Meta learning with Memory Augmented Neural Networks
Contents
- Introduction
- Meta-Learning Methodology
- Episode
- MANN (Memory Augmented Neural Networks)
- Read head
- Write head
- LRUA (Least Recently Used Access)
1. Introduction
MANN (Memory Augmented Neural Networks)을 제안
MANN = “(1) NTM + (2) One-shot Learning”
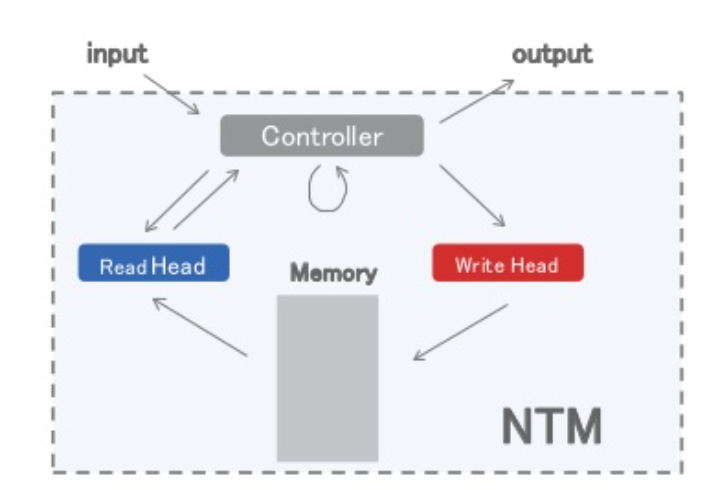
NTM(Neural Turing Machine) (링크) 참고
(1) Neural Turing Machine
-
External Memory에 read/write할 수 있는 NN
-
미분 가능! Back-prop OK
(2) One-Shot Learning
- 하나의 sample만으로도 학습 가능하도록!
- “학습”보다는 “기억”에 가깝게!
\(\rightarrow\) NTM + One-shot Learning :
“NTM을 사용하여, 적은 sample로도 잘 기억하도록!”
Abstract
-
1) NTM을 기반으로 한 MANN 제안
-
2) One-Shot Learning 수행
-
3) High Performance ( Omniglot dataset )
Omniglot Dataset 소개
-
많은 class (1623 종류), 적은 sample 수(20개/종류)
-
Train(1200) : Test(423)로 split
2. Meta-Learning Methodology
아래의 loss ( = cost “across a distribution of datasets \(p(D)\)” ) 를 최소화하도록 학습
\(\theta^{*}=\operatorname{argmin}_{\theta} E_{D \sim p(D)}[\mathcal{L}(D ; \theta)]\).
- where \(D=\left\{d_{t}\right\}_{t=1}^{T}=\left\{\left(\mathbf{x}_{t}, y_{t}\right)\right\}_{t=1}^{T}\),
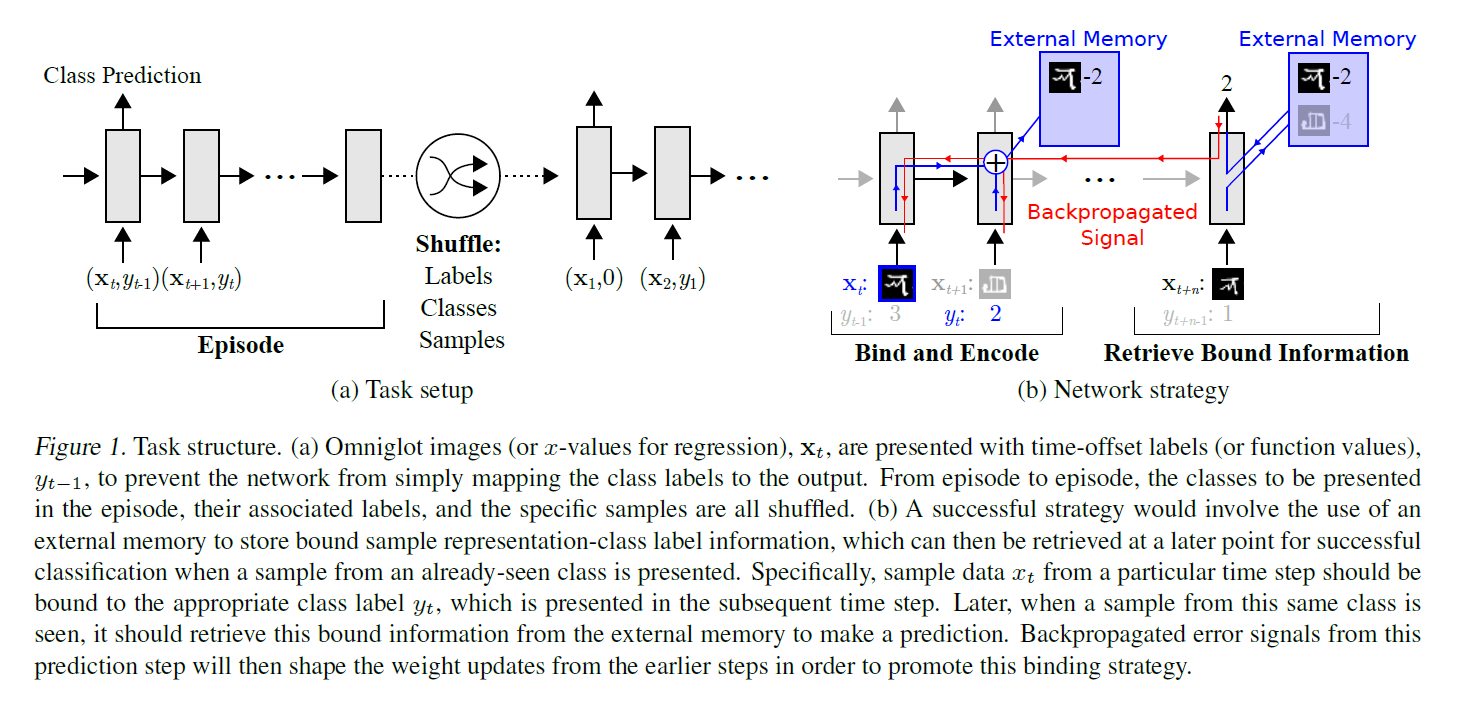
MANN paper에서의 setup :
-
\(y_t\)는 target임과 동시에, \(\mathbf{x_t}\)와 함께 input으로도 들어간다
-
time \(t\) 시점에, 이전 step의 정답 (\(y_{t-1}\))와, 현재 시점의 input (\(\mathbf{x_t}\))가 같이들어간다.
-
shuffle은 필수! ( slow learning 방지 )
궁극적인 목표 : predictive distribution \(p\left(y_{t} \mid \mathbf{x}_{t}, D_{1: t-1} ; \theta\right)\)를 학습하기!
3. Episode
One-shot Learning
- “NTM을 사용하여, 적게 본 것도 잘 맞추자!”
Episode : “정답 맞추기 과정”
-
초반 ) Random Guess
-
후반 ) 축적된 경험치로 점차 정답률 UP
Episode Setting
-
1) 1200 class 중, random하게 5 class sample
-
2) class 별 image 10개 sample ( 5x10=50개 )
-
3) 50개를 random하게 shuffle
-
4) \(x_t\) 보여주고, guess! 그런 뒤, 정답 \(y_t\) 보여줘서 결과 확인!
( 그렇게 t=1…50까지 진행 )
Test Time ) 423개의 class를 대상으로 예측
4. MANN (Memory Augmented Neural Networks)
MANN = NTM + LRUA (Least Recently Used Access)
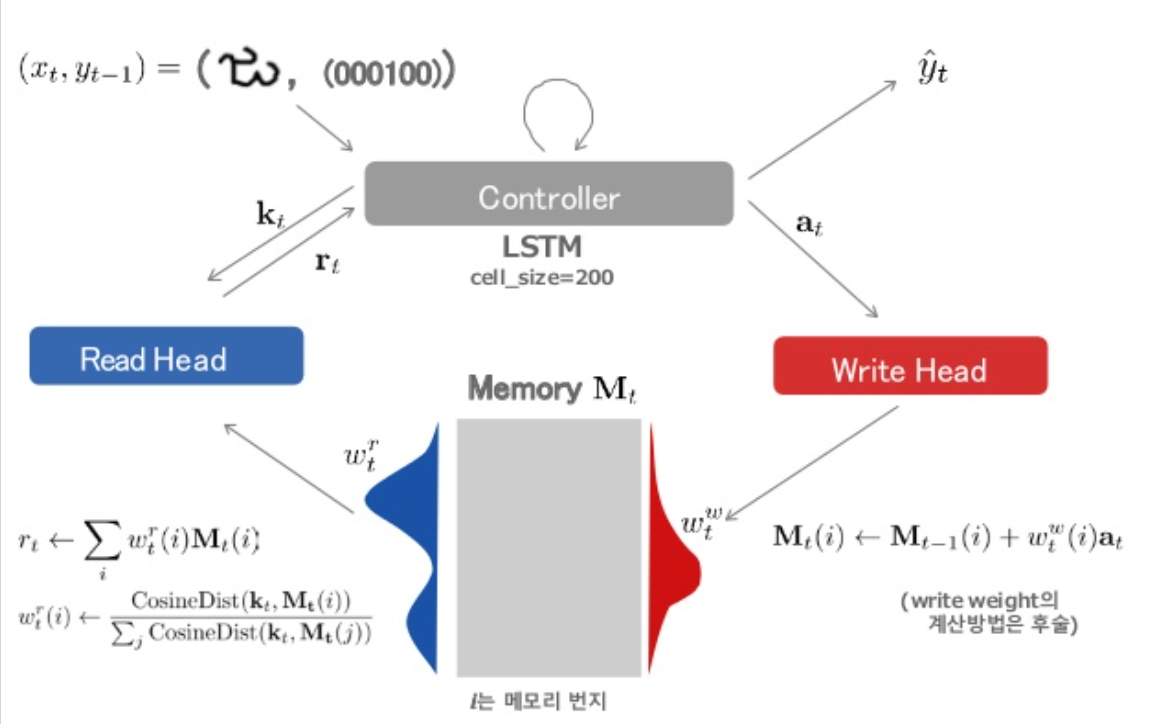
(1) READ head
수식 1) 유사도 계산
- \(w_{t}^{r}(i) \leftarrow \frac{\exp \left(K\left(\mathbf{k}_{t}, \mathbf{M}_{t}(i)\right)\right)}{\sum_{j} \exp \left(K\left(\mathbf{k}_{t}, \mathbf{M}_{t}(j)\right)\right)}\), where \(K\left(\mathbf{k}_{t}, \mathbf{M}_{t}(i)\right)=\frac{\mathbf{k}_{t} \cdot \mathbf{M}_{t}(i)}{\left\|\mathbf{k}_{t}\right\|\left\|\mathbf{M}_{t}(i)\right\|}\) ( cosine similarity )
수식 2) memory의 특정 row가 아닌, linear combination
- \(\mathbf{r}_{t} \leftarrow \sum_{i} w_{t}^{r}(i) \mathbf{M}_{t}(i)\).
여기서 읽어진 \(\mathbf{r_t}\)는 used by the controller as …
- Classifier의 input
- 다음 controller state의 Additional input
(2) WRITE head :
key point : Least Recently Used Access (LRUA)
\(\rightarrow\) \(w^{lu}\)를 사용한다!
( \(w^{lu}\) = least used weight. 최근에 사용되지 않은 Memory 영역에 write하기! )
직관적인 이해 : 새로운 지식을 memory에 집어 넣을 때, 이왕이면 빈 memory공간에 집어넣자!
-
\(\mathbf{w}_{t}^{w} \leftarrow \sigma(\alpha) \mathbf{w}_{t-1}^{r}+(1-\sigma(\alpha)) \mathbf{w}_{t-1}^{l u}\).
-
\(\mathbf{M}_{t}(i) \leftarrow \mathbf{M}_{t-1}(i)+w_{t}^{w}(i) \mathbf{a}_{t}\)>
(3) LRUA (Least Recently Used Access)
- MANN과 NMT의 차이점 : LRUA
\(w^{lu}\)는 다음과 같이 설정
- \(w_{t}^{l u}(i)=\left\{\begin{array}{ll} 0 & \text { if } w_{t}^{u}(i)>m\left(\mathbf{w}_{t}^{u}, n\right) \\ 1 & \text { if } w_{t}^{u}(i) \leq m\left(\mathbf{w}_{t}^{u}, n\right) \end{array}\right.\).
직관적 이해)
-
기존에 있던 메모리 사용 중인 공간이 크면, 0 ( 여기에 적지 마! )
-
기존에 있던 메모리 사용 중인 공간이 작으면, 1 ( 여기에 적어! )
( 상위 M개의 값을 1로 한다 ( = 빈 공간 Top M개 사용하기 ) )
\(\mathbf{w}_{t}^{u} \leftarrow \gamma \mathbf{w}_{t-1}^{u}+\mathbf{w}_{t}^{r}+\mathbf{w}_{t}^{w}\).
Reference
-
https://www.slideshare.net/ssuser06e0c5/metalearning-with-memory-augmented-neural-networks
