[Paper Review] 15. Image Generators with Conditionally-Independent Pixel Synthesis
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Method
- Positional Encoding (PE)
0. Abstract
Most of existing GAN …. rely on spatial convolutions ( + self-attention blocks )
Present a new architecture for image generator!
-
color value AT EACH PIXEL is computed INDEPENDENTLY,
given the value of (1) random latent vector & (2) coordinate of that pixel
-
NO spatial convolutions
1. Introduction
Recently, some architectures WITHOUT spatial convolutions have been suggested
\(\rightarrow\) HOWEVER,, restricted to individual scenses
This paper designed & trained deep generative architectures for diverse classes of images that achieve similar quality of StyleGANv2 … called CIPS ( = Conditionally-Independent Pixel Synthesis )
2. Method
CIPS synthesize images of fixed resolution \(H \times W\)!
Input
- 1) random vector \(\mathbf{z} \in \mathcal{Z}\)
- 2) pixel coordinates \((x, y) \in \{0 \ldots W-1\} \times\{0 \ldots H-1\}\)
Mapping
-
\(G:(x, y, \mathbf{z}) \mapsto \mathbf{c}\).
where RGB value \(\mathbf{c} \in[0,1]^{3}\)
To compute whole input image \(I\),….
- \(G\) is evaluated at each pair \((x,y)\) of grid, while keeping \(\mathbf{z}\) fixed!
- \(I=\{G(x, y ; \mathbf{z}) \mid(x, y) \in \operatorname{mgrid}(H, W)\}\).
- where \(\operatorname{mgrid}(H, W)=\{(x, y) \mid 0 \leq x<W, 0 \leq y<H\}\).
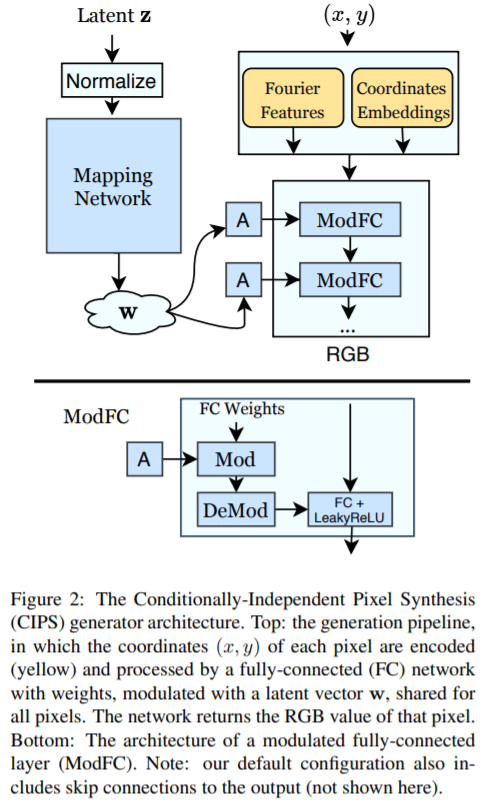
[ Similar to StyleGAN ]
mapping network \(M\)
- style vector \(\mathbf{w} \in \mathcal{W}, M: \mathbf{z} \mapsto \mathbf{w}\).
StyleGANv2
- use weight modulation
- ModFC (= Modulated Fully-Connected) : \(\psi \in \mathbb{R}^{m}=\hat{B} \phi+\mathbf{b}\)
- \(\psi \in \mathbb{R}^{m}\) : output
- \(\phi \in \mathbb{R}^{n}\) : input
- \(\hat{B}\) : learnable weight
- \(\hat{B}_{i j}=\frac{s_{j} B_{i j}}{\sqrt{\epsilon+\sum_{k=1}^{n}\left(s_{k} B_{i k}\right)^{2}}}\).
- \(B \in \mathbb{R}^{m \times n}\) : modulated with the style \(\mathbf{w}\)
- scale vector \(\mathbf{s} \in \mathbb{R}^{n}\)
- \(\hat{B}_{i j}=\frac{s_{j} B_{i j}}{\sqrt{\epsilon+\sum_{k=1}^{n}\left(s_{k} B_{i k}\right)^{2}}}\).
- \(\mathbf{w}, \mathbf{b} \in \mathbb{R}^{m}\) : learnable bias
-
After linear mapping, apply Leaky ReLU
-
add skip connections for every 2 layers of intermediate feature maps
-
PARALLELIZABLE at inference time
( \(\because\) independence of pixel generation process )
2-1. Positional Encoding (PE)
2 slightly different versions of PE
- 1) SIREN
- perceptron with a principled weight initialization
- activation function : sine
- 2) Fourier features
Proposed : use somewhat between 1) & 2)
-
use sine function to obtain Fourier embedding \(e_{f o}\)
- \(e_{f o}(x, y)=\sin \left[B_{f o}\left(x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}\right)^{T}\right]\).
- where \(x^{\prime}=\frac{2 x}{W-1}-1\) and \(y^{\prime}=\frac{2 y}{H-1}-1\) are pixel coordinates
- \(e_{f o}(x, y)=\sin \left[B_{f o}\left(x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}\right)^{T}\right]\).
-
[coordinate embeddings]
- also train separate vector \(e_{c o}^{(x, y)}\) for each spatial position
-
concatenate those two!
-
\(e(x, y)=\operatorname{concat}\left[e_{f o}(x, y), e_{c o}^{(x, y)}\right]\).
-
can be viewed as … \(G(x, y ; \mathbf{z})=G^{\prime}(e(x, y) ; M(\mathbf{z}))\)
-
