Multimodal Learning (2) Translation
참고 논문 :
Baltrušaitis, Tadas, Chaitanya Ahuja, and Louis-Philippe Morency. “Multimodal machine learning: A survey and taxonomy.” IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 41.2 (2018): 423-443.
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Multimodal Representations
- Unimodal Representation
- Multimodal Representation의 2 종류
- Joint representation 모델
- Coordinated representation 모델
- 요약
- Translation
- Example-based
- Generative approaches
- Model Evaluation
- Alignment
- Explicit alignment
- Implicit alignment
- 요약
- Fusion
- Model-agnostic approaches
- Model-based approaches
- 요약
- Co-learning
- Parallel data
- Non-parallel data
- Hybrid data
- 요약
- Conclusion
3. Translation
“하나의 modality에서 다른 modality로 mapping”
- ex) image가 주어졌을 때, 이를 설명하는 text 생성
두 category로 나눌 수 있음
- 1) Example-based
- dictionary 사용
- 2) Generative approaches
- translation을 수행하는 model 학습
- 더 challenging
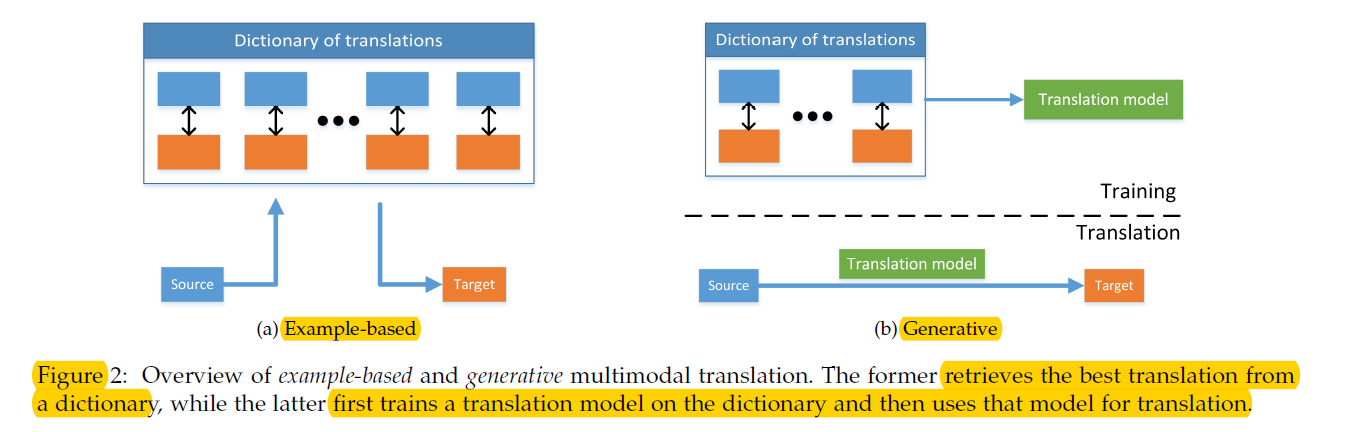
(1) Example-based
- “dictionary” 사용
- 2 종류의 알고리즘
- 1) retrieval based : modifying없이 바로 retrieved translation 사용
- 2) combination based : 더 complex rule 사용
Retrieval-based Models
- simplest form
- dictionary내 가장 가까운 sample 찾아서 결과로 사용
- unimodal space & intermediate semantic space에서 검색
Unimodal Space
- ex) 이미지 - visual feature space
Intermediate Semantic Space
- 검색 중 similarity comparison 위해
- ex) 문장 & 이미지를 <object, action, scene> space에 mapping
- bi-directional translation도 가능
- Unimodal보다 더 좋은 성능
Combination-based Models
- retrieval-based model보다 한 단계 더 나아가!
- 단지 retrieve로 끝나는 것이 아니라, 이들을 combine하여 보다 meaningful한 translation!
(2) Generative approaches
-
unimodal source가 들어왔을 때 multimodal translation을 수행하는 모델
-
학습하기 쉽지 않다!
- source modality에 대한 “understand 능력”
- 새로운 modality를 생성하는 “generative 능력”
모두 필요하다!
-
평가하기도 쉽지 않다
- 정답이 1개가 아니다!
-
이 논문에서는 3개의 modalities에 집중
- 1) language / 2) vision / 3) sound
-
3 categories of generative models
- 1) grammar-based
- 2) encoder-decoder
- 3) continuous generation
Grammar-based models
-
<subject, object, verb> 템플렛의 문장으로 처리함으로써 task 단순화
-
장점 ) 의미/논리적으로 더 말이 되는 output을 generate할 가능성이 있음
( 정해진 template에 따라 생성하기 때문에)
-
단점 ) creative translation 불가 & complex piplines
( 각 concept에 separate model )
Encoder-decoder models
-
step 1) [ Encoder ] encode source modality
step 2) [ Decoder ] generate target modality
-
end-to-end model & most popular
-
SINGLE pass pipeline
-
Decoding은 주로 RNN/LSTM 기반 모델로!
-
RNN 기반 모델의 단점?
\(\rightarrow\) single vector를 통해 생성해야! 따라서 long sequence generation은 어려울 수 있음!
-
Generative attention-based RNNs
-
Continuous generation
-
generate target modality “continuously”
( base don stream of source modality inputs )
-
매 timestep마다 output 생성
-
(초창기 모델) graphical / latent variable model
- shared Gaussian process latent variable models
- HMM (Hidden Markov models)
-
최근에는 encoder-decoder model 사용
(3) Model Evaluation
evaluation이 매우 어렵다! ( 하나의 정답만이 존재하는 것이 아니기 때문에 )
다양한 방법
- human judgement
-
( 여러 개의 translation 사이의 ) preference studies
- automatic alternatives
- BLEU / ROUGE / Meteor / CIDEr
Evaluation issue는 매우 중요하다.!
단지 결과 비교만을 위해서가 아니라, optimization을 위한 objective function을 위해서도 필수적!
