Temporal Pattern Attention for Multivariate Time Series Forecasting (2018, 164)
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Temporal Pattern Attention
- Problem Formulation
- Temporal Pattern Detection using CNN
- Proposed Attention Mechanism
0. Abstract
MTS forecasting!
crucial to model long-term dependency \(\rightarrow\) RNNs with Attention mechanism
Typical attention
-
fails to capture temporal patterns across multiple time steps!
\(\rightarrow\) propose using a set of filters to extract “time-invariant temporal patterns”
-
also, propose a novel attention mechanism to select relevant TS
& use its frequency domain information
1. Introduction
propose the TEMPORAL PATTERN ATTENTION
-
temporal pattern = any time-invariant pattern across multiple steps
-
consider which TS is important!
-
instead of selecting the “relevant time step” (X),
select the “relevant time series” (O)
-
introduce CNN in attention
Previous works
- LSTNets : add “recurrent-skip layer” or “typical attention mechanism”
- 3 major shortcomings
- 1) skip-length : manually tuned
- 2) specifically designed for MTS
- 3) attention in LSTNet-ATNN : selects a relevant “hidden state” ( not “time series”)
2. Temporal Pattern Attention
-
[problem 1] if MTS, fails to ignore variables which are noisy(not useful)
-
[problem 2] typical attention : averages the information “across multiple steps”
\(\rightarrow\) fails to detect “temporal patterns”
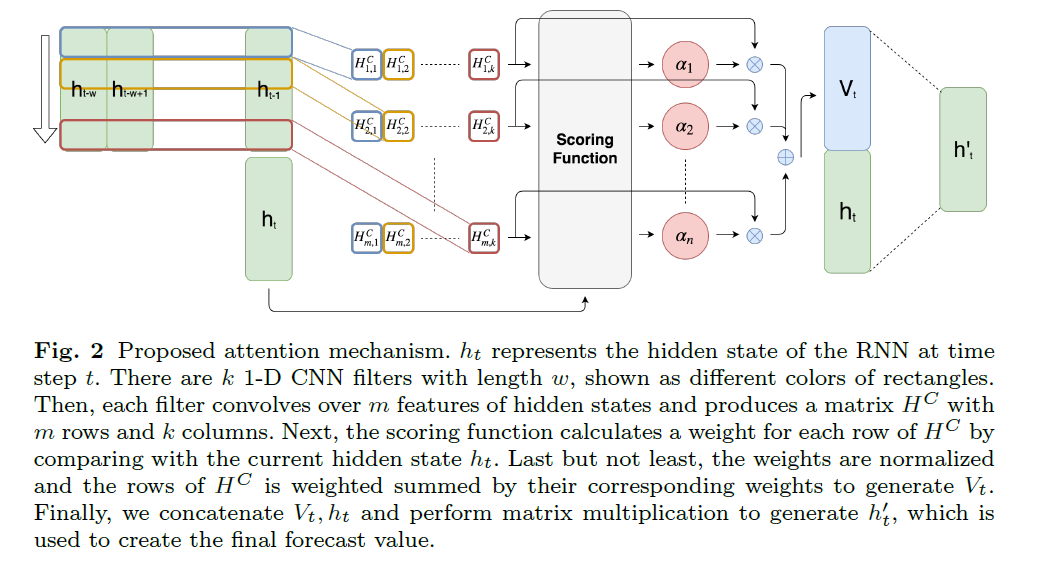
(1) Problem Formulation
\(X=\left\{x_{1}, x_{2}, \ldots, x_{t-1}\right\}\).
- \(x_{i} \in \mathbb{R}^{n}\) : observed value at time \(i\), with \(n\) dimension
task : predict \(x_{t-1+\Delta}\), with input \(\left\{x_{t-w}, x_{t-w+1}, \ldots, x_{t-1}\right\}\)
- \(w\) : window size
- \(\Delta\) : fixed horizon
(2) Temporal Pattern Detection using CNN
\(k\) filters \(C_{i} \in \mathbb{R}^{1 \times T}\)
-
\(T\) : maximum length paying attention to
( if unspecified, \(T=w\) …. no sliding )
(3) Proposed Attention Mechanism
\(v_t\) : weighted sum of row vectors of \(H^C\)
\(f: \mathbb{R}^{k} \times \mathbb{R}^{m} \mapsto \mathbb{R}\) : scoring function
- evaluate relevance as …. \(f\left(H_{i}^{C}, h_{t}\right)=\left(H_{i}^{C}\right)^{\top} W_{a} h_{t},\)
- where \(H_{i}^{C}\) is the \(i\)-th row of \(H^{C}\)
- \(W_{a} \in \mathbb{R}^{k \times m}\).
- attention weight : \(\alpha_{i}=\operatorname{sigmoid}\left(f\left(H_{i}^{C}, h_{t}\right)\right) .\)
Context vector :
- \(v_{t}=\sum_{i=1}^{n} \alpha_{i} H_{i}^{C}\).
integrate \(v_{t}\) and \(h_{t}\) to yield the final prediction
- \(h_{t}^{\prime}=W_{h} h_{t}+W_{v} v_{t}\).
- \(y_{t-1+\Delta}=W_{h^{\prime}} h_{t}^{\prime}\).
