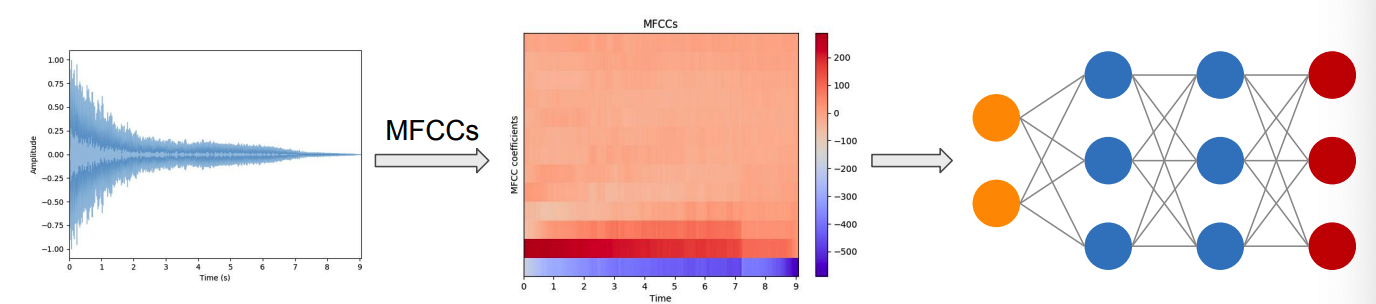
Audo data for DL
참고 : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fMqL5vckiU0&list=PL-wATfeyAMNrtbkCNsLcpoAyBBRJZVlnf
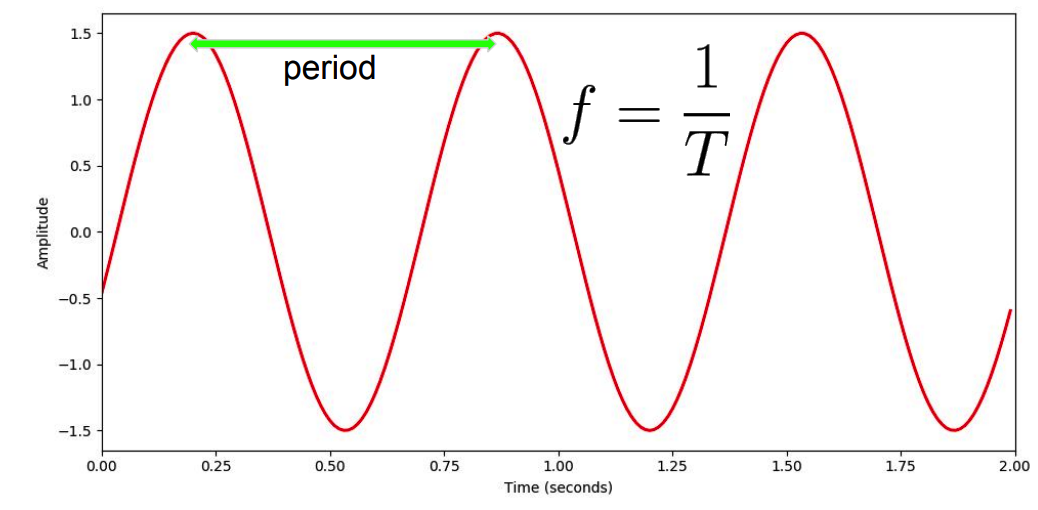
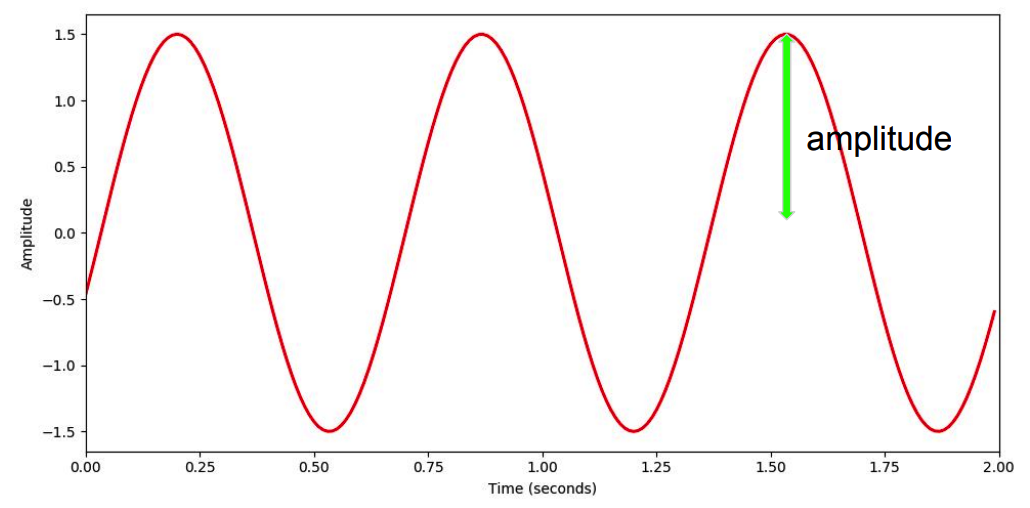
1. Waveform
Key concpets
- Period ( = seconds / cycle )
- inverse: Frequency ( = cycle / second )
- Amplitude

Mathematical expression
\(y(t)=A \sin (2 \pi f t+\varphi)\).
- \(t\) : time index
- \(A\) : amplitude
- \(f\) : frequency
- \(\varphi\) : phase
2. Frequency/pitch & Amplitude/loudness
LOW frequency / LOW amplitude
HIGH frequency / HIGH amplitude
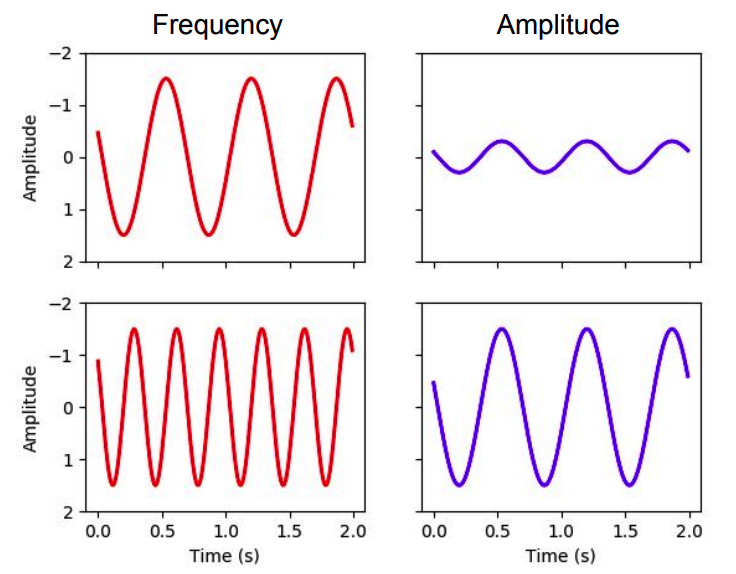
HIGH frequency \(\rightarrow\) HIGH pitch
HIGH amplitude \(\rightarrow\) LOWD sound
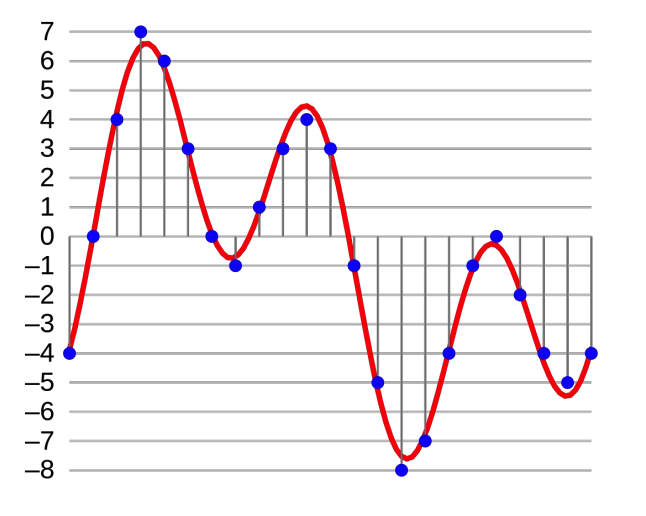
3. Sampling
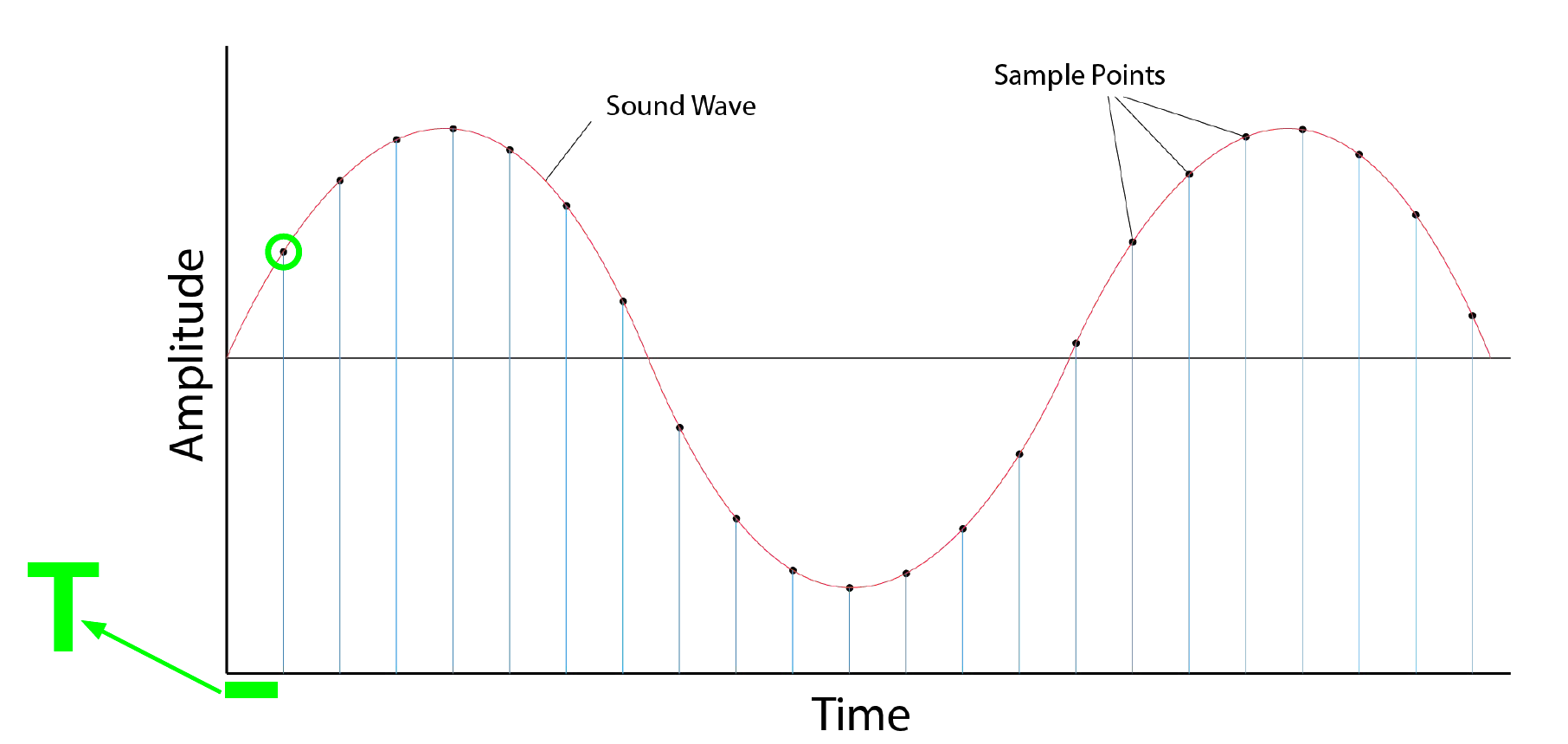
- sampling period : \(T\)
- time index: \(t_n = n \cdot T\)
- samplig rate : \(1/T\)
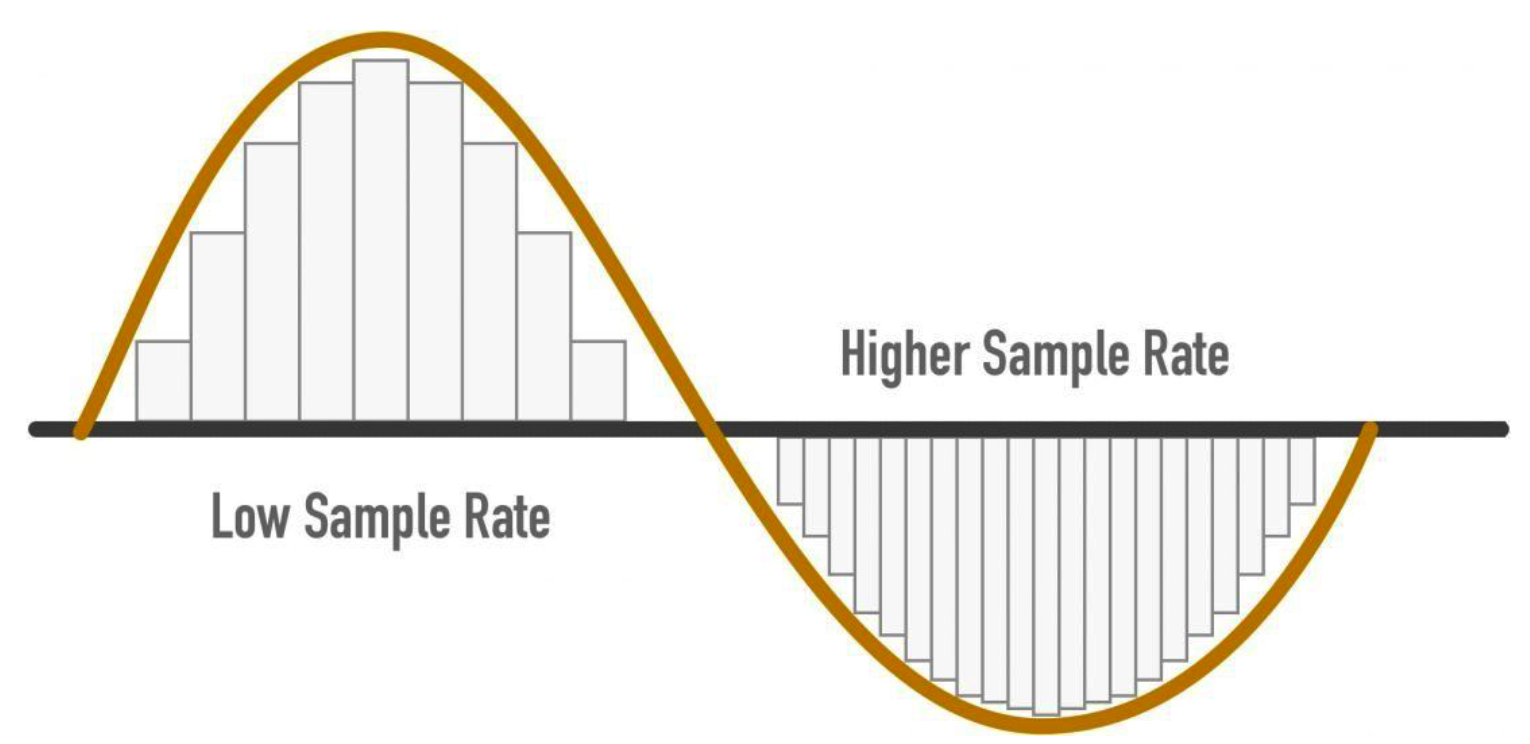
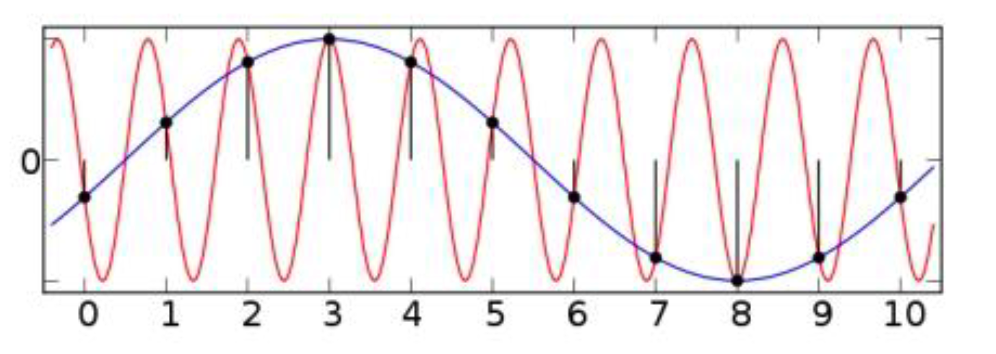
4. Aliasing vs. Quantization
(1) Aliasing ( = X-axis )
- original signal (RED) : high frequency
- reconstructed signal (BLUE) : low frequency
\(\rightarrow\) removing certain frequencyes ABOVE ceratin threshold
(2) Quantization ( = Y-axis )
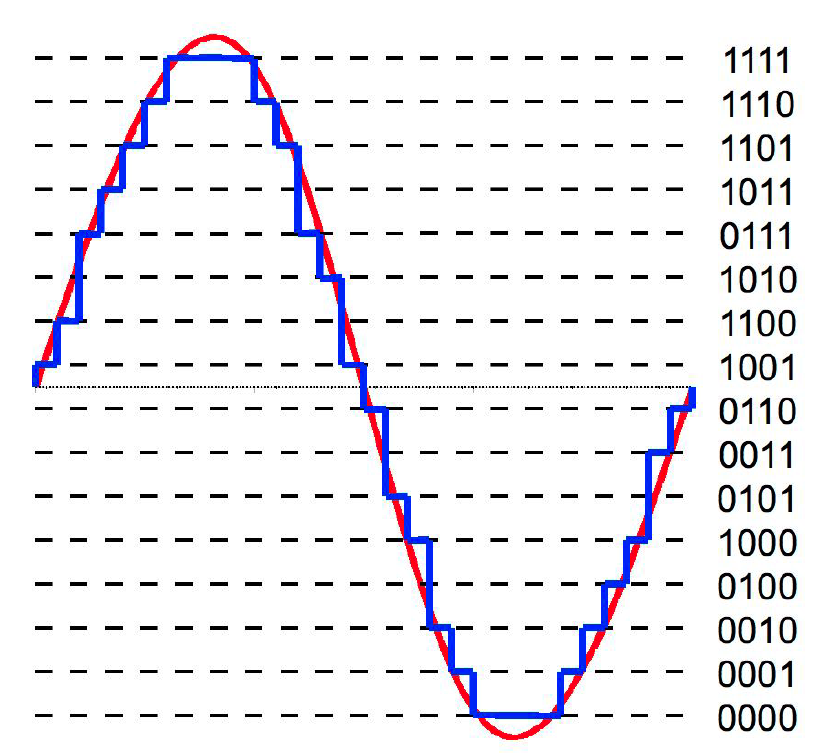
5. Analiog Digital Conversion (ADC)
[X] sample signal at uniform time intervals
[Y] quantize with (limited number of) bits
ex) CD :
- sample rate = 44100 Hz ( frequency )
- Bit = 16 bits / channel
6. 1 min = xx Byte?
Sampling rate = 44100Hz
- 44100 points per second
Bit depth = 16 bit
- amplitude is quantized into 16 bits ( \(2^{16}\) possibilities)
Total Memory of Sound in 1 minute ( in .wav file )
- number of bits per second : \(16 \times 44,100\)
- number of megabits per second : \((16 \times 44,100) / 1,048,576\)
- number of megabytes per second : \((16 \times 44,100) / (1,048,576\times8)\)
- number of megabytes per mintue : \((16 \times 44,100) / (1,048,576\times8)\) \(\times 60 = 5.49\text{MB}\)
\(\rightarrow\) to shrink memory, we use .mp3 file!
4. Fourier Transform
*from TIME domain to FREQUENCY domain
( but time information is lost )
decompse sound into sum of sine waves ( oscillating at different frequencies )
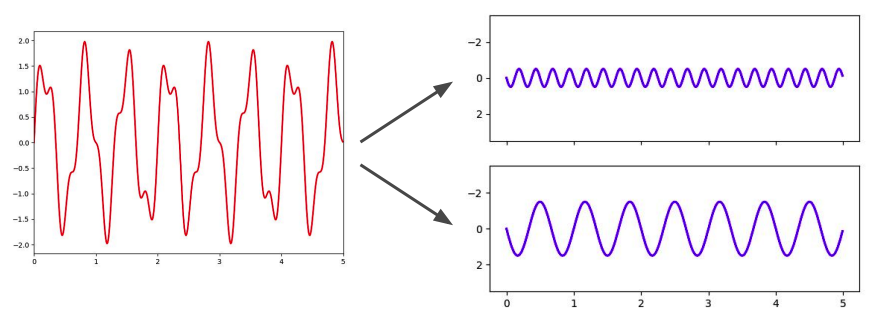
ex) decompose into 2 sine waves
\(s=A_1 \sin \left(2 \pi f_1 t+\varphi_1\right)+A_2 \sin \left(2 \pi f_2 t+\varphi_2\right)\).
- \(A_1=0.5, f_1=4, \varphi_1=0\\\).
- \(A_2=1.5, f_2=1.5, \varphi_2=0\).
- decompose into mulitple waves
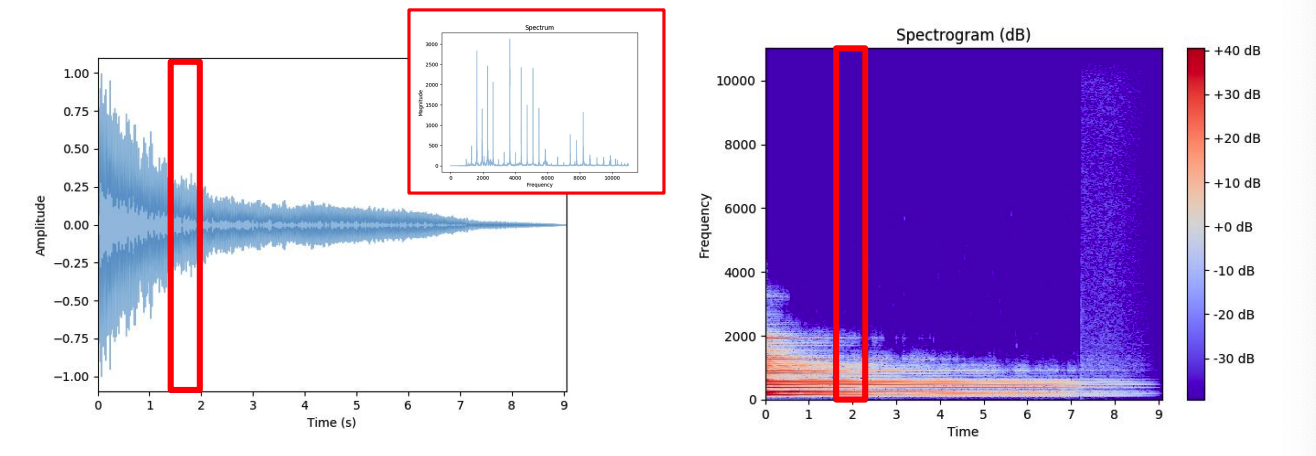
5. Short Time Fourier Transform (STFT)
problem: TIME INFORMATION is lost due to FT
solution : Short Time Fourier Transform (STFT)
-
(1) compute multiple FFT at different intervals
- able to preserve TIME info
-
(2) FIXED frame size
- ex) 2048 samples per interval
-
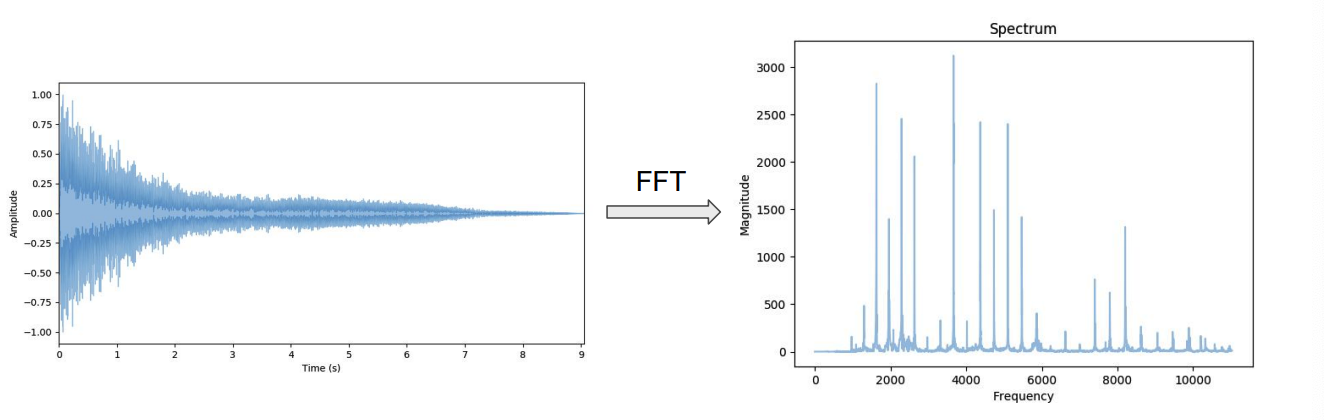
(3) output = SPECTOGRAM
( = time + frequency + magnitude )
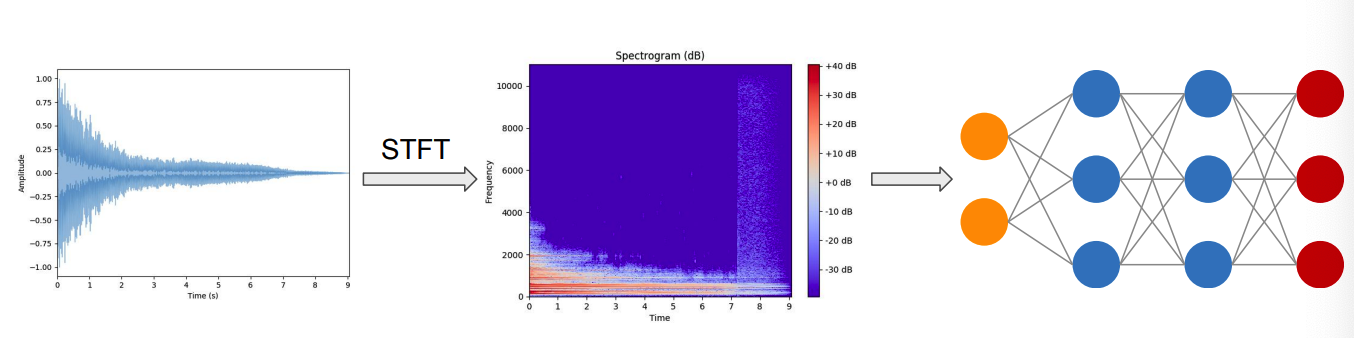
6. Pre-processing pipeline for Audio
(1) DL
(2) (Traditional) ML
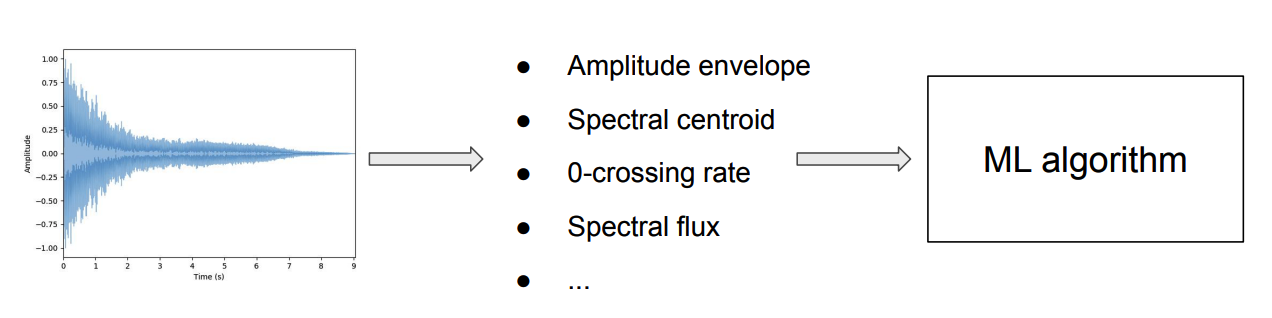
\(\rightarrow\) requires much feature engineering!
7. Mel frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs)
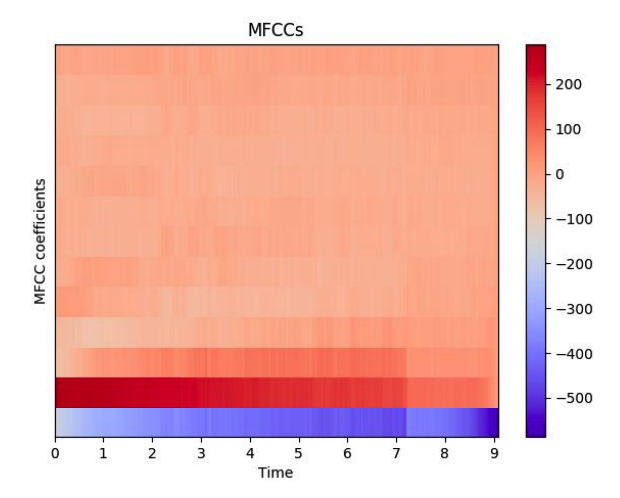
MFCCs
- Frequency domain feature
- Capture timbral/textural aspects of sound
- Approximate human auditory system
- 13 to 40 coefficient
- Calculated at each frame
- need to perform SFTF first!
Applications:
- speech recognition
- music genre classificaiton