(code review) Matching Network
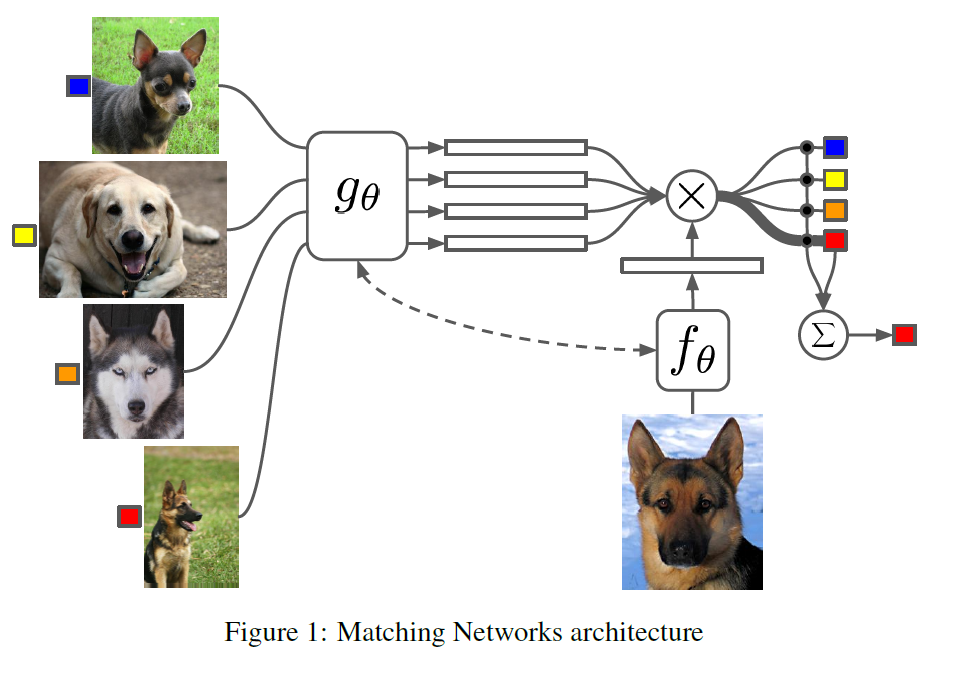
1. Task Sampler
- (1) 랜덤하게/고정되게 task를 샘플하기
- ex) class A vs class D를 비교하는 task
- (2) 해당 task에 사용되는(=task의 class label을 가지는) 데이터셋 불러오기
- ex) class A & class D에 해당하는 데이터셋
- (3) 불러온 두 데이터셋을 둘로 나눔
- (a) Support Set ( ex. A1,A5,A9,…D1,D2,D6,.. )
- (b) Query Set ( ex. A2,A3,A4,…,D3,D4,D5… )
- (4) 두 데이터셋에서 각각 n_shot개, num_Q개만큼을 샘플
- (a 일부) Support Set 일부 ( ex. A1,A5,A13,A15 & D1,D6,D10,D11 )
- (b 일부) Query Set 일부 ( ex. A3,A4 & D2,D7 )
- (5) (a 일부)+(b 일부) 합쳐서 return
class NShotTaskSampler(Sampler):
def __init__(self,dataset,episodes_per_epoch,
n_shot,k_way,num_Q,num_tasks= 1,
fixed_tasks: List[Iterable[int]] = None):
super(NShotTaskSampler, self).__init__(dataset)
self.episodes_per_epoch = episodes_per_epoch
self.dataset = dataset
self.num_tasks = num_tasks
self.k_way = k_way
self.n_shot = n_shot
self.num_Q = num_Q
self.fixed_tasks = fixed_tasks
self.task_idx = 0
def __len__(self):
return self.episodes_per_epoch
def __iter__(self):
# (1) unique한 class명
class_names=self.dataset.df['class_id'].unique()
# (2) 1번의 epsiode 동안
for _ in range(self.episodes_per_epoch):
id_batches = []
for task in range(self.num_tasks):
## case 1) 랜덤 task의 class id(이름)들
if self.fixed_tasks is None:
episode_classes = np.random.choice(class_names,self.k, replace=False)
## case 2) 정해진 task의 class id(이름)들
else:
episode_classes = self.fixed_tasks[self.task_idx % len(self.fixed_tasks)]
self.task_idx += 1
## df = 해당 class id들을 가진 dataset
df = self.dataset.df[self.dataset.df['class_id'].isin(episode_classes)]
support_k = {k: None for k in episode_classes}
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# class_k1 : S (support) -> 이 중 "n_shot개"만을 sample할 것
# class_k2 : Q (query) -> 이 중 "num_Q개"만을 sample할 것
# class_k1, class_k2 모두 "같은 class들", but 서로 다른 데이터
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
### (1) S에서 batch 샘플하기
### 해당 batch에는 n_shot개 만큼의 데이터
for k in episode_classes:
class_k1 = df[df['class_id'] == k]
support = class_k1.sample(self.n_shot)
support_k[k] = support
for i, s in support.iterrows():
id_batches.append(s['id'])
### (2) Q에서 batch 샘플하기
### 해당 batch에는 num_Q개 만큼의 데이터
for k in episode_classes:
class_k2=df[(df['class_id'] == k) & (~df['id'].isin(support_k[k]['id']))]
query = class_k2.sample(self.num_Q)
for i, q in query.iterrows():
id_batches.append(q['id'])
yield np.stack(id_batches)
2. Sub modules
(1) Flatten
- 3d의 input image를 1차원으로 flatten 시키는 함수
class Flatten(nn.Module):
def forward(self, input):
return input.view(input.size(0), -1)
(2) Conv Block
- “Convolution layer & Batch Normalization & ReLU & Max Pooling”의 과정을 거치는 함수
def conv_block(in_,out_):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_, out_, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
)
(3) get_few_shot_encoder
def get_few_shot_encoder(num_input_channels=1):
return nn.Sequential(
conv_block(num_input_channels, 64),
conv_block(64, 64),
conv_block(64, 64),
conv_block(64, 64),
Flatten(),
)
3. Models

- 보다 복잡한 “full context embedding” 상황 하에서
(1) Embedding function of \(S\) : \(g\)
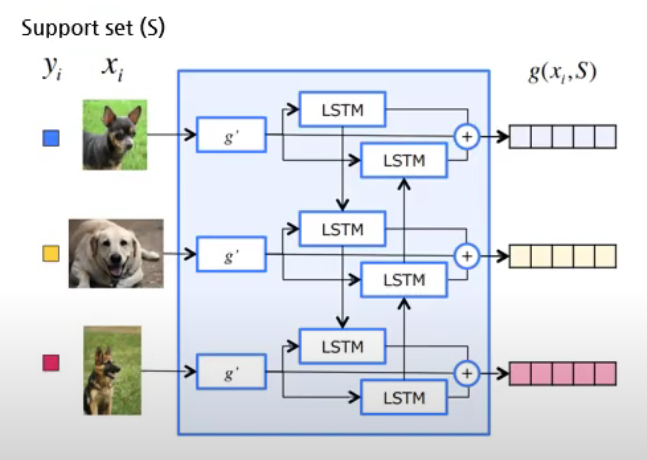
class BidrectionalLSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, num_layers):
super(BidrectionalLSTM, self).__init__()
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.batch_size = 1
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=input_dim,
num_layers=num_layers,
hidden_size=input_dim,
bidirectional=True)
def forward(self, S):
output,(h, c) = self.lstm(S, None)
# (1) LEFT
output_forw = output[:, :, :self.lstm.hidden_size]
# (2) RIGHT
output_back = output[:, :, self.lstm.hidden_size:]
# [FINAL] LEFT + RIGHT + main
output_concat = output_forw + output_back + S
return output_concat, h, c
(2) Embedding function of \(Q\) : \(f\)
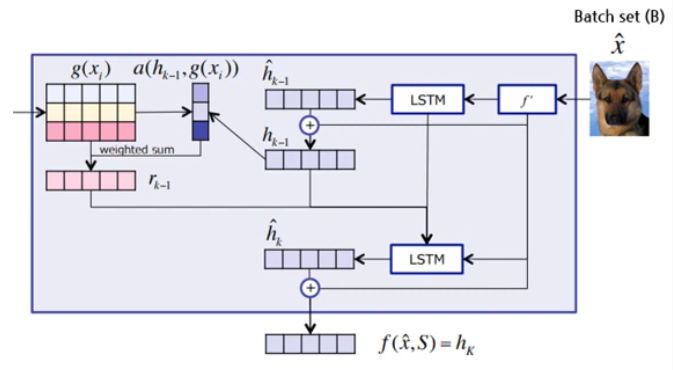
class AttentionLSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,input_dim, unrolling_steps):
super(AttentionLSTM, self).__init__()
self.unrolling_steps = unrolling_steps
self.lstm_cell = nn.LSTMCell(input_size=input_dim,
hidden_size=input_dim)
def forward(self, S, Q):
batch_size = Q.shape[0] # Q의 개수 (= num_Q)
embedding_dim = Q.shape[1] # Q의 차원
h = torch.zeros_like(Q).cuda().double() # (num_Q x 1)
c = torch.zeros(batch_size, embedding_dim).cuda().double() # (num_Q x dim)
for k in range(self.unrolling_steps):
#---------------------------------------------
# (1) hidden state ( cumulative sum )
# Query set에 계속해서 hidden state를 더한다
# Hidden state의 변화 : Q -> Q+h1 -> Q+h1+h2 -> ... Q+h1+..+hk
h_ = h + Q
#---------------------------------------------
# (2) attention ( hidden state & embed(S) )
# 누적의 Hidden state & Support set의 attention
att = torch.mm(h_, S.t()).softmax(dim=1)
#---------------------------------------------
# (3) readout
# Support set x Attention
readout = torch.mm(att, S)
#---------------------------------------------
# (4) run LSTM
# Input : Query set
# Hidden : 누적의 Hiddenstate + readout
# Cell : c
h, c = self.lstm_cell(Q, (h_ + readout, c))
# 최종 Output : hidden + Query set
H = h + Q
return H
(3) Matching Network (MN)
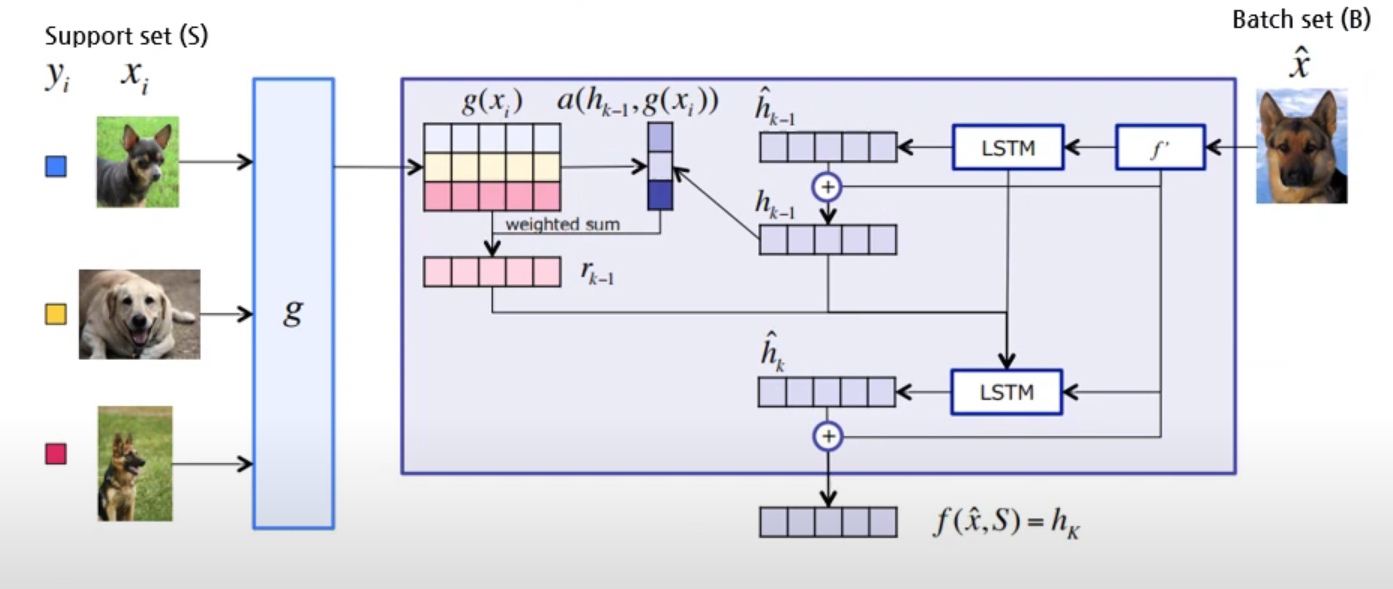
class MatchingNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_shot,k_way,num_Q,full_context, num_input_channels,
lstm_layers, lstm_input_dim, unrolling_steps, device):
super(MatchingNet, self).__init__()
self.n_shot = n_shot
self.k_way = k_way
self.num_Q = num_Q
self.full_context = full_context
self.num_input_channels = num_input_channels
self.encoder = get_few_shot_encoder(self.num_input_channels)
if self.full_context:
# (1) g ( for S 임베딩 )
self.g = BidrectionalLSTM(lstm_input_dim, lstm_layers).to(device, dtype=torch.double)
# (2) f ( for Q 임베딩 )
self.f = AttentionLSTM(lstm_input_dim, unrolling_steps=unrolling_steps).to(device, dtype=torch.double)
def forward(self, inputs):
pass
4. Training
(1) One Step GD
하나의 batch에 대해
- (1) prediction
- (2) loss 계산
- (3) back-prop
def gradient_step(model, opt, loss_fn, x, y, **kwargs):
model.train()
opt.zero_grad()
y_pred = model(x)
loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y)
loss.backward()
opt.step()
return loss, y_pred
(2) One Episode
def matching_net_epsiode(model,opt,loss_fn,X,y,n_shot,k_way,num_Q,dist_func,full_context,train):
#---------------------------------------------
# (1) Settings ( Train or Test )
if train:
model.train()
opt.zero_grad()
else:
model.eval()
#---------------------------------------------
# (2) Embed inputs
## "COMMON" embedding for all input ( before getting into f/g function )
Emb = model.encoder(x)
#---------------------------------------------
# (3) Divide input into S(support) & Q(query)
S = Emb[:n_shot * k_way]
Q = Emb[n_shot * k_way:]
#---------------------------------------------
# [Optional] Full Context Embedding
## embed, considering support set (S)
## g : biLSTM
## f : attLSTM
if full_context:
S, _, _ = model.g(S.unsqueeze(1))
S = S.squeeze(1)
Q = model.f(S, Q)
#---------------------------------------------
# (4) distance between (1) Q & (2) S
# ( 여기서 f(Q), g(S) 계산 시 context(S) 고려 X )
dist = pairwise_distances(Q, S, dist_func)
att_dist = (-dist).softmax(dim=1)
#---------------------------------------------
# (5) Prediction
y_pred = MN_predict(att_dist, n_shot, k_way, num_Q)
#---------------------------------------------
# (6) Loss (NLL)
# Clip predictions ( for numerical stability )
y_pred = y_pred.clamp(EPSILON, 1 - EPSILON)
loss = loss_fn(y_pred.log(), y)
#---------------------------------------------
# (7) Back Propagation
if train:
loss.backward()
clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), 1)
opt.step()
return loss, y_pred
5. Prediction
ex) (k_way =) 3 class, with (n_shot =) 5 data per each class
- [0],[0],[0],[0],[0],[1],[1],[1],[1],[1],[2],[2],[2],[2],[2],
def k_n_labels(k_way, n_shot):
y = torch.arange(0, k_way, 1 / n_shot).long()
return y.unsqueeze(-1)
\(\begin{aligned} &P\left(\hat{y}_{k}=1 \mid \hat{x}, \delta\right)=\sum_{i=1}^{k} a\left(\hat{x}, x_{i}\right) y_{i} \\ &a(\hat{x}, x)=\frac{\exp (c(f(\hat{x}), g(x)))}{\sum_{i=1}^{K} \exp \left(c\left(f(\hat{x}), g\left(x_{i}\right)\right)\right)} \end{aligned}\).
def MN_predict(att_dist,n_shot,k_way,num_Q):
if att_dist.shape != (num_Q * k_way, k_way * n_shot):
raise(ValueError(f'Attention matrix shape error! Should be (q * k, k * n) = ({q * k, k * n})'))
label_mask = k_n_labels(k_way, n_shot)
y_onehot = torch.zeros(k_way * n_shot, k_way)
y_onehot = y_onehot.scatter(1, label_mask, 1)
y_pred = torch.mm(att_dist, y_onehot.cuda().double())
return y_pred
