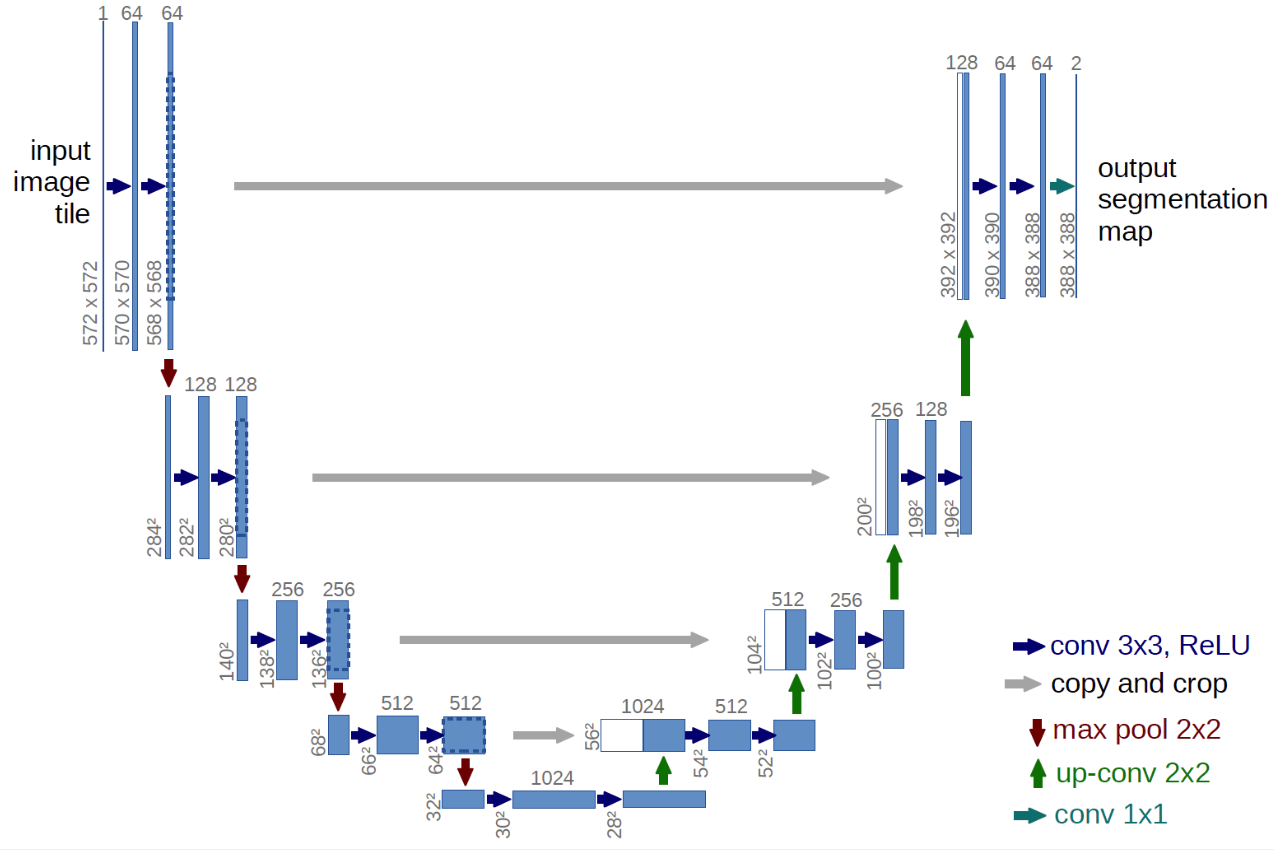
( https://lmb.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/people/ronneber/u-net/ )
Build 2 types of function :
- downsampling (
ConvLayer) - upsampling (
UpConvLayer)
ConvLayer
- used in Encoder
def ConvLayer(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1):
layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, padding=padding),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, padding=padding),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
return layers
UpConvLayer
- used in Decoder
def UpConvLayer(in_channels, out_channels):
layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=2, stride=2),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
return layers
(1) Encoder of U-Net
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv_block1 = ConvLayer(in_channels=3, out_channels=64)
self.conv_block2 = ConvLayer(in_channels=64, out_channels=128)
self.conv_block3 = ConvLayer(in_channels=128, out_channels=256)
self.conv_block4 = ConvLayer(in_channels=256, out_channels=512)
self.conv_block5 = ConvLayer(in_channels=512, out_channels=1024)
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
def forward(self, x):
encode_features = [] # for connection to the DECODER part
out = self.conv_block1(x)
encode_features.append(out) # add
out = self.pool(out)
out = self.conv_block2(out)
encode_features.append(out) # add
out = self.pool(out)
out = self.conv_block3(out)
encode_features.append(out) # add
out = self.pool(out)
out = self.conv_block4(out)
encode_features.append(out) # add
out = self.pool(out)
out = self.conv_block5(out)
return out, encode_features
(2) Decoder of U-Net
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.upconv_layer1 = UpConvLayer(in_channels=1024, out_channels=512)
# 512+512 = orignal + connection
self.conv_block1 = ConvLayer(in_channels=512+512, out_channels=512)
self.upconv_layer2 = UpConvLayer(in_channels=512, out_channels=256)
self.conv_block2 = ConvLayer(in_channels=256+256, out_channels=256)
self.upconv_layer3 = UpConvLayer(in_channels=256, out_channels=128)
self.conv_block3 = ConvLayer(in_channels=128+128, out_channels=128)
self.upconv_layer4 = UpConvLayer(in_channels=128, out_channels=64)
self.conv_block4 = ConvLayer(in_channels=64+64, out_channels=64)
def forward(self, x, encoder_features):
# add the connections from the ENCODER part
out = self.upconv_layer1(x)
out = torch.cat([out, encoder_features[-1]], dim=1)
out = self.conv_block1(out)
out = self.upconv_layer2(out)
out = torch.cat([out, encoder_features[-2]], dim=1)
out = self.conv_block2(out)
out = self.upconv_layer3(out)
out = torch.cat([out, encoder_features[-3]], dim=1)
out = self.conv_block3(out)
out = self.upconv_layer4(out)
out = torch.cat([out, encoder_features[-4]], dim=1)
out = self.conv_block4(out)
return out
(3) Example
( not done! we need to add prediction head )
encoder = Encoder(pretrained=False)
decoder = Decoder()
x_rand = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
z, feature_maps = encoder(x_rand)
out = decoder(z, feature_maps)
#-------------------------------------------------------#
print(z.shape, len(feature_maps)) # (B,C,H,W)
print(out.shape)
print('-')*20
for fm in feature_maps:
print(fm.shape)
torch.Size([1, 1024, 14, 14]) 4
torch.Size([1, 64, 224, 224])
--------------------
torch.Size([1, 64, 224, 224])
torch.Size([1, 128, 112, 112])
torch.Size([1, 256, 56, 56])
torch.Size([1, 512, 28, 28])
(4) U-Net ( = Enc + Dec )
( + Prediction Head, with output dim = num_classes )
class UNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes, pretrained):
super().__init__()
self.encoder = Encoder(pretrained)
self.decoder = Decoder()
self.head = nn.Conv2d(64, num_classes, kernel_size=1)
def forward(self, x):
out, encode_features = self.encoder(x)
out = self.decoder(out, encode_features)
out = self.head(out)
return out
model = UNet(num_classes=4, pretrained=False)
x_rand = torch.randn(64, 3, 224, 224)
out = model(x_rand)
print(out.shape) # ( B=64, num_classes=3+1, H=224, W=224)
torch.Size([64, 4, 224, 224])
6. Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC)
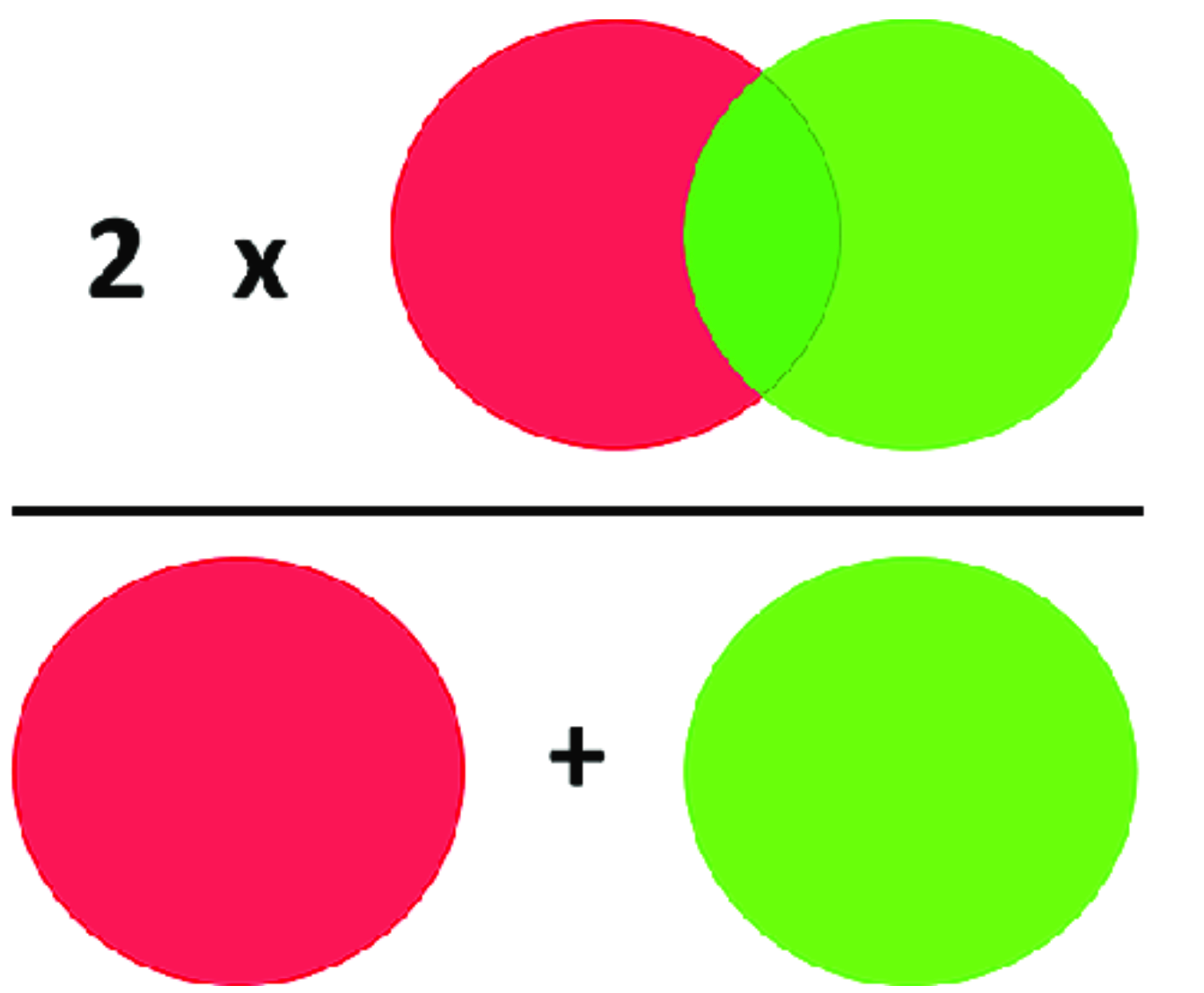
( https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Scheme-to-explain-how-Dice-coefficient-is-calculated-The-light-red-and-light-green_fig4_352895635 )
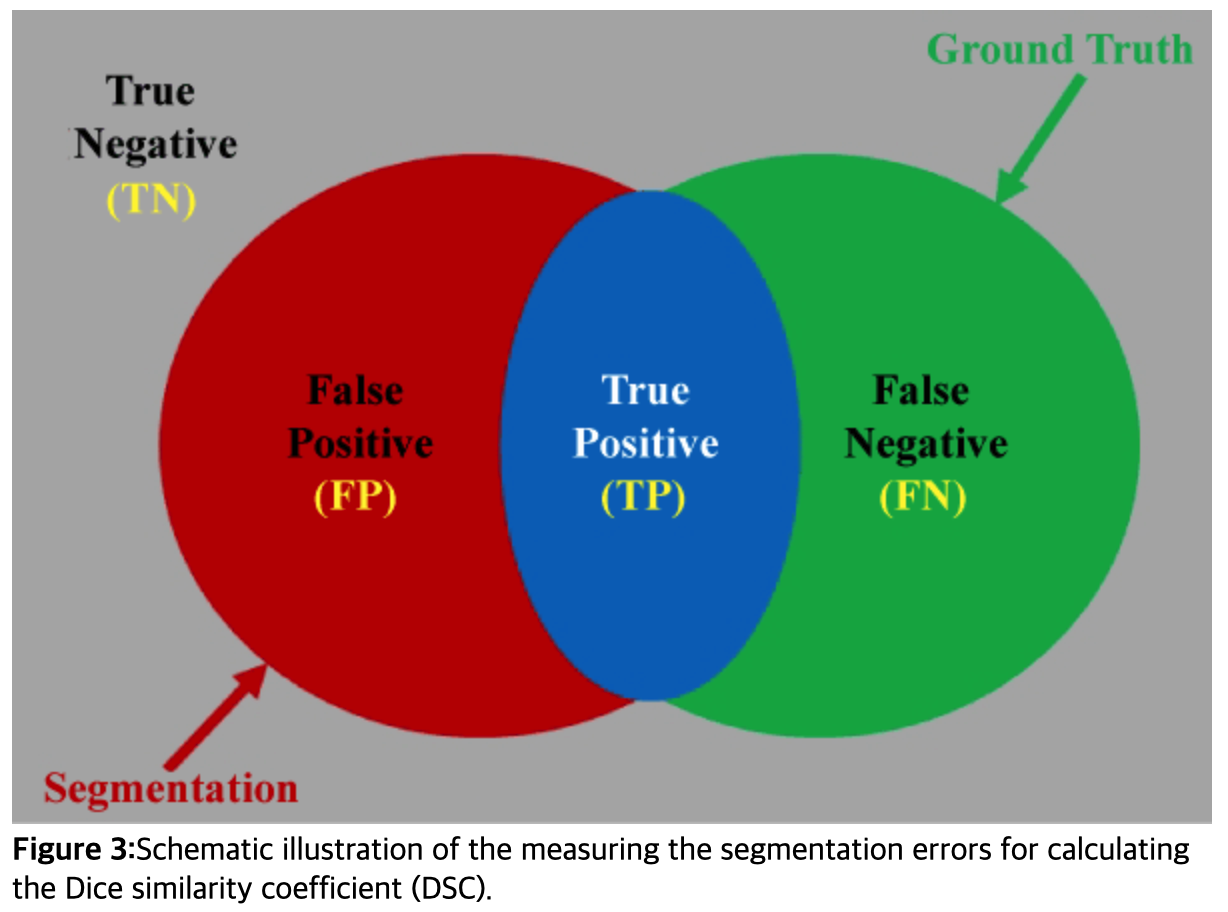
( https://www.omicsonline.org/articles-images/JCSB-07-209-g003.html )
DSC : generalization of F1 score
-
DSC of “binary segmentation task” = F1 score
-
DSC loss = 1 - DSC
for index, batch in enumerate(tr_dataloader):
images = batch[0]
targets = batch[1]
predictions = model(images)
break
print(predictions.shape) # (B, C, H, W)
torch.Size([4, 4, 224, 224])
num_classes = 4 # ( = number of channels )
# get the maximum channel!
## (B,C,H,W) -> (B,H,W)
predictions_ = torch.argmax(predictions, dim=1)
# one-hot encode the maximum value & reshape
## step 1) (B,H,W) -> (B,H,W,"C")
## step 2) (B,H,W,"C") -> (B,"C",H,W)
onehot_pred = F.one_hot(predictions_, num_classes=num_classes).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
onehot_target = F.one_hot(targets, num_classes=num_classes).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
print(predictions_.shape)
print(onehot_pred.shape)
print(onehot_target.shape)
torch.Size([4, 224, 224])
torch.Size([4, 4, 224, 224])
torch.Size([4, 4, 224, 224])
Calculate DSC with example prediction
-
add DSC for all classes(channels) (=4)
( then, divide with the number of classes )
-
but, actually no need for background!
\(\rightarrow\)
range(1, num_classes)
y_pred = onehot_pred[0]
y_true = onehot_target[0]
dice_coeff = 0
for class_index in range(1, num_classes):
#-------------------------------------------------------#
y_pred_class = y_pred[class_index]
y_true_class = y_true[class_index]
y_pred_class_flat = y_pred[class_index].reshape(-1).float()
y_true_class_flat = y_true[class_index].reshape(-1).float()
#-------------------------------------------------------#
set_inter = torch.dot(y_pred_class_flat, y_true_class_flat)
set_sum = y_pred_class_flat.sum() + y_true_class_flat.sum()
#-------------------------------------------------------#
dice_coeff += (2 * set_inter) / (set_sum + 1e-9)
dice_coeff /= (num_classes-1)
dice_loss = 1. - dice_coeff
print(dice_coeff)
tensor(0.0141)
7. UNet metric
implement metric as class
class UNet_metric():
def __init__(self, num_classes):
self.num_classes = num_classes
def __call__(self, pred, target):
onehot_pred = F.one_hot(torch.argmax(pred, dim=1), num_classes=self.num_classes).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
onehot_target = F.one_hot(target, num_classes=self.num_classes).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
dice_loss = self._get_dice_loss(onehot_pred, onehot_target)
dice_coefficient = self._get_batch_dice_coefficient(onehot_pred, onehot_target)
return dice_loss, dice_coefficient
# (1) get dice for SINGLE class
def _get_dice_coeffient(self, pred, target):
set_inter = torch.dot(pred.reshape(-1).float(), target.reshape(-1).float())
set_sum = pred.sum() + target.sum()
if set_sum.item() == 0:
set_sum = 2 * set_inter
dice_coeff = (2 * set_inter) / (set_sum + 1e-9)
return dice_coeff
# (2) get dice for MULTI class
def _get_multiclass_dice_coefficient(self, pred, target):
dice = 0
for class_index in range(1, self.num_classes):
dice += self._get_dice_coeffient(pred[class_index], target[class_index])
return dice / (self.num_classes - 1)
# (2) get dice for MULTI class with BATCH
def _get_batch_dice_coefficient(self, pred, target):
num_batch = pred.shape[0]
dice = 0
for batch_index in range(num_batch):
dice += self._get_multiclass_dice_coefficient(pred[batch_index], target[batch_index])
return dice / num_batch
def _get_dice_loss(self, pred, target):
return 1 - self._get_batch_dice_coefficient(pred, target)
criterion = UNet_metric(num_classes=4)
loss = criterion(predictions, targets)
print(loss) # 1 : loss, 2 : dice
(tensor(2.1879, grad_fn=<AddBackward0>), tensor(0.0054))
8. Train Code
( same code as xxx )
def train_one_epoch(dataloaders, model, optimizer, criterion, device):
losses = {}
dice_coefficients = {}
for phase in ["train", "val"]:
running_loss = 0.0
running_dice_coeff = 0.0
if phase == "train":
model.train()
else:
model.eval()
for index, batch in enumerate(dataloaders[phase]):
images = batch[0].to(device)
targets = batch[1].to(device)
with torch.set_grad_enabled(phase == "train"):
predictions = model(images)
loss, dice_coefficient = criterion(predictions, targets)
if phase == "train":
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item()
running_dice_coeff += dice_coefficient.item()
if phase == "train":
if index % 100 == 0:
text = f"{index}/{len(dataloaders[phase])}" + \
f" - Running Loss: {loss.item():.4f}" + \
f" - Running Dice: {dice_coefficient.item():.4f}"
print(text)
losses[phase] = running_loss / len(dataloaders[phase])
dice_coefficients[phase] = running_dice_coeff / len(dataloaders[phase])
return losses, dice_coefficients
Train models
data_dir = "../DATASET/Segmentation/"
is_cuda = torch.cuda.is_available()
NUM_CLASSES = 4
IMAGE_SIZE = 224
BATCH_SIZE = 12
DEVICE = torch.device('cuda' if is_cuda else 'cpu')
dataloaders = build_dataloader(data_dir, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
model = UNet(num_classes=NUM_CLASSES)
model = model.to(DEVICE)
criterion = UNet_metric(num_classes=NUM_CLASSES)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr= 1E-3, momentum=0.9)
num_epochs = 10
best_epoch = 0
best_score = 0.0
train_loss, train_dice_coefficient = [], []
val_loss, val_dice_coefficient = [], []
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
losses, dice_coefficients = train_one_epoch(dataloaders, model, optimizer, criterion, DEVICE)
train_loss.append(losses["train"])
val_loss.append(losses["val"])
train_dice_coefficient.append(dice_coefficients["train"])
val_dice_coefficient.append(dice_coefficients["val"])
print(f"{epoch}/{num_epochs} - Train Loss: {losses['train']:.4f}, Val Loss: {losses['val']:.4f}")
print(f"{epoch}/{num_epochs} - Train Dice Coeff: {dice_coefficients['train']:.4f}, Val Dice Coeff: {dice_coefficients['val']:.4f}")
if (epoch > 3) and (dice_coefficients["val"] > best_score):
best_epoch = epoch
best_score = dice_coefficients["val"]
save_model(model.state_dict(), f"model_{epoch:02d}.pth")
print(f"Best epoch: {best_epoch} -> Best Dice Coeffient: {best_score:.4f}")
9. Test Code & Morphological filtering
NUM_CLASSES = 4
IMAGE_SIZE = 224
DEVICE = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
Load Model
def load_model(ckpt_path, num_classes, device):
checkpoint = torch.load(ckpt_path, map_location=device)
model = UNet(num_classes=num_classes)
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint)
model = model.to(device)
model.eval()
return model
ckpt_path = "./trained_model/model_05.pth"
model = load_model(ckpt_path, NUM_CLASSES, DEVICE)
(1) Morphological filtering
노이즈 제거를 위한 후처리 기법
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT,(ksize, ksize))사용
def morpholocal_process(mask, num_classes, ksize=7):
new_mask = mask.copy()
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT,(ksize, ksize))
for class_index in range(1, num_classes):
binary_mask = (mask == class_index).astype(np.uint8)
closing = cv2.morphologyEx(binary_mask, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
new_mask[closing.astype(np.bool_)] = class_index
return new_mask
(2) To RGB
colors (channels) that match each class
- ex: background (0) = (0,0,0)
from utils import CLASS_ID_TO_RGB
CLASS_ID_TO_RGB
{0: (0, 0, 0), 1: (255, 0, 0), 2: (0, 255, 0), 3: (0, 0, 255)}
def decode_segmap(mask, num_classes):
mask_H, mask_W = mask.shape # (H,W)
R_channel = np.zeros((mask_H, mask_W), dtype=np.uint8) # R channel
G_channel = np.zeros((mask_H, mask_W), dtype=np.uint8) # G channel
B_channel = np.zeros((mask_H, mask_W), dtype=np.uint8) # B channel
for class_index in range(1, num_classes):
R_channel[mask == class_index] = CLASS_ID_TO_RGB[class_index][0] # R
G_channel[mask == class_index] = CLASS_ID_TO_RGB[class_index][1] # G
B_channel[mask == class_index] = CLASS_ID_TO_RGB[class_index][2] # B
RGB_mask = cv2.merge((B_channel, G_channel, R_channel))
return RGB_mask
(3) Prediction
Transform the test images ( just like train images )
transformer = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])
from PIL import Image
@torch.no_grad()
def predict_segment(image, model, num_classes, device):
# (1) Import Test Image ( + convert + to device )
PIL_image = Image.fromarray(image)
tensor_image = transformer(PIL_image)
tensor_image = tensor_image.to(device)
# (2) Make prediction ( mask )
pred_mask = model(torch.unsqueeze(tensor_image, dim=0))
pred_mask = torch.argmax(pred_mask.squeeze(0).cpu(), dim=0)
pred_mask = pred_mask.numpy()
# (3) Morpohological filtering on output
pred_mask = morpholocal_process(pred_mask, num_classes)
# (4) Into RGB
rgb_mask = decode_segmap(pred_mask, num_classes)
return rgb_mask
(4) Predict images from video
video_path = "../DATASET/Segmentation/video/test/ID00411637202309374271828.mp4"
cnt = 0
vidcap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
while (vidcap.isOpened()):
ret, frame = vidcap.read()
if ret:
rgb_mask = predict_segment(frame, model, NUM_CLASSES, DEVICE)
rgb_mask = cv2.resize(rgb_mask, dsize=frame.shape[:2])
alpha = 0.6
blend = cv2.addWeighted(frame, alpha, rgb_mask, 1-alpha, 0)
cv2.imshow('output', blend)
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
if key == 27:
break
if key == ord('s'):
cv2.waitKey(0)
else:
break
vidcap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
