( 출처 : 연세대학교 데이터베이스 시스템 수업 (CSI6541) 강의자료 )
Chapter 3. Introduction to SQL
(1) SQL의 분류
DDL (Definition) : 데이터 정의어
- schema를 정의/수정/삭제
- CREATE TABLE
- ALTER TABLE
- DROP TABLE
DML (Manipulation) : 데이터 조작어
- data의 삽입/삭제/수정/검색 등
- SELECT
- INSERT
- UPDATE
- DELETE
DCL (Control) : 데이터 제어어
- 내부적으로 필요한 규칙/기법을 정의하기 위해
- GRANT (권한 부여)
- REVOKE (권한 취소)
(2) Domain Types in SQL
-
char(n): Fixed length character string, with user-specified length n
-
varchar(n): Variable length character string, with user-specified maximum length n
-
int: Integer (machine-dependent)
-
smallint: Small integer (machine-dependent)
-
numeric(p,d): Fixed pointer number, with user-specified precision of p digits, with d digits to the right of decimal point
-
real, double precision: Floating point and double-precision floating point numbers (machine-dependent)
(3) CREATE TABLE
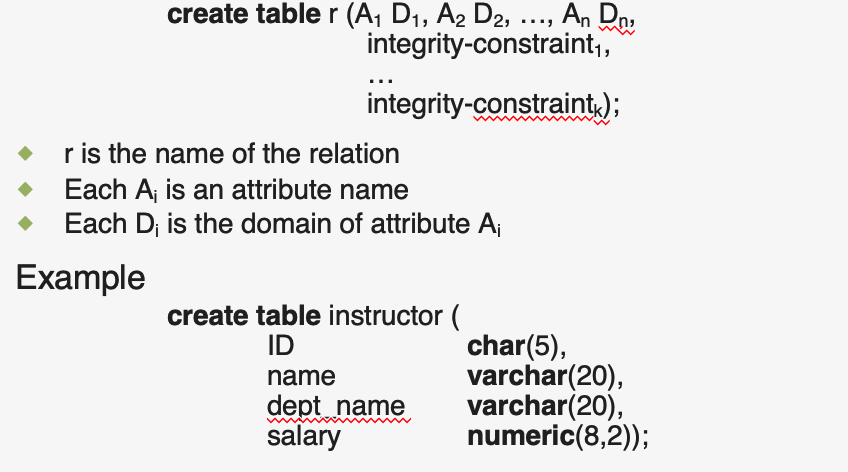
integrity-constraint
-
NOT NULL
-
PRIMARY KEY (\(A_1, \cdots A_n\))
( automatically ensures NOT NULL )
-
FOREIGN KEY (\(A_1, \cdots A_n\)) REFERENCES \(r\)
other examples )


참조 무결성 제약조건
- foreign key(외래 키)를 통해 관계를 맺고 있는 2개의 테이블의 경우!
(4) Updates to Tables
INSERT INTO instructor VALUES (‘10211’, ‘Smith’, ‘Biology’, 66000);
DELETE FROM student;
DROP TABLE r;
ALTER TABLE r ADD A D;
ALTER TABLE r DROP A;
(5) Basic Query Structure
SELECT A1, A2, ..., An
FROM r1, r2, ..., rm
WHERE P
to eliminate/keep duplicates …
SELECT DISTINCT dept_name
FROM instructure
SELECT ALL dept_name
FROM instructure
to rename…
- AS can be ommited!
SELECT ID, name, salary/12 AS monthly_salary;
FROM instructor
Where Clause
# AND, OR, NOT, IN, NOT IN ...
WHERE dept_name = ‘Comp. Sci.’ AND salary > 80000
Order by
SELECT DISTINCT name
FROM instructor
ORDER BY name
Examples )
SELECT name
FROM instructor
WHERE salary BETWEEN 90000 AND 100000
# tuple comparison
SELECT name, course_id
FROM instructor, teaches
WHERE (instructor.ID, dept_name) = (teaches.ID, ‘Biology’)
SELECT name, course_id
FROM instructor, teaches
WHERE instructor.ID = teaches.ID AND instructor.dept_name = ‘Art’
SELECT DISTINCT T.name
FROM instructor AS T, instructor AS S
WHERE T.salary > S.salary AND S.dept_name = ‘Comp. Sci.’;
(6) String Operations
string-matching operator : like
- uses patterns, that are described using…
- (1)
%: matches any substring - (2)
_: matches any character
- (1)
Example ) whose name includes dar
SELECT name
FROM instructor
WHERE name LIKE '%dar%'
(7) Set Operations
(~) UNION (~)
(~) INTERSECT (~)
(~) EXCEPT (~)
to retain dupliactes…
(~) UNION ALL (~)
(~) INTERSECT ALL (~)
(~) EXCEPT ALL (~)
(8) Null values
SELECT name
FROM instructor
WHERE salary IS NULL
(9) Aggregate functions
- avg, min, max, sum, count
SELECT count(*)
FROM course
SELECT avg(salary)
FROM instructor
WHERE dept_name = ‘Comp. Sci.’
SELECT count(distinct ID)
FROM teaches
WHERE semester = ‘Spring’ AND year = 2010
(10) Aggregate functions + Group By
SELECT dept_name, avg(salary)
FROM instructor
GROUP BY dept_name
HAVING avg(salary) > 42000
(11) ORDER of EXECUTION !!
SQL : non-procedural language ( 비절차적인 언어 )
( but, have execution order! )
F W G H C O
Example
\[\begin{array}{ll} \text { SELECT } & \text { custid, COUNT(*) AS 도서수량 } \\ \text { FROM } & \text { Orders } \\ \text { WHERE } & \text { saleprice }>=8000 \\ \text { GROUP BY } & \text { custid } \\ \text { HAVING } & \text { count }\left(^*\right)>1 \\ \text { ORDER BY } & \text { custid; } \end{array}\begin{array}{ll} \end{array}\]- step 1) FROM
- step 2) WHERE
- step 3) GROUP BY
- step 4) HAVING
- step 5) COUNT
- step 6) ORDER BY
(12) Null values & Aggregate
SELECT sum(salary)
FROM instructor
- ignores null amounts
- all aggregation operations, except “
count(*)”, ignore null values!
(13) Nested Subqueries
subquery : SELECT - FROM - WHERE expression, that is nested within another query
select distinct course_id
from section
where semester = ‘Fall’
and year = 2009
and course_id not in (
select course_id
from section
where semester = ‘Spring’
and year = 2010);
(14) Set Comparison
some clause
ex) salary greater than that of some (at least one) instructor ~
-
version 1) w.o some
select distinct T.name from instructor as T, instructor as S where T.salary > S.salary and S.dept_name = ‘Biology’ -
version 2) with some
select name from instructor where salary > some (select salary from instructor where dept_name = ‘Biology’);
all clause
ex) salary greater than all of ~
select name
from instructor
where salary > all (select salary
from instructor
where dept_name = ‘Biology’);
(15) Test for Empty Relations
- exists
- not exists
ex) “Find all courses taught both in Fall 2009 and in Spring 2010”
select course_id
from section as S
where semester = ‘Fall’
and year = 2009
and exists (select *
from section as T
where semester = ‘Spring’
and year = 2010
and S.course_id = T.course_id);
ex) Find all students who have taken all courses offered in the Biology department
select distinct S.ID, S.name
from student as S
where not exists (
(select course_id
from course
where dept_name = ‘Biology’ )
except
(select T.course_id
from takes as T
where S.ID = T.ID));
(16) Test for absence of duplicate tuples
unique
- tests whether a subqery has any duplicate tuples in the result
- TRUE, if no duplciates
ex) Find all courses that were offered at most once in 2009
select T.course_id
from course as T
where unique (select R.course_id
from section as R
where T.course_id = R.course_id
and R.year = 2009);
(17) Database Modification
[ Delete ]
ex) Delete all instructors from the Finance dept
delete from instructor
where dept_name = ‘Finance’
ex) Delete all instructors whose salary is less than the average salary of instructors
delete from instructor
where salary < (select avg (salary)
from instructor)
[ Insert ]
ex) Add a new tuple to course:
insert into course
values (‘CS-437’, ‘Database Systems’, ‘Comp. Sci’, 4);
insert into course (course_id, title, credits, dept_name)
values (‘CS-437’, ‘Database Systems’, 4, ‘Comp. Sci’);
ex) Add all instructors to the student relation with tot_creds set to 0
insert into student
select ID, name, dept_name, 0
from instructor
[ Update ]
ex) Increase salaries of instructors whose salary is over $100,000 by 3% and all others receive 5% raise:
update instructor
set salary = salary * 1.03
where salary > 100000;
update instructor
set salary = salary * 1.05
where salary <= 100000;
( Can be done better using the case statement )
update instructor
set salary =
case
when salary <= 100000 then salary *1.05
else salary * 1.03
end ;
